リスク・ナビゲーター: 代替となる証拠金計算機能
弊社では証拠金レベルを定期的に見直し、市況の許す法定最小限以上に上げるための変更を行います。 こういった変更がポートフォリオに与える影響をご理解いただくサポートとして、弊社では「代替となる証拠金計算機能」をリスクナビゲーター内でご提供しています。下記は証拠金へのインパクトを左右する「What-if(仮想)」ポートフォリオ作成のステップとなります。
ステップ 1: 新しい「What-if(仮想)」ポートフォリオを開く
クラシックTWS取引プラットフォームからは、 分析ツール、リスク・ナビゲーターと進み、新しいWhat-Ifを開くメニューを選択してください(表示1)。
表示 1
.png)
モザイクTWS取引プラットフォームからは、新規ウィンドウ、リスク・ナビゲーターと進み、新しいWhat-Ifを開くメニューを選択してください。
ステップ 2: 開始時のポートフォリオを設定する
ポップアップ・ウィンドウが表示され(表示 2)、お客様の現在のポートフォリオから仮想ポートフォリオを作成するか、または新しいポートフォリオを作成するか質問されます。「はい」をクリックすると既存のポジションが新しい「What-If」ポートフォリオにダウンロードされます。
表示 2
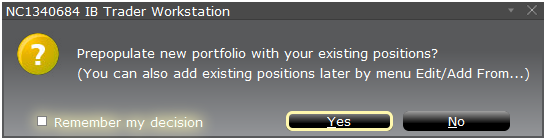
「いいえ」をクリックするとポジションは入力せずに「What-If」ポートフォリオが開きます。
リスク・ダッシュボード
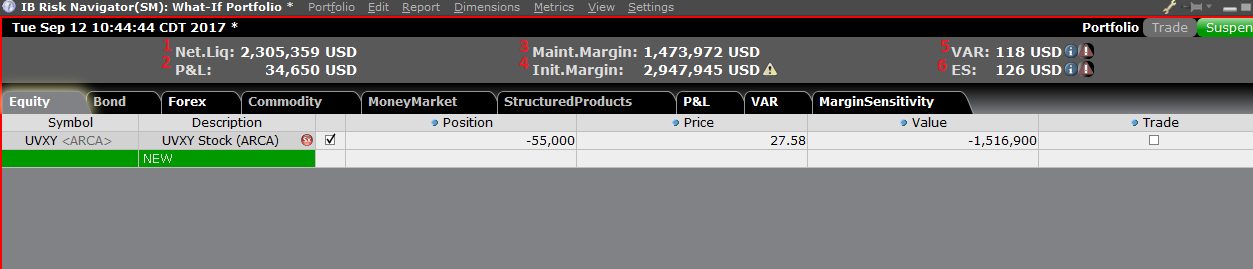
リスク・ダッシュボードは商品タブに並んでピンされ、「what-if」および実際のポートフォリオの両方に利用できます。「What-if」ポートフォリオの場合には値がオンデマンドで計算されます。ダッシュボードには以下を含める口座情報が一目で分かるように表示されます:
1) 流動性資産価値: 口座の流動性資産価値
2) 損益: ポートフォリオ全体の日次の損益合計
3) 維持証拠金: 現在の維持証拠金の合計
4) 委託証拠金: 委託証拠金の合計
5) VAR: ポートフォリオ全体のバリューアットリスク(VAR)
6) 予想される不足額(ES): 最悪のシナリオにおけるポートフォリオのリターンである予想される不足額(平均リューアットリスク)
代替となる証拠金計算機能
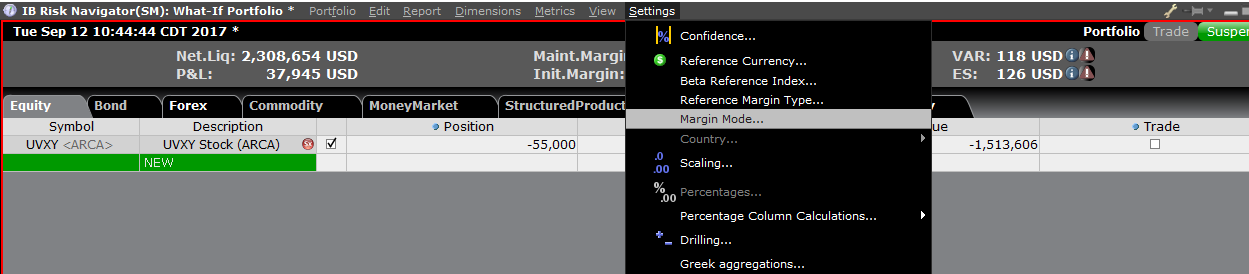
設定メニューより証拠金モード(表示 3)をクリックしてアクセスできる「代替となる証拠金計算機能」は、証拠金が変更された場合の必要証拠全体金への影響を割り出します。
表示 3
ステップ 3: 証拠金モード設定の選択
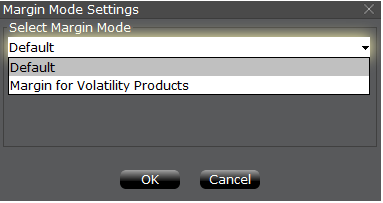
証拠金モード設定とタイトルのついたポップアップ・ウィンドウが表示されます(表示 4)。ウィンドウ内のドロップダウンメニューを利用して、証拠金計算をデフォルト(現在のポリシー)から、新しい証拠金設定(新しい証拠金ポリシーとして)の新しいタイトル に変更します。選択したらウィンドウ内の「OK」ボタンをクリックしてください。
表示 4
新しい証拠金モード設定が指定され次第、リスク・ナビゲーターのダッシュボードがこれを反映して自動的に更新されます。証拠金モード設定はどちらにでも簡単に切り替えることができます。現在の証拠金モードはリスク・ナビゲーターのウィンドウ(表示 5)の左下端に表示されます。
表示 5
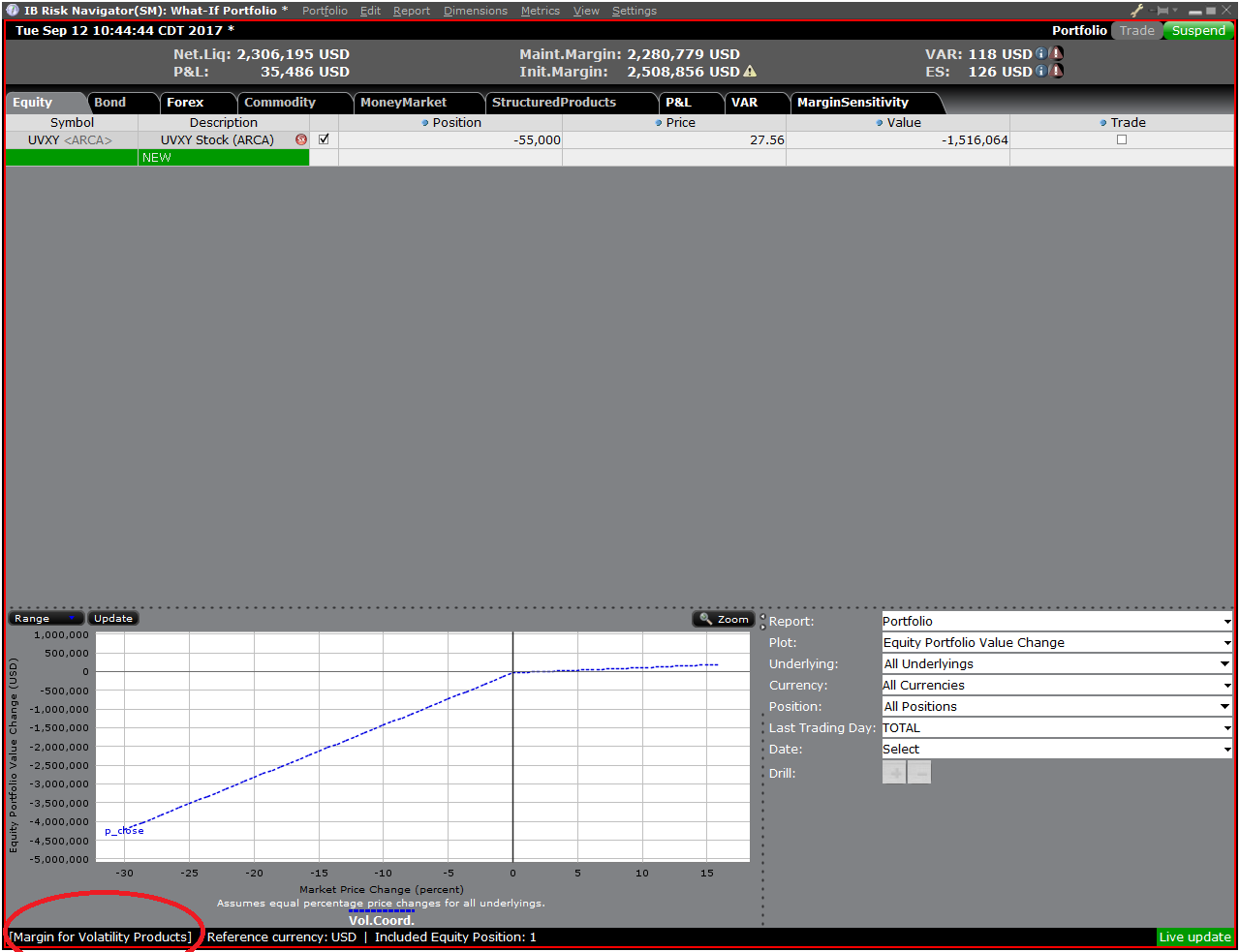
ステップ 4: ポジションの追加
「What-If」ポートフォリオにポジションを追加するには、先ず「新規」とタイトルのついた緑色の列をクリックしてから原資産シンボルを入力してください(表示 6)。この後、商品タイプを指定してから(表示 7)ポジションの数量を入力してください(表示 8)。
表示 6
表示 7
表示 8
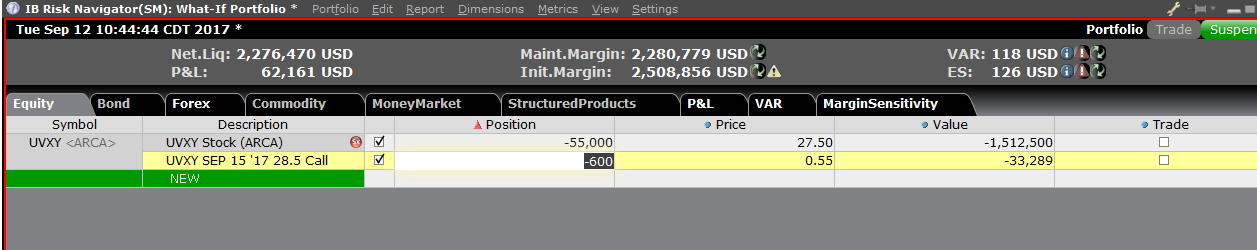
ポジションを変更して、これによる証拠金への影響を見ることができます。ポジションの変更後は証拠金額の右にある再計算アイコン(![]() )をクリックして、アップデートしてください。アイコンが表示されている場合には、証拠金額がWhat-If ポートフォリオの内容と一致していないことを意味します。
)をクリックして、アップデートしてください。アイコンが表示されている場合には、証拠金額がWhat-If ポートフォリオの内容と一致していないことを意味します。
満期前のオプション割当て
アメリカスタイルのオプションの売り手(ライター)は、オプションが満期になるまでいつでも権利行使を割当てられる可能性があります。これはオプションの売り手が、オプションを売却したあと満期になるまで、またはオプションコントラクトの売り手が買い戻してクローズするまで、いつでも割当ての対象となることを意味します。早期の権利行使はコールまたはプットの所有者が満期になる前に自分の権利を行使しようとする場合に発生します。オプションの売り手は割当てをコントロールすることはできず、またこれがいつ発生するかを正確に把握することはできません。一般的に割当てのリスクは満期に近づくほど高くなりますが、アメリカスタイルのオプション取引にはいつでも割当てが発生する可能性があります。
ショートプット
プットを売却する際、売り手は原資産株か資産を特定の価格(権利行使価格)と特定の時間枠(満期日)で購入する義務があります。オプションの権利行使価格が株式の現在の市場価格より低い場合、市場価格の方が権利行使価格より高いため、オプション保有者は株式の売却によって利益を得ることがありません。逆にオプションの権利行使価格が株式の現在の市場価格より高い場合、オプションの売り手には割当てのリスクが発生します。
ショートコール
コールの所有者は売却によって、売り手から特定の時間枠で株式を購入、または「コール」する権利を得ることができます。株式の市場価格がオプションの権利行使価格より低い場合、コール所有者は市場価格以上で株式をコールしても利益を得ることがありません。 株式の市場価格がオプションの権利行使価格より高い場合、コール所有者は市場価格以下で株式をコールすることができます。ショートコールはインザマネーの場合や、配当金が予定されていてショートコールの付帯的価値が配当金より低い場合には、割当てのリスクが発生します。
オプションはどうなりますか?
ショートコールが割当てられる場合、ショートコールの所有者には空売り株が割当てられます。例えば、ABC社の株式が$55で取引されていてショートコールが$50の権利行使価格で割当てられる場合、ショートコールは$50で株式の空売り株に変換されます。口座保有者はこの後、株式を市場価格の$55で買い戻してショートポジションをクローズすることができます。100株の場合の損失額の合計は$500になり、 コールの売却によってクレジットが元より下がります。
ショートプットが割当てられる場合、ショートプットの所有者にはプットの権利行使価格でロングの株式が発生します。例えば、XYZ社の株式が$90で取引されていてショートプットの売り手に$96の権利行使価格で株式が割当てられる場合、プットの売り手には権利行使価格の$96以上の市場価格で、株式を購入する義務が発生します。口座保有者が$90で株式のロングポジションをクローズすると仮定すると、100株の場合の損失額の合計は$600になり、プットの売却によってクレジットが元より下がります。
オプションの割当てによる証拠金不足
割当てが満期前に行われ株式のポジションが証拠金不足につながる場合には、弊社の証拠金ポリシーに基づき、証拠金不足を解消するために口座は自動強制決済の対象になります。強制決済はオプションポジションの結果として発生した株式に限られません。
またオプションスプレッドのショートレッグに割当てられた口座に対し、弊社ではこの口座の保有するロングオプションを権利行使することはありません。 IBKRではロングオプション保有者の意図を推測できません。また満期前のロングオプションの権利行使は、オプションの売却によって実現可能な時間価値の喪失につながる可能性があります。
満期後のエクスポージャー、コーポレートアクション、および権利落ちなどのイベント
弊社では特定の満期やコーポレートアクション関連のイベントに基づいて、リスクを軽減する手順をご用意しています。満期に関する弊社のポリシーは、IBKRナレッジーベース「満期に関わる強制決済」をご参照ください。
口座をお持ちのお客様は、口座申請の時点でオプションの取引資格の対象となるすべてのお客様に対してIBKRよりご提供させていただいている「一般的なオプション取引に掛る商品性とリスクに関するディスクロージャー」をご参照の上、ここに明記される割当てに関するリスクをご確認ください。 こちらの資料はOCCのウェブサイトからもご参照可能です。
Risk Based Margin Considerations
| LLC Risk Based (i.e. Portfolio Margin) | Non-LLC Risk Based Margin | |
| $110,000 initial value requirement | Yes | N/A |
| Minimum equity to operate on margin | USD 100,000 | IB-HK: USD 2,000 IB-AU: AUD 2,000 IB-LUX, IB-IE and IB-CE: EUR 2,000 IB-SG: SGD 2,000 |
| Full options trading approval | Yes | N/A |
| PDT | Yes | N/A |
| Stress testing | Yes | Yes |
| Dynamic House Scanning Charges (TOMS) ¹ | Yes | Yes |
| Shifts in option Implied Volatility (IV) | Yes | Yes |
| A $0.375 multiplied by the index per contract minimum is computed (Only applied to Portfolio Margin eligble products) | Yes | Yes |
| Initial margin will be 110% of Maintenance Margin (US securities only) | Yes | Yes |
| Initial margin will be 125% of Maintenance Margin (Non-US securities) | Yes | Yes |
| Extreme Price Scans | Yes | Yes |
| Large Position Charge (A position which is 1% or more of shares outstanding) | Yes | Yes |
| Days to Liquidate (A large position in relation to the average daily trading volume, which may result in higher initial margin requirements) | Yes | Yes |
| Global Concentration Charge (2 riskiest position stressed +/-30% remaining assets +/-5%) | Yes | Yes |
| Singleton Margin Method for Small Cap Stocks (Stress Test which simulates a price change reflective of a $500 million USD in market capitalization)² | Yes | Yes |
| Singleton Margin Method for stocks domiciled in China (Stress Test which simulates a price change reflective of a $1.5 billion USD in market capitalization)² | Yes | Yes |
| Default Singleton Margin Method (Stress Test which simulates a price change +30% and down -25%)² | Yes | Yes |
| Singleton Margin Method for HK Real Estate Stocks (Stress test +/-50%)² | Yes | Yes |
1 Dynamic House Scanning Charges are available only on select exchanges (Asian Exchanges and MEXDER)
2 IBKR will calculate the potential loss for each stock and its derivates by subjecting them to a stress test. The requirement for the stock (and its derivatives) which projects the greatest loss in the above scenario will be compared to what would otherwise be the aggregate portfolio margin requirement, and the greater of the two will be the margin requirement for the portfolio
U.S. 2020 Election Margin Increase
In light of the potential market volatility associated with the upcoming United States presidential election, Interactive Brokers will implement an increase in the margin requirement for all U.S. traded equity index futures and derivatives and Dow Jones Futures listed on the OSE.JPN exchange.
Clients holding a position in a U.S. equity index future and their derivatives and/or Down Jones Futures listed on the OSE.JPN exchange should expect the margin requirement to increase by approximately 35% above the normal margin requirement. The increase is scheduled to be implemented gradually over a 20-calendar day period with the maintenance margin increase starting on October 5, 2020 through October 30, 2020.
The table below provides examples of the margin increases projected for some of the more widely held products
| Future Symbol |
Description | Listing Exchange | Trading Class | Current Rate (Price scan range)* | Projected Rate (Price scan range) |
| ES | E-mini S&P 500 | CME | ES | 7.13 | 9.63 |
| YM | MINI DJIA | CBOT | YM | 6.14 | 8.29 |
| RTY | Russell 2000 | CME | RTY | 6.79 | 9.17 |
| NQ | NASDAQ E-MINI | CME | NQ | 6.57 | 8.87 |
| DJIA | OSE Dow Jones Industrial Average | OSE.JPN | DJIA | 5.14 | 6.94 |
*As of 10/2/20 open.
NOTE: IBKR's Risk Navigator can help you determine the impact the new maintenance margin requirements will have on your current portfolio or any other portfolio you would like to construct or test. For more information about the Alternative Margin Calculator feature, please see KB Article 2957: Risk Navigator: Alternative Margin Calculator and from the margin mode setting in Risk Navigator, select " US Election Margin".
Overview of Central Bank of Ireland CFD Rules Implementation for Retail Clients at IBIE
|
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 61% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with IBKR. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money. |
The Central Bank of Ireland (CBI) enacted new rules applicable to retail clients trading CFDs, effective 1st August 2019. Professional clients are unaffected.
The rules consist of: 1) leverage limits; 2) a margin close out rule on a per account basis; 3) negative balance protection on a per account basis; 4) a restriction on the incentives offered to trade CFDs; and 5) a standardized risk warning.
Most clients (excepting regulated entities) are initially categorised as Retail Clients. IBKR may in certain circumstances agree to reclassify a Retail Client as a Professional Client, or a Professional Client as a Retail Client. Please see MiFID Categorisation for further detail.
The following sections detail how IBKR has implemented the CBI Decision.
1 Leverage Limits
1.1 Margins
Leverage limits were set by CBI at different levels depending on the underlying:
- 3.33% for major currency pairs; Major currency pairs are any combination of USD; CAD; EUR; GBP; CHF; JPY
- 5% for:
- Non-major currency pairs are any combination that includes a currency not listed above, e.g., USD.CNH
- Major indices are IBUS500; IBUS30; IBUST100; IBGB100; IBDE40; IBEU50; IBFR40; IBJP225; IBAU200
- Gold
- 10% for non-major equity indices; IBES35; IBCH20; IBNL25; IBHK50
- 20% for individual equities
1.2 Applied Margins - Standard Requirement
In addition to the CBI Margins, IBKR establishes its own margin requirements (IB Margins) based on the historical volatility of the underlying, and other factors. We will apply the IB Margins if they are higher than those prescribed by CBI .
Details of applicable IB and CBI margins can be found here.
1.2.1 Applied Margins - Concentration Minimum
A concentration charge is applied if your portfolio consists of a small number of CFD and/or Stock positions, or if the three largest positions have a dominant weight. We stress the portfolio by applying a 30% adverse move on the three largest positions and a 5% adverse move on the remaining positions. The total loss is applied as the maintenance margin requirement if it is greater than the standard requirement for the combined Stock and CFD positions. Note that the concentration charge is the only instance where CFD and Stock positions are margined together.
1.3 Funding of Initial Margin Requirements
You can only use cash to post initial margin to open a CFD position.
Initially all cash used to fund the account is available for CFD trading. Any initial margin requirements for other instruments and cash used to purchase cash stock reduce the available cash. If your cash stock purchases have created a margin loan, no funds are available for CFD trades even if your account has significant equity. We cannot increase a margin loan to fund CFD margin under the CBI rules.
Realized CFD profits are included in cash and are available immediately; the cash does not have to settle first. Unrealized profits however cannot be used to meet initial margin requirements.
2 Margin Close Out Rule
2.1 Maintenance Margin Calculations & Liquidations
The CBI requires IBKR to liquidate CFD positions latest when qualifying equity falls below 50% of the initial margin posted to open the positions. IBKR may close out positions sooner if our risk view is more conservative. Qualifying equity for this purpose includes CFD cash and unrealized CFD P&L (positive and negative). Note that CFD cash excludes cash supporting margin requirements for other instruments.
The basis for the calculation is the initial margin posted at the time of opening a CFD position. In other words, and unlike margin calculations applicable to non-CFD positions, the initial margin amount does not change when the value of the open position changes.
2.1.1 Example
You have EUR 2000 cash in your account and no open positions. You want to buy 100 CFDs of XYZ at a limit price of EUR 100. You are first filled 50 CFDs and then the remaining 50. Your available cash reduces as your trades are filled:
|
|
Cash |
Equity* |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Pre Trade |
2000 |
2000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2000 |
|
|
Post Trade 1 |
2000 |
2000 |
50 |
100 |
5000 |
0 |
1000 |
500 |
1000 |
No |
|
Post Trade 2 |
2000 |
2000 |
100 |
100 |
10000 |
0 |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
No |
*Equity equals Cash plus Unrealized P&L
The price increases to 110. Your equity is now 3000, but you cannot open additional positions because your available cash is still 0, and under the CBI rules IM and MM remain unchanged:
|
|
Cash |
Equity |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Change |
2000 |
3000 |
100 |
110 |
11000 |
1000 |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
No |
The price then drops to 95. Your equity declines to 1500 but there is no margin violation since it is still greater than the 1000 requirement:
|
|
Cash |
Equity |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Change |
2000 |
1500 |
100 |
95 |
9500 |
(500) |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
No |
The price falls further to 85, causing a margin violation and triggering a liquidation:
|
|
Cash |
Equity |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Change |
2000 |
500 |
100 |
85 |
8500 |
(1500) |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
Yes |
3 Negative Equity Protection
The CBI Decision limits your CFD-related liability to the funds dedicated to CFD-trading. Other financial instruments (e.g., shares or futures) cannot be liquidated to satisfy a CFD margin-deficit.*
Therefore, non-CFD assets are not part of your capital at risk for CFD trading.
Should you lose more than the cash dedicated to CFD trading, IB must write off the loss.
As Negative Equity Protection represents additional risk to IBKR, we will charge retail investors an additional financing spread of 1% for CFD positions held overnight. You can find detailed CFD financing rates here.
*Although we cannot liquidate non-CFD positions to cover a CFD deficit, we can liquidate CFD positions to cover a non-CFD deficit.
Margin Considerations for Intramarket Futures Spreads
Background
Clients who simultaneously hold both long and short positions of a given futures contract having different delivery months are often provided a spread margin rate that is less than the margin requirement for each position if considered separately. However, as the settlement prices of each contract may deviate significantly as the front month contract approaches its close out date, IBKR will reduce the benefit of the spread margin rate to reflect the risk of this price deviation.
Spread Margin Adjustment
This reduction is accomplished by effectively decoupling or breaking the spread in phases on each of the 3 business days preceding the close out date of the front contract month, as follows:
- On the 3rd business day prior to close out, the initial and maintenance margin requirements will be equal to 10% of their respective requirements on each contract month as if there was no spread, plus 90% of the spread requirement;
- On the 2nd business day prior to close out, the initial and maintenance margin requirements will be equal to 20% of their respective requirements on each contract month as if there was no spread, plus 80% of the spread requirement;
- On the business day prior to close out, the initial and maintenance margin requirements will be equal to 30% of their respective requirements on each contract month as if there was no spread, plus 70% of the spread requirement.
Working Example
Assume a hypothetical futures contract XYZ with the margin requirements as outlined in the table below:
| XYZ | Front Month - 1 Short Contract (Uncovered) | Back Month - 1 Long Contract (Uncovered) | Spread - 1 Short Front Month vs. 1 Long Back Month |
| Initial Margin | $1,250 | $1,500 | $500 |
| Maintenance Margin | $1,000 | $1,200 | $400 |
Further assume a position consisting of 1 short front month contract and 1 long back month contract with the front month contract close out date = T. using this hypothetical example, the initial margin requirement over the 3 business day period preceding close out date is outlined in the table below:
| Day | Initial Margin Requirement | Calculation Details |
| T-4 | $500 | Unadjusted |
| T-3 | $725 | .1($1,250 + $1,500) + .9($500) |
| T-2 | $950 | .2($1,250 + $1,500) + .8($500) |
| T-1 | $1,175 | .3($1,250 + $1,500) + .7($500) |
| T | $1,175 | Positions not in compliance with close out requirements are subject to liquidation. |
Concentrated Positions in Low Cap Stocks
The margin requirement for accounts holding concentrated positions in low cap stocks is as follows:
- An alternative stress test will be considered following the margin calculation currently in place. Here, each stock and its derivatives will be subject to a stress test which simulates a price change reflective of a $500 million decrease in capitalization (e.g., 25% in the case of a stock with a market capitalization of $2 billion; 30% for a stock with a market capitalization of $1.5 billion; etc.). Stocks with a market capitalization of $500 million or below will be subject to a stress test as if the price has fallen to $0.
- For the stock which projects the greatest loss assuming a $500 million decrease in capitalization, that loss will be compared to the initial margin as determined under the preceding calculation for the aggregate portfolio and, if greater, will become the initial margin requirement.
- If the initial margin requirement is increased, the maintenance margin for that same stock and its derivatives will increase to approximately 90% of the initial requirement for the aggregate portfolio.
Overview of ESMA CFD Rules Implementation at IBKR (UK) - Retail Investors Only
|
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage.
61% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with IBKR.
You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money. |
The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) enacted new rules applicable to retail clients trading CFDs, effective 1st August 2018. Professional clients are unaffected.
The rules consist of: 1) leverage limits; 2) a margin close out rule on a per account basis; 3) negative balance protection on a per account basis; 4) a restriction on the incentives offered to trade CFDs; and 5) a standardized risk warning.
Most clients (excepting regulated entities) are initially categorised as Retail Clients. IBKR may in certain circumstances agree to reclassify a Retail Client as a Professional Client, or a Professional Client as a Retail Client. Please see MiFID Categorisation for further detail.
The following sections detail how IBKR (UK) has implemented the ESMA Decision.
1 Leverage Limits
1.1 ESMA Margins
Leverage limits were set by ESMA at different levels depending on the underlying:
- 3.33% for major currency pairs; Major currency pairs are any combination of USD; CAD; EUR; GBP; CHF; JPY
- 5% for non-major currency pairs and major indices;
- Non-major currency pairs are any combination that includes a currency not listed above, e.g. USD.CNH
- Major indices are IBUS500; IBUS30; IBUST100; IBGB100; IBDE40; IBEU50; IBFR40; IBJP225; IBAU200
- 10% for non-major equity indices; IBES35; IBCH20; IBNL25; IBHK50
- 20% for individual equities
1.2 Applied Margins - Standard Requirement
In addition to the ESMA Margins, IBKR (UK) establishes its own margin requirements (IB Margins) based on the historical volatility of the underlying, and other factors. We will apply the IB Margins if they are higher than those prescribed by ESMA.
Details of applicable IB and ESMA margins can be found here.
1.2.1 Applied Margins - Concentration Minimum
A concentration charge is applied if your portfolio consists of a small number of CFD positions, or if the three largest positions have a dominant weight. We stress the portfolio by applying a 30% adverse move on the three largest positions and a 5% adverse move on the remaining positions. The total loss is applied as the maintenance margin requirement if it is greater than the standard requirement.
1.3 Funds Available for Initial Margin
You can only use cash to post initial margin to open a CFD position. Realized CFD profits are included in cash and are available immediately; the cash does not have to settle first. Unrealized profits however cannot be used to meet initial margin requirements.
1.4 Automatic Funding of Initial Margin Requirements (F-segments)
IBKR (UK) automatically transfers funds from your main account to the F-segment of your account to fund initial margin requirements for CFDs.
Note however that no transfers are made to satisfy CFD maintenance margin requirements. Therefore if qualifying equity (defined below) becomes insufficient to meet margin requirements, a liquidation will occur even if you have ample funds in your main account. If you wish to avoid a liquidation you must transfer additional funds to the F-segment in Account Management.
2 Margin Close Out Rule
2.1 Maintenance Margin Calculations & Liquidations
ESMA requires IBKR to liquidate CFD positions latest when qualifying equity falls below 50% of the initial margin posted to open the positions. IBKR may close out positions sooner if our risk view is more conservative. Qualifying equity for this purpose includes cash in the F-segment (excluding cash in any other account segment) and unrealized CFD P&L (positive and negative).
The basis for the calculation is the initial margin posted at the time of opening a CFD position. In other words, and unlike margin calculations applicable to non-CFD positions, the initial margin amount does not change when the value of the open position changes.
2.1.1 Example
You have EUR 2000 cash in your CFD account. You want to buy 100 CFDs of XYZ at a limit price of EUR 100. You are first filled 50 CFDs and then the remaining 50. Your available cash reduces as your trades are filled:
| Cash | Equity* | Position | Price | Value | Unrealized P&L | IM | MM | Available Cash | MM Violation | |
| Pre Trade | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | |||||||
| Post Trade 1 | 2000 | 2000 | 50 | 100 | 5000 | 0 | 1000 | 500 | 1000 | No |
| Post Trade 2 | 2000 | 2000 | 100 | 100 | 10000 | 0 | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | No |
*Equity equals Cash plus Unrealized P&L
The price increases to 110. Your equity is now 3000, but you cannot open additional positions because your available cash is still 0, and under the ESMA rules IM and MM remain unchanged:
| Cash | Equity | Position | Price | Value | Unrealized P&L | IM | MM | Available Cash | MM Violation | |
| Change | 2000 | 3000 | 100 | 110 | 11000 | 1000 | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | No |
The price then drops to 95. Your equity declines to 1500 but there is no margin violation since it is still greater than the 1000 requirement:
| Cash | Equity | Position | Price | Value | Unrealized P&L | IM | MM | Available Cash | MM Violation | |
| Change | 2000 | 1500 | 100 | 95 | 9500 | (500) | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | No |
The price falls further to 85, causing a margin violation and triggering a liquidation:
| Cash | Equity | Position | Price | Value | Unrealized P&L | IM | MM | Available Cash | MM Violation | |
| Change | 2000 | 500 | 100 | 85 | 8500 | (1500) | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | Yes |
3 Negative Equity Protection
The ESMA Decision limits your CFD-related liability to the funds dedicated to CFD-trading. Other financial instruments (e.g. shares or futures) cannot be liquidated to satisfy a CFD margin-deficit.*
Therefore assets in the security and commodity segments of your main account, and non-CFD assets held in the F-segment, are not part of your capital at risk for CFD trading. However, all cash in the F-segment can be used to cover losses arising from CFD trading.
As Negative Equity Protection represents additional risk to IBKR, we will charge retail investors an additional financing spread of 1% for CFD positions held overnight. You can find detailed CFD financing rates here.
*Although we cannot liquidate non-CFD positions to cover a CFD deficit, we can liquidate CFD positions to cover a non-CFD deficit.
4 Incentives Offered to trade CFDs
The ESMA Decision imposes a ban on monetary and certain types of non-monetary benefits related to CFD trading. IBKR does not offer any bonus or other incentives to trade CFDs.
SMAとそのしくみ
SMAとは「Special Memorandum Account」のことです。この口座に保有されるのは株式や現金ではなく、Reg. Tの信用取引口座にある有価証券の時価が上昇したときに発生する信用枠を指します。SMAの目的は含み益による次の買い付けのために買付力を維持することにあります。これができない場合には次の買付の際に余剰の株式を取りくずして資金化することになるため、SMAは安定した口座価値を維持し、不必要な資金調達取引を最小限に抑えるのに役立ちます。
有価証券の価値が上昇するとSMAも上昇しますが、 有価証券の価値が下がる場合でもSMAが下がることはありません。SMAが減少するのは有価証券を購入したり現金を引き出す場合のみであり、SMAの使用に関する唯一の制限は、追加の購入や引出しによって口座が維持証拠金額の要件を下回らないことになります。SMAを増加させる取引には、現金預金、受取利息、または受取配当金(1ドル単位)、有価証券の売却(純収入の50%)などがあります。注意すべき点は、SMA残高は過去の記帳項目をすべてを集計したものであり、口座開設時からの残高に影響を与えるということです。長期間分の大量のエントリーが含まれているため、日々のアクティビティステートメントから現在のSMAのレベルを計算し確認することは、可能ではあるものの現実的には困難です。
SMAがどのように機能するか、例を使って考えてみます。ある口座保有者が$5,000を入金し、ローンバリューが50%の有価証券を$10,000購入したと仮定します(または必要証拠金が1-ローンバリュー、または50%に等しいとします)。この場合、口座開設前と開設後の値は以下のようになります:
|
項目
|
詳細
|
イベント1 - 初回入金
|
イベント2 - 株式購入
|
|
A.
|
キャッシュ
|
$5,000
|
($5,000)
|
|
B.
|
ロング株式市場価格
|
$0
|
$10,000
|
|
C.
|
流動性総資産/EWL* (A + B)
|
$5,000
|
$5,000
|
|
D.
|
委託証拠金(B * 50%)
|
$0
|
$5,000
|
|
E
|
委託証拠金余力(C - D)
|
$5,000
|
$0
|
|
F.
|
SMA
|
$5,000
|
$0
|
|
G.
|
購買力
|
$10,000
|
$0
|
次に、買い持ち銘柄の価値が$12,000に上昇したとします。この$2,000の市場価格の上昇により、$1,000のSMAが発生し、口座保有者は次のうちのいずれかが可能となります: 1)追加の資金を預けることなく、50%の証拠金率を想定して$2,000の価値のある有価証券を追加で購入する。または、2)現金で$1,000を引出す(口座に現金がない場合には、借方の残高を増やすことで資金を調達することができます)。以下をご覧ください:
|
項目
|
詳細
|
イベント2 – 株式購入
|
イベント3 - 株価上昇
|
|
A.
|
キャッシュ
|
($5,000)
|
($5,000)
|
|
B.
|
ロング株式市場価格
|
$10,000
|
$12,000
|
|
C.
|
流動性総資産/EWL* (A + B)
|
$5,000
|
$7,000
|
|
D.
|
委託証拠金(B * 50%)
|
$5,000
|
$6,000
|
|
E
|
委託証拠金余力(C - D)
|
$0
|
$1,000
|
|
F.
|
SMA
|
$0
|
$1,000
|
|
G.
|
購買力
|
$0
|
$2,000
|
*EWLは貸付金額を含む資産価値のことであり、この例では流動性資産を指します。
SMAはReg. Tに基づく考え方です。IB LLCの証券口座がオーバーナイトの必要証拠金を遵守していることを確認するために使用されるものであり、日中やオーバーナイトの維持証拠金に対する遵守の確認をするためには使用されません。また、コモディティ口座の証拠金遵守の確認に使用されることもありません。同様に、オーバーナイトつまりReg. T必要証拠金が必要となる時間(米国東部標準時15:50)にSMAがマイナスである口座は、Reg. T必要証拠金遵守のため、ポジションの強制決済の対象となります。
Risk Navigator: Alternative Margin Calculator
IB routinely reviews margin levels and will implement changes which serve to increase requirements above statutory minimums as market conditions warrant. To assist clients with understanding the effects of such changes on their portfolio, a feature referred to as the "Alternative Margin Calculator" is provided within the Risk Navigator application. Outlined below are the steps for creating a “what-if” portfolio for the purpose of determining the impact of such margin changes.
Step 1: Open a new “What-if” portfolio
From the Classic TWS trading platform, select the Analytical Tools, Risk Navigator, and then Open New What-If menu options (Exhibit1).
Exhibit 1
.png)
From the Mosaic TWS trading platform, select New Window, Risk Navigator, and then Open New What-If menu options.
Step 2: Define starting portfolio
A pop-up window will appear (Exhibit 2) from which you will be prompted to define whether you would like to create a hypothetical portfolio starting from your current portfolio or a newly created portfolio. Clicking on the "yes" button will serve to download existing positions to the new “What-If” portfolio.
Exhibit 2

Clicking on the "No" button will open up the “What – If” Portfolio with no positions.
Risk Dashboard
The Risk Dashboard is pinned along the top of the product tab-sets, and is and is available for what-if as well as active portfolios. The values are calculated on demand for what-if portfolios. The dashboard provides at-a-glance account information including:
1) Net Liquidation Value: The total Net Liquidation Value for the account
2) P&L: The total daily P&L for the entire portfolio
3) Maintenance Margin: Total current maintenance margin
4) Initial Margin: Total initial margin requirements
5) VAR: Shows the Value at risk for the entire portfolio
6) Expected Shortfall (ES): Expected Shortfall (average value at risk) is expected return of the portfolio in the worst case

Alternative Margin Calculator
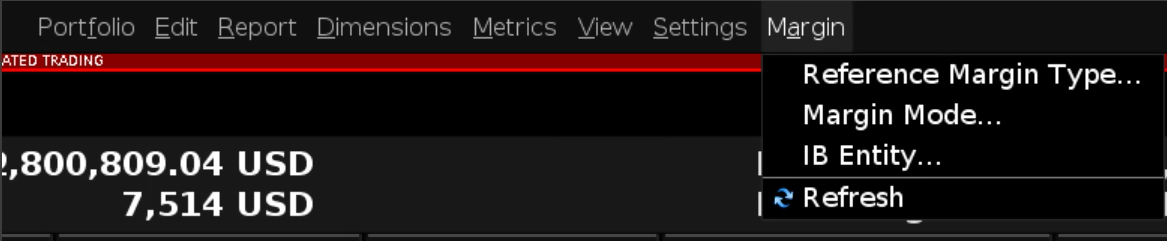
The Alternative Margin Calculator, accessed from the Margin menu and clicking on the Margin Mode (Exhibit 3), shows how the margin change will affect the overall margin requirement, once fully implemented.
Exhibit 3
Step 3: Selecting Margin Mode Settings
A pop-up window will appear (Exhibit 4) entitled Margin Mode Setting. You can use the drop-down menu in that window to change the margin calculations from Default (being the current policy) to the new title of the new Margin Setting (being the new margin policy). Once you have made a selection click on the OK button in that window.
Exhibit 4

Once the new margin mode setting is specified, the Risk Navigator Dashboard will automatically update to reflect your choice. You can toggle back and forth between the Margin Mode settings. Note that the current Margin Mode will be shown in the lower left hand corner of the Risk Navigator window (Exhibit 5).
Exhibit 5

Step 4: Add Positions
To add a position to the "What - If" portfolio, click on the green row titled "New" and then enter the underlying symbol (Exhibit 6), define the product type (Exhibit 7) and enter position quantity (Exhibit 8)
Exhibit 6

Exhibit 7

Exhibit 8

You can modify the positions to see how that changes the margin. After you altered your positions you will need to click on the recalculate icon (![]() ) to the right of the margin numbers in order to have them update. Whenever that icon is present the margin numbers are not up-to-date with the content of the What-If Portfolio.
) to the right of the margin numbers in order to have them update. Whenever that icon is present the margin numbers are not up-to-date with the content of the What-If Portfolio.
