Knock-out (Turbo) Tutorial
Introduction
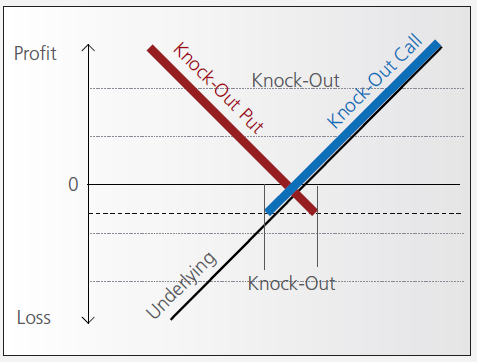
Knock-out warrants (turbos), like vanilla warrants, derive their value from the difference between the price of the underlying and the strike. They differ significantly however from vanilla warrants in many important respects:
- They can expire (knock-out) prematurely if the price of the underlying instrument touches or falls below (in the case of knock-out calls) or exceeds (in the case of knockout puts) a predetermined barrier-level. It expires worthless if the barrier equals the strike, or it may have a residual stop-loss value if the barrier is set higher than the strike (in the case of a call).
- Changes in implied volatility have little or no impact on knock-out products, therefore their pricing is easier for investors to comprehend than that of warrants.
- They have little or no time value (because of the presence of the knock-out barrier), and therefore have a higher degree of leverage than a warrant with the same strike. This is because the absence of time value makes the instrument “cheaper”.
Pay-out Profile
Leverage
As discussed above, knock-out warrants exhibit high degrees of leverage, particularly as the price of the underlying nears the strike/barrier. Consider the following example of a long turbo on the Dow Jones Index, compared to a vanilla warrant:
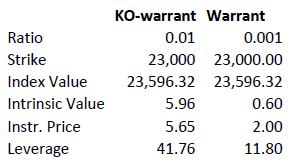
Intrinsic value = (index value – strike) x ratio
Leverage = Index Value x Ratio / Instrument Price
A vanilla warrant retains significant time value even as the underlying price approaches the strike, sharply reducing its leverage compared to a knock-out warrant.
Product types
As discussed above, the barrier may either equal the strike, or be set above (calls) or below (puts). In the latter cases a small residual value remains after knock-out, corresponding to the difference between the barrier (the stop-loss level) and the strike.
Moreover, knock-out products may either have an expiration date or may be open-ended. This makes a difference in the way interest is accounted for. If the contract has an expiration date interest is included in the premium, the amount of which reduces over time and is zero on expiration. This is analogous to a standard vanilla warrant.
in relation to an expiration date. The price of the contract therefore corresponds exactly to its intrinsic value. Interest however must be accounted for. This is done by a daily adjustment of the barrier and strike. The following example shows the daily adjustment for a long open-end turbo on the Dow Jones Index:
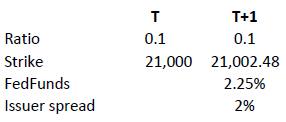
The adjustment = Strike T x (1+ FedFunds/360 + Issuer Spread/360).
The intrinsic value of the instrument is correspondingly reduced as follows, assuming no change in the value of the DJ Index):

Intrinsic value = (index value – strike) x ratio
Discount Certificates Tutorial
Introduction
Discount certificates are designed to provide an enhanced return in sideways markets, compared to a direct investment in the underlying.
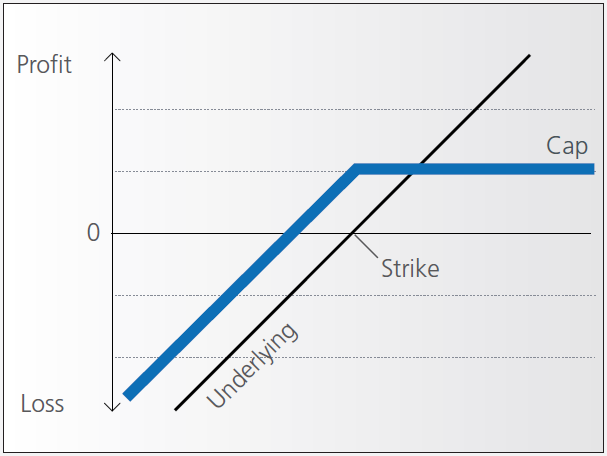
Discount certificates make it possible for you to buy an underlying instrument for less than its current market price. However, the maximum payback on a discount certificate is limited to a predetermined amount (cap).
Discount certificates normally have a term to maturity of one to three years. At maturity, a determination is made of where the price of the underlying instrument stands.
If it is at or above the cap, you’ll earn the maximum return and receive payment of the amount reflected by the cap.
If the price of the underlying instrument is below the cap on the maturity date, you’ll receive either the corresponding number of shares or a cash settlement reflecting the value of the underlying instrument on the maturity date.
Pay-out Profile
Example
Assume a discount certificate on ABC share. The certificate has a cap of EUR 40.00, and a purchase price of EUR 36.00. The table below shows scenarios depending on the final price of the underlying.
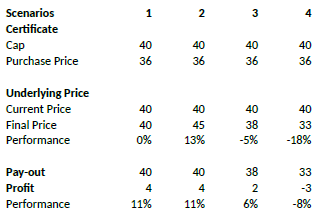
Factor Certificates Tutorial
Introduction
Factor certificates employ a daily leverage factor that multiplies the daily performance of the underlying instrument. Unlike knock-out warrants and mini-futures, factor certificates do not have a knock-out barrier. To avoid a loss greater than the investment, the calculation resets intraday if the performance of the underlying threatens to render the certificate worthless.
Daily Leverage
The performance of the certificate is calculated daily, without reference to previous days’ values. If the underlying returns 1% on the day, the value of 3x certificate increases by 3%, a 5x by 5%. The next day the process is repeated, referencing the prior day’s underlying close.
As such, factor certificates are particularly suitable for day-traders.
However, for a period of more than one day, the cumulative performance of the underlying cannot be simply multiplied by a factor of 3 as the previous day’s price always forms the new basis of calculating each day’s performance for the certificate. To illustrate with an example:

Cumulatively, the factor certificate has returned less than 3x the performance of the underlying.
Intraday Reset
If an underlying for a factor certificate loses more than a certain percentage of its value intraday, the calculation is reset by simulating a new day. The reset threshold varies depending on the leverage factor.
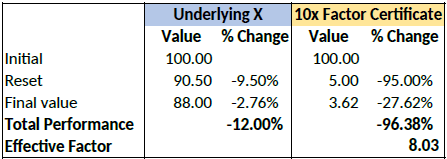
Let’s assume a long factor certificate with a 10x leverage factor. According to the terms of the certificate, a reset will be triggered if the underlying loses more than 9.5% during the calculation day.
Let’s now assume that the underlying loses 12% of its value during a particular day. The reset
and final performance will be as follows:
Complex Position Size
For complex, multi-leg options positions comprising two or more legs, TWS might not track all changes to this position, e.g. a vertical spread where the short leg is assigned and the user re-writes the same leg the next day, or if the user creates a the position over multiple trades, or if the order is not filled as a native combination at the exchange.
Immissione e sottrazione di liquidità
L'obiettivo del presente articolo è quello di fornire una comprensione adeguata delle tariffe borsistiche, delle tariffe per l'immissione e la sottrazione di liquidità e del piano delle singole commissioni.
Il concetto di immissione e sottrazione di liquidità si applica sia ai titoli azionari sia alle opzioni su azioni e indici. L'eventuale immissione o sottrazione di liquidità da parte dell'ordine dipende dal fatto che l'ordine sia o meno inviabile a mercato.
Gli ordini inviabili a mercato SOTTRAGGONO liquidità.
Gli ordini inviabili a mercato sono ordini a mercato, OPPURE ordini di acquisto/vendita il cui limite è equivalente al o al di sopra/sotto del prezzo di mercato corrente.
1. Nel caso degli ordini limite di acquisto inviabili a mercato, il prezzo limite è equivalente o superiore al corso lettera.
2. Nel caso degli ordini limite di vendita inviabili a mercato, il prezzo limite è equivalente o inferiore al corso denaro.
Esempio:
La/il quantità/prezzo del corso LETTERA (offerta) corrente del titolo XYZ è di 400 azioni a 46.00. Si ipotizzi di inserire un ordine limite di acquisto di 100 azioni del titolo XYZ a 46.01. L'ordine sarà considerato inviabile a mercato, in quanto si verificherà un'esecuzione immediata. Qualora sia previsto l'addebito di una tariffa borsistica per la sottrazione della liquidità, il cliente si vedrà addebitare tale tariffa.
Gli ordini non inviabili a mercato sono ordini di acquisto/vendita nei quali il prezzo limite è inferiore/superiore al prezzo di mercato corrente.
1. Nel caso degli ordini limite di acquisto non inviabili a mercato, il prezzo limite è inferiore al corso lettera.
2. Nel caso degli ordini limite di vendita non inviabili a mercato, il prezzo limite è superiore al corso denaro.
Esempio:
La/il quantità/prezzo del corso LETTERA (offerta) corrente del titolo XYZ è di 400 azioni a 46.00. Si ipotizzi di inserisce un ordine limite di acquisto di 100 azioni del titolo XYZ a 45.99. L'ordine sarà considerato non inviabile a mercato, in quanto, anziché essere immediatamente eseguito, sarà pubblicato nel mercato come miglior corso denaro.
Qualora qualcun altro inviasse un ordine di vendita inviabile a mercato con conseguente esecuzione del proprio ordine limite di acquisto, si dovrebbe ricevere un rimborso (credito), a condizione che siano disponibili crediti per l'immissione di liquidità.
ATTENZIONE:
1. Tutti i conti che effettuino transazioni su opzioni saranno soggetti all'addebito delle tariffe per la sottrazione di liquidità o all'accredito per l'immissione di liquidità eventualmente previsti dalle Borse delle opzioni.
2. Come indicato nel sito web di IB, solamente i numeri negativi del piano relativo alla sottrazione e immissione di liquidità sono rimborsi (crediti).
https://www.interactivebrokers.com/it/index.php?f=5688
Perché le commissioni addebitate sulle opzioni statunitensi sono di tipo variabile?
L'addebito delle commissioni sulle opzioni previsto da IB si divide in due parti:
1. La commissione di esecuzione spettante a IB. Per quanto concerne gli ordini indirizzati tramite il sistema SmartRouting, la tariffa è fissata a 0.70 dollari per contratto, ridotta ad appena 0.15 dollari per contratto in caso di ordini eccedenti i 100,000 contratti in un dato mese (si prega di consultare il sito web per conoscere i costi degli ordini indirizzati direttamente, le tariffe ridotte per le opzioni a basso premio e le tariffe minime addebitabili sugli ordini); e
2. Le tariffe esterne (borsistiche, regolamentari e/o sulle transazioni).
Nel caso delle tariffe esterne, determinate Borse delle opzioni statunitensi mantengono una struttura tariffa/rimborso rispetto alla liquidità che, una volta aggregata alla commissione di esecuzione di IB e alle eventuali altre tariffe regolamentari e/o sulle transazioni, potrebbe comportare l'addebito di una commissione complessiva per contratto variabile in funzione dell'ordine. Ciò è imputabile alla parte del calcolo della Borsa, che dipende da una serie di fattori al di fuori del controllo di IB, inclusi gli attributi d'ordine del cliente e le quotazioni denaro-lettera prevalenti, e il cui risultato potrebbe essere un pagamento in favore del cliente anziché l'addebito di una tariffa.
Le Borse valori che operano secondo questo modello di tariffa/rimborso rispetto alla liquidità prevedono l'addebito di una tariffa per gli ordini di sottrazione della liquidità (cioè, ordini inviabili a mercato) e l'erogazione di un credito per gli ordini di immissione della liquidità (cioè, ordini limite non inviabili a mercato). Le tariffe possono variare a seconda della Borsa valori, del tipo di cliente (es. pubblico, intermediario, società, market-maker, professionale, ecc.) e del sottostante dell'opzione, dove i rimborsi (crediti) per i clienti pubblici sono generalmente compresi tra 0.10 e 0.42 dollari e le tariffe addebitabili ai clienti pubblici tra 0.15 e 0.50 dollari.
IB ha l'obbligo di indirizzare gli ordini di opzioni inviabili a mercato sulla Borsa valori che offre il miglior prezzo di esecuzione. Per determinare la specifica Borsa valori sulla quale indirizzare l'ordine, nel caso in cui il mercato interno sia condiviso da più Borse valori, il sistema SmartRouting terrà in considerazione le tariffe per la sottrazione della liquidità (es. l'ordine sarà indirizzato sulla Borsa valori che offre la tariffa minore o nessuna tariffa). Di conseguenza, il sistema SmartRouting indirizzerà l'ordine a mercato sulla Borsa valori che addebita la tariffa più elevata solamente se consentirà di superare il prezzo di mercato di almeno 0.01 dollari (il che, dato il moltiplicatore standard delle opzioni di 100, mostrerebbe un miglioramento del prezzo di 1.00 dollaro, valore superiore alla tariffa più elevata per la sottrazione di liquidità).
Per maggiori informazioni in merito al concetto di immissione/sottrazione di liquidità, compresi alcuni esempi, si prega di fare riferimento all'articolo KB201.
Risks of Volatility Products
Trading and investing in volatility-related Exchange-Traded Products (ETPs) is not appropriate for all investors and presents different risks than other types of products. Among other things, ETPs are subject to the risks you may face if investing in the components of the ETP, including the risks relating to investing in complex securities (such as futures and swaps) and risks associated with the effects of leveraged investing in geared funds. Investors should be familiar with the diverse characteristics of each ETF, ETN, future, option, swap and any other relevant security type. We have summarized several risk factors (as identified in prospectuses for ETPs and in other sources) and included links so you can conduct further research. Please keep in mind that this is not a complete list of the risks associated with these products and investors are responsible for understanding and familiarizing themselves completely before entering into risk-taking activities. By providing this information, Interactive Brokers (IB) is not offering investment or trading advice regarding ETPs to any customer. Customers (and/or their independent financial advisors) must decide for themselves whether ETPs are an appropriate investment for their portfolios.
Priorità degli ordini di clienti professionali
Nel quarto trimestre del 2009 determinate Borse delle opzioni statunitensi (CBOE, ISE) hanno applicato disposizioni volte a contraddistinguere gli ordini provenienti da un gruppo di clienti pubblici ritenuti "professionali" (ovvero, soggetti o entità aventi accesso a informazioni e/o risorse tecnologiche che consentono loro di negoziare con le stesse modalità impiegate dagli operatori indipendenti) da quelli dei clienti retail. Secondo quanto previsto da tali disposizioni, tutti i conti dei clienti che non siano operatori indipendenti, e che in un determinato mese immettano una media giornaliera di oltre 390 ordini di opzioni quotate (eseguiti o meno) tra tutte le Borse delle opzioni a vantaggio del/i proprio/i conto/i, saranno classificati come "professionali". Dal momento dell'attuazione iniziale da parte del CBOE e dell'ISE, la maggior parte delle altre Borse delle opzioni statunitensi ha introdotto disposizioni analoghe per contraddistinguere gli ordini aventi provenienza "professionale".
Ai fini della priorità di esecuzione, gli ordini inviati a tali Borse delle opzioni a nome dei clienti ritenuti "professionali" saranno trattati alla stregua degli ordini degli operatori indipendenti; inoltre, saranno soggetti a una commissione di transazione per contratto compresa tra storni di ($0.65) e una tariffa di $1.12 (a seconda della categoria delle opzioni).
I broker sono tenuti a condurre una verifica trimestrale per identificare i clienti che eccedono la soglia dei 390 ordini in ciascun mese di tale trimestre e devono essere classificati come "professionali" per il trimestre successivo. Si prega di notare che, ai fini di tale disposizione, le singole componenti dello spread non sono considerate ordini singoli, bensì ciascun ordine di spread costituisce in sé un ordine unico. IB provvederà a informare i clienti coinvolti da tali disposizioni. Si ricorda, inoltre, che il sistema di indirizzamento SmartRouting di IB è progettato per tenere in considerazione tali nuove commissioni di Borsa al momento della scelta dell'indirizzamento.
Per maggiori dettagli, si prega di fare riferimento ai seguenti link:
Allocation of Partial Fills
How are executions allocated when an order receives a partial fill because an insufficient quantity is available to complete the allocation of shares/contracts to sub-accounts?
Overview:
From time-to-time, one may experience an allocation order which is partially executed and is canceled prior to being completed (i.e. market closes, contract expires, halts due to news, prices move in an unfavorable direction, etc.). In such cases, IB determines which customers (who were originally included in the order group and/or profile) will receive the executed shares/contracts. The methodology used by IB to impartially determine who receives the shares/contacts in the event of a partial fill is described in this article.
Background:
Before placing an order CTAs and FAs are given the ability to predetermine the method by which an execution is to be allocated amongst client accounts. They can do so by first creating a group (i.e. ratio/percentage) or profile (i.e. specific amount) wherein a distinct number of shares/contracts are specified per client account (i.e. pre-trade allocation). These amounts can be prearranged based on certain account values including the clients’ Net Liquidation Total, Available Equity, etc., or indicated prior to the order execution using Ratios, Percentages, etc. Each group and/or profile is generally created with the assumption that the order will be executed in full. However, as we will see, this is not always the case. Therefore, we are providing examples that describe and demonstrate the process used to allocate partial executions with pre-defined groups and/or profiles and how the allocations are determined.
Here is the list of allocation methods with brief descriptions about how they work.
· AvailableEquity
Use sub account’ available equality value as ratio.
· NetLiq
Use subaccount’ net liquidation value as ratio
· EqualQuantity
Same ratio for each account
· PctChange1:Portion of the allocation logic is in Trader Workstation (the initial calculation of the desired quantities per account).
· Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user
· Inline Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user.
· Model1:
Roughly speaking, we use each account NLV in the model as the desired ratio. It is possible to dynamically add (invest) or remove (divest) accounts to/from a model, which can change allocation of the existing orders.
Basic Examples:
Details:
CTA/FA has 3-clients with a predefined profile titled “XYZ commodities” for orders of 50 contracts which (upon execution) are allocated as follows:
Account (A) = 25 contracts
Account (B) = 15 contracts
Account (C) = 10 contracts
Example #1:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 10 am (ET) the order begins to execute2but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 2 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 7 of the 50 contracts are filled or 14%). For each account the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 14% of 25 = 3.5 rounded down to 3
Account (B) = 14% of 15 = 2.1 rounded down to 2
Account (C) = 14% of 10 = 1.4 rounded down to 1
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.10).
A: final allocation of 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 2 contract, which is 2/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.20)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #2:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be filled3 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 1 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is executed (i.e., 5 of the 50 contracts are filled or 10%).For each account, the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 10% of 25 = 2.5 rounded down to 2
Account (B) = 10% of 15 = 1.5 rounded down to 1
Account (C) = 10% of 10 = 1 (no rounding necessary)
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. to Account B which currently has a ratio of 0.067).
A: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #3:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be executed2 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 12 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 3 of the 50 contracts are filled or 6%). Normally the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers, however for a fill size of less than 4 shares/contracts, IB first allocates based on the following random allocation methodology.
In this case, since the fill size is 3, we skip the rounding fractional amounts down.
For the first share/contract, all A, B and C have the same initial fill ratio and fill quantity, so we randomly pick an account and allocate this share/contract. The system randomly chose account A for allocation of the first share/contract.
To Summarize3:
A: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
C: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
Next, the system will perform a random allocation amongst the remaining accounts (in this case accounts B & C, each with an equal probability) to determine who will receive the next share/contract.
The system randomly chose account B for allocation of the second share/contract.
A: 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
The system then allocates the final [3] share/contract to an account(s) with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.00).
A: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Available allocation Flags
Besides the allocation methods above, user can choose the following flags, which also influence the allocation:
· Strict per-account allocation.
For the initially submitted order if one or more subaccounts are rejected by the credit checking, we reject the whole order.
· “Close positions first”1.This is the default handling mode for all orders which close a position (whether or not they are also opening position on the other side or not). The calculation are slightly different and ensure that we do not start opening position for one account if another account still has a position to close, except in few more complex cases.
Other factor affects allocations:
1) Mutual Fund: the allocation has two steps. The first execution report is received before market open. We allocate based onMonetaryValue for buy order and MonetaryValueShares for sell order. Later, when second execution report which has the NetAssetValue comes, we do the final allocation based on first allocation report.
2) Allocate in Lot Size: if a user chooses (thru account config) to prefer whole-lot allocations for stocks, the calculations are more complex and will be described in the next version of this document.
3) Combo allocation1: we allocate combo trades as a unit, resulting in slightly different calculations.
4) Long/short split1: applied to orders for stocks, warrants or structured products. When allocating long sell orders, we only allocate to accounts which have long position: resulting in calculations being more complex.
5) For non-guaranteed smart combo: we do allocation by each leg instead of combo.
6) In case of trade bust or correction1: the allocations are adjusted using more complex logic.
7) Account exclusion1: Some subaccounts could be excluded from allocation for the following reasons, no trading permission, employee restriction, broker restriction, RejectIfOpening, prop account restrictions, dynamic size violation, MoneyMarketRules restriction for mutual fund. We do not allocate to excluded accountsand we cancel the order after other accounts are filled. In case of partial restriction (e.g. account is permitted to close but not to open, or account has enough excess liquidity only for a portion of the desired position).
Footnotes:
