TWS / IB Gateway and their interaction with Proxy servers
Table of contents
Configuration instructions
- Can the TWS / IB Gateway operate through a Proxy server, and how?
- If I use a SOCKS Proxy server, do I need to configure the TWS / IB Gateway?
- If I use a SOCKS Proxy server, do I need to configure the client machines where TWS / IB Gateway runs?
- If I use a Web (HTTP) Proxy server, do I need to configure the TWS / IB Gateway?
- What alternatives do I have in case I cannot implement a proxy solution on my network?
Common issues
Technical Background
Configuration instructions
1. Can the TWS / IB Gateway operate through a Proxy?
Upon start-up and during the run-time, the TWS / IB Gateway must establish and maintain direct network connections to our gateways and market data servers1. Such connections are created from random local TCP ports (above 1024) and are directed to TCP ports 4000 and TCP 4001. Since those are not HTTP connections, they cannot be serviced by a Web (HTTP) Proxy. They can only be serviced by a SOCKS Proxy.
From within the TWS interface, you can access several external services, such as IBKR Client Portal, Statements, Contract details, Bond Search, etc. Those services, being web-based, can be accessed through a Web (HTTP) Proxy (see section 6 for details and configuration) or through a SOCKS Proxy (see sections 4. and 5. for details and configuration).
2. If I use a SOCKS Proxy server, do I need to configure the TWS / IB Gateway?
The TWS / IB Gateway does not contemplate an option for SOCKS proxy forwarding. Therefore, it does not have a place where an explicit SOCKS Proxy host/port can be configured. This does not mean that the TWS / IB Gateway cannot work with a Proxy. It simply means that the TWS / IB Gateway is unaware of the underlying SOCKS proxy setup (proxy-agnostic).
Important Note: While it is impossible for us to determine whether a Proxy is enabled on your network, we assure you that all IBKR platforms, including the TWS, do not impact nor influence your network configuration.
3. If I use a SOCKS Proxy server, do I need to configure the client machines where TWS / IB Gateway runs?
The connections started by the TWS / IB Gateway can be redirected to a SOCKS (Application) Proxy through a specific client machine setup. We mention some of them below. Please note that the final decision is yours and none of the below suggestions can be recommended by us as best adapted to your setup and requirements.
3a. Using a Proxy Client software installed on the client machine where TWS / IB Gateway is running
With this setup, the Proxy client will intercept the connections (not only HTTP but for other ports as well) initiated by the TWS / IB Gateway and redirect them to a SOCKS proxy server. The typical benefits of a transparent proxy include a standard enterprise configuration where all clients routed to the Internet will always be filtered and protected no matter what the end users do, or change, on their machines and the added benefit of reduction in typical user’s client-proxy configuration troubleshooting.
3b. Using a so-called Proxifier
This configuration is very similar to the one at point 5a with the only difference that the Proxifier software can be set to redirect to a Proxy all the requests started by a specific process (e.g., C:\Jts\tws.exe; C:\JTS\ibgateway\XYZ\ibgateway.exe), hence instating a process level packet forwarding instead of a port level forwarding. This setup allows handling environments where different proxy servers are used for different applications or where you would like to address a specific application requirement without modifying/disrupting the connectivity schema for other software installed. The advantage of this solution is minimal maintenance since the connectivity schema is bound to the process and not to the hosts/ports.
3c. Using specific network routing on a client machine
With this setup, you can modify the client machine standard network routes, adding new ones in order to forward packets with specific destinations (e.g., Order routing and Market Data servers1) to a different gateway.
This gateway will then be in charge of routing those requests to the destination hosts. This solution has as well the benefit of not modifying/disrupting the connectivity schema for other software installed but usually requires more maintenance on the gateway and on the client machine in case the IP of the destination servers are changed or in case new servers are added.
4. If I use a Web (HTTP) Proxy server, do I need to configure the TWS / IB Gateway?
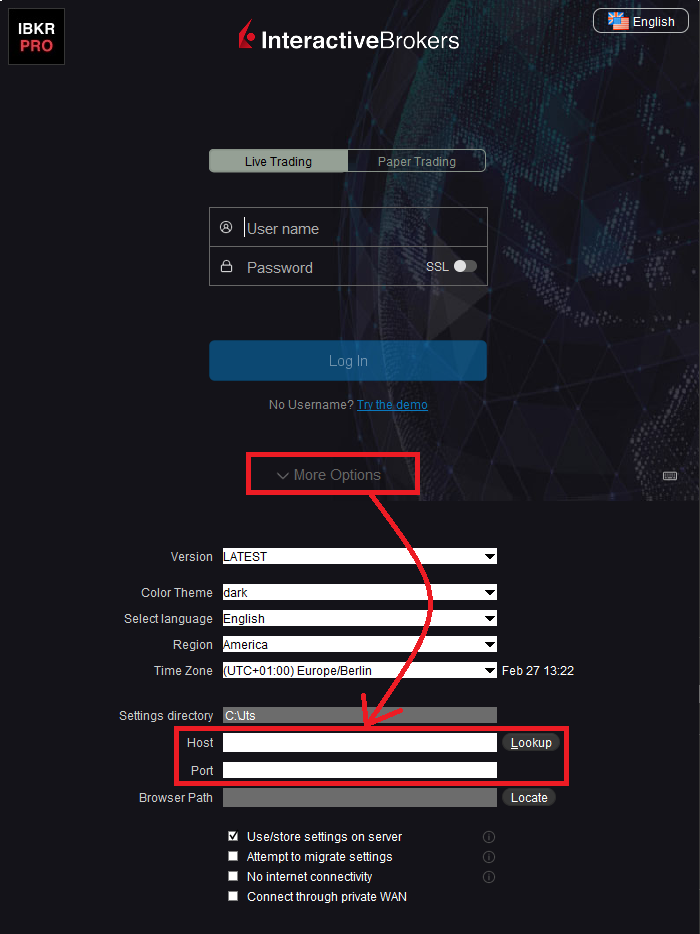
If the Workstations on your local network access the Web content through a Web (HTTP) Proxy, you need to specify the Web Proxy IP Address and port. To do this, click More Options at the bottom of the TWS Login Screen, and enter your Proxy server details in the fields Host and Port (see Figure 1 below). The same fields are present in the IB Gateway Login Screen.
Figure 1.
The Web Proxy you set there will ONLY be used to fetch the web content accessible from within the TWS (e.g., Client Portal, Statements, Product Details, etc.)
5. What alternatives do I have in case I cannot implement a proxy solution on my network?
In this case, you might orient yourself towards a different type of access to the IBKR infrastructure, which includes a special connection type and a FIX/CTCI engine setup. This setup would, on the other hand, have different requirements in terms of commissions2.
Common Issues
6. What happens if the proxy configuration on your computer is wrong or outdated?
Occasionally, third-party software, even if already uninstalled, may leave behind a SOCKS proxy configuration on your computer. This may also happen if your computer has been infected with malware. In such cases, the proxy server, although configured, is non-existent or not accessible on the network. In such scenarios, the TWS will show an error message (e.g., No Internet Connectivity) and/or start the "Connection attempt #" loop upon login. The same will happen if the Proxy server exists, but has not been correctly configured on the client machines.
6a. How can I correct the proxy configuration if wrong?
When applicable, we recommend you always consult the IT / Networking team of your company first and ask for guidance.
If you are autonomously managing your network, please follow the instructions below according to the Operating System of your machine/s:
Windows
W.1 Press CTRL+S to open the Windows search
W.2 Type Proxy Settings and press Enter
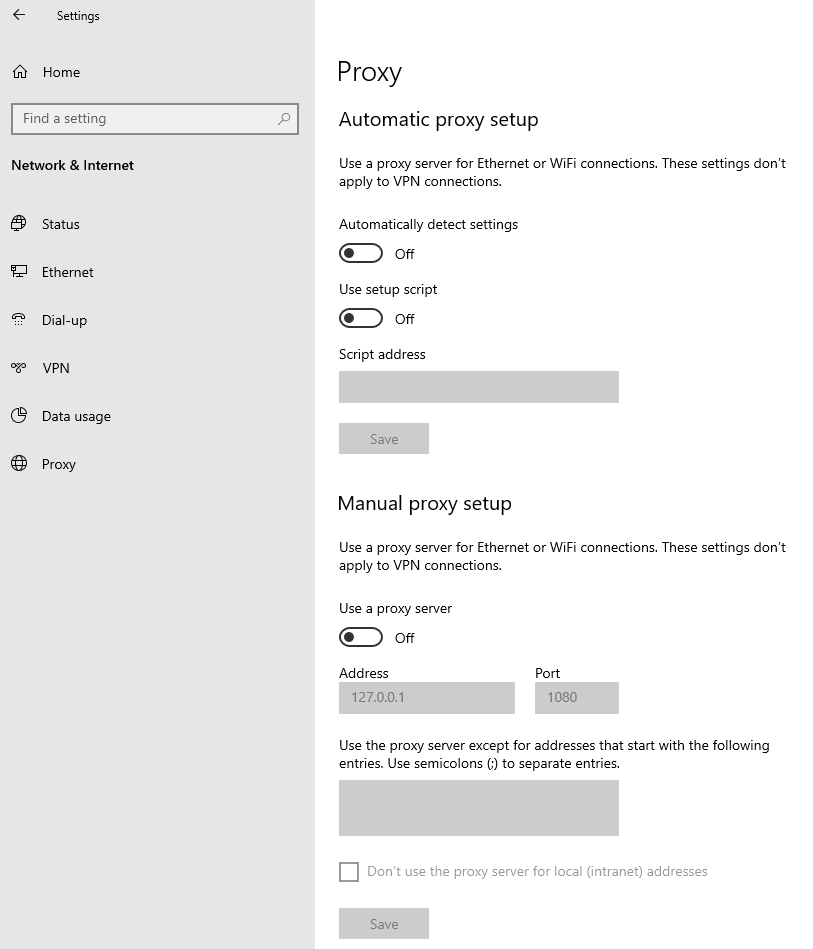
W.3 If no Proxy is present on your network, make sure the switch "Use a proxy server" is deactivated (see Figure 2 below). If a Proxy server is active on your network, make sure the Address (or hostname) and Port are correctly defined.
Figure 2.
Mac
M.1 Click on the Apple icon at the top left corner of the screen and select System Preferences
M.2 Click on Network
M.3 Select the Network connection you are using to access the Internet (e.g. Wi-Fi) and click on it
M.4 Click on the Advanced button and then on the Proxies tab
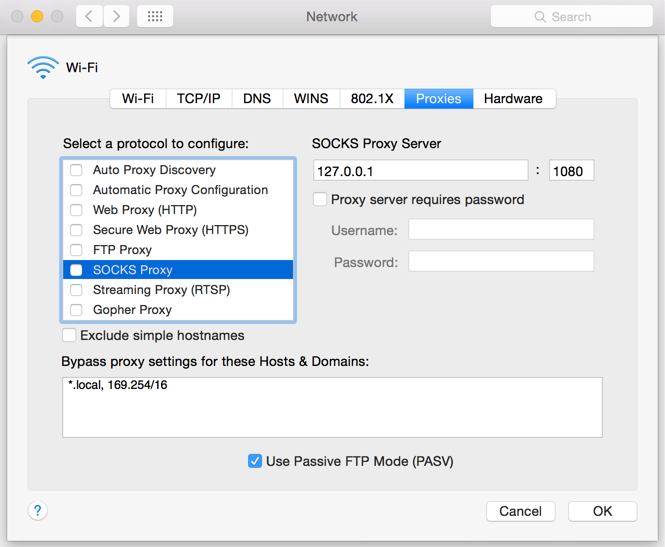
5. If no proxy is present on your network, make sure all the checkboxes (SOCKS Proxy, Web Proxy, Secure Web Proxy) are deactivated (see Figure 3 below). If a Proxy is present on your network, ensure the Protocol, Address (or hostname) and Port are correct.
Figure 3.
7. You are using Public proxies and proxy chains to hide your presence or identity
There are public proxy and proxy chain services purposed to disguise or hide the identity and the activity of the subscriber or to bypass regional restrictions. One of the most famous services is the "Tor" network.
While those services may not necessarily be used for criminal purposes, they render subscriber traceability very difficult when not impossible. Since IBKR is obliged by the financial industry regulators to maintain records of trading activities and trade initiators, we do not allow our clients to reach our systems while using an anonymizing service. If you are using such a service, your TWS connection attempts will be automatically rejected by our gateways.
Technical Background
A proxy server usually acts as a gateway and as a barrier between your local network and the Internet. The proxy listens for outgoing connection requests from the internal workstation/s and forwards them to the desired target host or service on the Internet. When the target replies to such requests, the proxy routes the incoming responses back to the internal workstation/s that initiated the process.
Being the proxy, the only machine of your network actually accessing the Internet, it prevents the other machines and the internal segment of your network (LAN) from being accessible by external actors and hence from being exposed to threats and intrusion attempts.
Additionally, a proxy server can offer a variety of other services, such as web content caching and filtering.
9. Which types of Proxy servers are commonly used and where?
Proxy servers are commonly found within enterprise-grade networks. In the vast majority of cases, proxies are not used by individuals since private broadband connections are established through consumer-grade routers that already offer built-in proxy/firewall solutions. An exception is represented by public proxy or proxy chains discussed in detail in the section You are using Public proxies and proxy chains to hide your presence or identity
There are two main types of Proxy servers:
The HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) defines the rules and the standards for fetching Web content from a Web server and rendering such content on your Web Browser.
A Web Proxy handles only the routing of HTTP requests and HTTP responses. Those requests are transparently generated and sent by your browser whenever you access a Web page. Such requests are normally sent using specific ports (TCP 80 and TCP 443). Hence a Web Proxy usually listens for outgoing HTTP requests coming from your internal network (LAN) only on the TCP ports mentioned above.
SOCKS (Socket Secure) Proxies are designed to handle any type of traffic (not only HTTP/S traffic), generated by any protocol or program (including Trader Workstation).
Notes
1. More information about the servers accessed by the TWS is available in IBKB2816.
2. For an overview of the different special connection options and related requirements, please click here.
For an overview of the FIX infrastructure, please click here.