Complex Position Size
For complex, multi-leg options positions comprising two or more legs, TWS might not track all changes to this position, e.g. a vertical spread where the short leg is assigned and the user re-writes the same leg the next day, or if the user creates a the position over multiple trades, or if the order is not filled as a native combination at the exchange.
Risks of Volatility Products
Trading and investing in volatility-related Exchange-Traded Products (ETPs) is not appropriate for all investors and presents different risks than other types of products. Among other things, ETPs are subject to the risks you may face if investing in the components of the ETP, including the risks relating to investing in complex securities (such as futures and swaps) and risks associated with the effects of leveraged investing in geared funds. Investors should be familiar with the diverse characteristics of each ETF, ETN, future, option, swap and any other relevant security type. We have summarized several risk factors (as identified in prospectuses for ETPs and in other sources) and included links so you can conduct further research. Please keep in mind that this is not a complete list of the risks associated with these products and investors are responsible for understanding and familiarizing themselves completely before entering into risk-taking activities. By providing this information, Interactive Brokers (IB) is not offering investment or trading advice regarding ETPs to any customer. Customers (and/or their independent financial advisors) must decide for themselves whether ETPs are an appropriate investment for their portfolios.
Allocation of Partial Fills
How are executions allocated when an order receives a partial fill because an insufficient quantity is available to complete the allocation of shares/contracts to sub-accounts?
Overview:
From time-to-time, one may experience an allocation order which is partially executed and is canceled prior to being completed (i.e. market closes, contract expires, halts due to news, prices move in an unfavorable direction, etc.). In such cases, IB determines which customers (who were originally included in the order group and/or profile) will receive the executed shares/contracts. The methodology used by IB to impartially determine who receives the shares/contacts in the event of a partial fill is described in this article.
Background:
Before placing an order CTAs and FAs are given the ability to predetermine the method by which an execution is to be allocated amongst client accounts. They can do so by first creating a group (i.e. ratio/percentage) or profile (i.e. specific amount) wherein a distinct number of shares/contracts are specified per client account (i.e. pre-trade allocation). These amounts can be prearranged based on certain account values including the clients’ Net Liquidation Total, Available Equity, etc., or indicated prior to the order execution using Ratios, Percentages, etc. Each group and/or profile is generally created with the assumption that the order will be executed in full. However, as we will see, this is not always the case. Therefore, we are providing examples that describe and demonstrate the process used to allocate partial executions with pre-defined groups and/or profiles and how the allocations are determined.
Here is the list of allocation methods with brief descriptions about how they work.
· AvailableEquity
Use sub account’ available equality value as ratio.
· NetLiq
Use subaccount’ net liquidation value as ratio
· EqualQuantity
Same ratio for each account
· PctChange1:Portion of the allocation logic is in Trader Workstation (the initial calculation of the desired quantities per account).
· Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user
· Inline Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user.
· Model1:
Roughly speaking, we use each account NLV in the model as the desired ratio. It is possible to dynamically add (invest) or remove (divest) accounts to/from a model, which can change allocation of the existing orders.
Basic Examples:
Details:
CTA/FA has 3-clients with a predefined profile titled “XYZ commodities” for orders of 50 contracts which (upon execution) are allocated as follows:
Account (A) = 25 contracts
Account (B) = 15 contracts
Account (C) = 10 contracts
Example #1:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 10 am (ET) the order begins to execute2but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 2 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 7 of the 50 contracts are filled or 14%). For each account the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 14% of 25 = 3.5 rounded down to 3
Account (B) = 14% of 15 = 2.1 rounded down to 2
Account (C) = 14% of 10 = 1.4 rounded down to 1
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.10).
A: final allocation of 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 2 contract, which is 2/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.20)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #2:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be filled3 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 1 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is executed (i.e., 5 of the 50 contracts are filled or 10%).For each account, the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 10% of 25 = 2.5 rounded down to 2
Account (B) = 10% of 15 = 1.5 rounded down to 1
Account (C) = 10% of 10 = 1 (no rounding necessary)
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. to Account B which currently has a ratio of 0.067).
A: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #3:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be executed2 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 12 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 3 of the 50 contracts are filled or 6%). Normally the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers, however for a fill size of less than 4 shares/contracts, IB first allocates based on the following random allocation methodology.
In this case, since the fill size is 3, we skip the rounding fractional amounts down.
For the first share/contract, all A, B and C have the same initial fill ratio and fill quantity, so we randomly pick an account and allocate this share/contract. The system randomly chose account A for allocation of the first share/contract.
To Summarize3:
A: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
C: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
Next, the system will perform a random allocation amongst the remaining accounts (in this case accounts B & C, each with an equal probability) to determine who will receive the next share/contract.
The system randomly chose account B for allocation of the second share/contract.
A: 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
The system then allocates the final [3] share/contract to an account(s) with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.00).
A: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Available allocation Flags
Besides the allocation methods above, user can choose the following flags, which also influence the allocation:
· Strict per-account allocation.
For the initially submitted order if one or more subaccounts are rejected by the credit checking, we reject the whole order.
· “Close positions first”1.This is the default handling mode for all orders which close a position (whether or not they are also opening position on the other side or not). The calculation are slightly different and ensure that we do not start opening position for one account if another account still has a position to close, except in few more complex cases.
Other factor affects allocations:
1) Mutual Fund: the allocation has two steps. The first execution report is received before market open. We allocate based onMonetaryValue for buy order and MonetaryValueShares for sell order. Later, when second execution report which has the NetAssetValue comes, we do the final allocation based on first allocation report.
2) Allocate in Lot Size: if a user chooses (thru account config) to prefer whole-lot allocations for stocks, the calculations are more complex and will be described in the next version of this document.
3) Combo allocation1: we allocate combo trades as a unit, resulting in slightly different calculations.
4) Long/short split1: applied to orders for stocks, warrants or structured products. When allocating long sell orders, we only allocate to accounts which have long position: resulting in calculations being more complex.
5) For non-guaranteed smart combo: we do allocation by each leg instead of combo.
6) In case of trade bust or correction1: the allocations are adjusted using more complex logic.
7) Account exclusion1: Some subaccounts could be excluded from allocation for the following reasons, no trading permission, employee restriction, broker restriction, RejectIfOpening, prop account restrictions, dynamic size violation, MoneyMarketRules restriction for mutual fund. We do not allocate to excluded accountsand we cancel the order after other accounts are filled. In case of partial restriction (e.g. account is permitted to close but not to open, or account has enough excess liquidity only for a portion of the desired position).
Footnotes:
Additional Information Regarding the Use of Stop Orders
U.S. equity markets occasionally experience periods of extraordinary volatility and price dislocation. Sometimes these occurrences are prolonged and at other times they are of very short duration. Stop orders may play a role in contributing to downward price pressure and market volatility and may result in executions at prices very far from the trigger price.
U.S. Securities Options Exercise Limits
INTRODUCTION
Option exercise limits, along with position limits (See KB1252), have been in place since the inception of standardized trading of U.S. securities options. Their purpose is to prevent manipulative actions in underlying securities (e.g., corners or squeezes) as well as disruptions in option markets where illiquidity in a given option class exists. These limits serve to prohibit an account, along with its related accounts, from cumulatively exercising within any five consecutive business day period, a number of options contracts in excess of the defined limit for a given equity options class (i.e., option contracts associated with a particular underlying security). This includes both early exercises and expiration exercises.
OVERVIEW
U.S. securities option exercise limits are established by FINRA and the U.S. options exchanges. The exercise limits are generally the same as position limits and they can vary by option class as they take into consideration factors such as the number of shares outstanding and trading volume of the underlying security. Limits are also subject to adjustment and therefore can vary over time. The Options Clearing Corporation (OCC), the central clearinghouse for U.S. exchange traded securities options, publishes a daily file with these limits on its public website. The link is as follows: http://www.optionsclearing.com/webapps/position-limits. FINRA Rule 2360(b)(4) addresses exercise limits and can be found via the following website link: http://finra.complinet.com/en/display/display.html?rbid=2403&record_id=16126&element_id=6306&highlight=2360#r16126).
Note that exercise limits are applied based upon the the side of the market represented by the option position. Accordingly, all exercises of call options over the past five business days are aggregated for purposes of determining the limit for the purposes of purchasing the underlying security. Similarly, a separate computation whereby all put exercises over the past five business days are aggregated is required for purposes of determining sales of the underlying.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
It's important to note that while exercise limits may be set at levels identical to position limits, it is possible for an account holder to reach an exercise limit without violating positions limits for a given option class. This is because exercise limits are cumulative and one could conceivably purchase options up to the position limit, exercise those options and purchase additional options which, if allowed to be exercised within the five business day window, would exceed the limit.
Account holders are responsible for monitoring their cumulative options exercises as well as the exercise limit quantities to ensure compliance. In addition, IB reserves the right to prohibit the exercise of any options, regardless of their intrinsic value or remaining maturity, if the effect of that exercise would be to violate the exercise limit rule.
"EMIR": Reporting to Trade Repository Obligations and Interactive Brokers Delegated Service to help meet your obligations
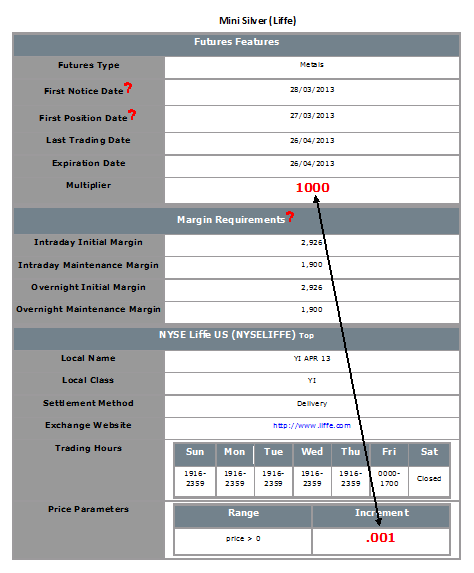
Determining Tick Value
Financial instruments are subject to minimum price changes or increments which are commonly referred to as ticks. Tick values vary by instrument and are determined by the listing exchange. IB provides this information directly from the Contract Search tool on the website or via the Trader Workstation (TWS). To access from TWS, enter a symbol on the quote line, right click and from the drop-down window select the Contract Info and then Details menu options. The contract specifications window for the instrument will then be displayed (Exhibit 1).
To determine the notional value of a tick, multiple the tick increment by the contract trade unit or multiplier. As illustrated in the example below, the LIFFE Mini Silver futures contact has a tick value or minimum increment of .001 which, when multiplied by the contract multiplier of 1,000 ounces, results in a minimum tick value of $1.00 per contract. Accordingly, every tick change up or down results in a profit or loss of $1.00 per LIFFE Mini Silver futures contract.
Exhibit 1
Considerations for Exercising Call Options Prior to Expiration
INTRODUCTION
Exercising an equity call option prior to expiration ordinarily provides no economic benefit as:
- It results in a forfeiture of any remaining option time value;
- Requires a greater commitment of capital for the payment or financing of the stock delivery; and
- May expose the option holder to greater risk of loss on the stock relative to the option premium.
Nonetheless, for account holders who have the capacity to meet an increased capital or borrowing requirement and potentially greater downside market risk, it can be economically beneficial to request early exercise of an American Style call option in order to capture an upcoming dividend.
BACKGROUND
As background, the owner of a call option is not entitled to receive a dividend on the underlying stock as this dividend only accrues to the holders of stock as of its dividend Record Date. All other things being equal, the price of the stock should decline by an amount equal to the dividend on the Ex-Dividend date. While option pricing theory suggests that the call price will reflect the discounted value of expected dividends paid throughout its duration, it may decline as well on the Ex-Dividend date. The conditions which make this scenario most likely and the early exercise decision favorable are as follows:
1. The option is deep-in-the-money and has a delta of 100;
2. The option has little or no time value;
3. The dividend is relatively high and its Ex-Date precedes the option expiration date.
EXAMPLES
To illustrate the impact of these conditions upon the early exercise decision, consider an account maintaining a long cash balance of $9,000 and a long call position in hypothetical stock “ABC” having a strike price of $90.00 and time to expiration of 10 days. ABC, currently trading at $100.00, has declared a dividend of $2.00 per share with tomorrow being the Ex-Dividend date. Also assume that the option price and stock price behave similarly and decline by the dividend amount on the Ex-Date.
Here, we will review the exercise decision with the intent of maintaining the 100 share delta position and maximizing total equity using two option price assumptions, one in which the option is selling at parity and another above parity.
SCENARIO 1: Option Price At Parity - $10.00
In the case of an option trading at parity, early exercise will serve to maintain the position delta and avoid the loss of value in long option when the stock trades ex-dividend, to preserve equity. Here the cash proceeds are applied in their entirety to buy the stock at the strike, the option premium is forfeited and the stock (net of dividend) and dividend receivable are credited to the account. If you aim for the same end result by selling the option prior to the Ex-Dividend date and purchasing the stock, remember to factor in commissions/spreads:
| SCENARIO 1 | ||||
|
Account Components |
Beginning Balance |
Early Exercise |
No Action |
Sell Option & Buy Stock |
| Cash | $9,000 | $0 | $9,000 | $0 |
| Option | $1,000 | $0 | $800 | $0 |
| Stock | $0 | $9,800 | $0 | $9,800 |
| Dividend Receivable | $0 | $200 | $0 | $200 |
| Total Equity | $10,000 | $10,000 | $9,800 | $10,000 less commissions/spreads |
SCENARIO 2: Option Price Above Parity - $11.00
In the case of an option trading above parity, early exercise to capture the dividend may not be economically beneficial. In this scenario, early exercise would result in a loss of $100 in option time value, while selling the option and buying the stock, after commissions, may be less beneficial than taking no action. In this scenario, the preferable action would be No Action.
| SCENARIO 2 | ||||
|
Account Components |
Beginning Balance |
Early Exercise |
No Action |
Sell Option & Buy Stock |
| Cash | $9,000 | $0 | $9,000 | $100 |
| Option | $1,100 | $0 | $1,100 | $0 |
| Stock | $0 | $9,800 | $0 | $9,800 |
| Dividend Receivable | $0 | $200 | $0 | $200 |
| Total Equity | $10,100 | $10,000 | $10,100 | $10,100 less commissions/spreads |
![]() NOTE:
NOTE:
Options have two components that make up their total premium value - intrinsic value and time value. The intrinsic value is the amount by which the option is in-the-money, while the time value represents the possibility that the option could become even more profitable before expiration as the underlying asset price fluctuates while providing protection against adverse moves.
Many options are American-style, which means they can be exercised early, ahead of their expiration date. Early exercise of an option eliminates the remaining time value component from the option's premium, since the option holder loses protection against unfavorable movements in the underlying asset’s price.
This makes early exercise suboptimal in most situations, as the option holder is willingly forfeiting a portion of the option's value.
There are a few specific circumstances where early exercise could make sense, such as:
- For call options on a stock that will pay dividends soon, where the dividend amount exceeds the remaining time value (and only if the exercise will settle on or prior to the record date for the dividend).
- For deep in-the-money options where the time value is negligible compared to the intrinsic value, and the option is expected to drop in value due to interest rate effects (PUTS), or expected stock loan benefits (CALLS).
The first case, exercising an in the money call immediately ahead of a dividend payment, is the most common economically-sensible early exercise. In most cases, it is advisable to hold or sell the option instead of exercising it early, in order to capture the remaining time value. An option should only be exercised early after carefully considering all factors and determining that the benefits of early exercise outweigh the time value being surrendered.
Account holders holding a long call position as part of a spread should pay particular attention to the risks of not exercising the long leg given the likelihood of being assigned on the short leg. Note that the assignment of a short call results in a short stock position and holders of short stock positions as of a dividend Record Date are obligated to pay the dividend to the lender of the shares. In addition, the clearinghouse processing cycle for exercise notices does not accommodate submission of exercise notices in response to assignment.
As example, consider a credit call (bear) spread on the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY) consisting of 100 short contracts in the March '13 $146 strike and 100 long contracts in the March '13 $147 strike. On 3/14/13, with the SPY Trust declared a dividend of $0.69372 per share, payable 4/30/13 to shareholders of record as of 3/19/13. Given the 3 business day settlement time frame for U.S. stocks, one would have had to buy the stock or exercise the call no later than 3/14/13 in order receive the dividend, as the next day the stock began trading Ex-Dividend.
On 3/14/13, with one trading day left prior to expiration, the two option contracts traded at parity, suggesting maximum risk of $100 per contract or $10,000 on the 100 contract position. However, the failure to exercise the long contract in order to capture the dividend and protect against the likely assignment on the short contracts by others seeking the dividend created an additional risk of $67.372 per contract or $6,737.20 on the position representing the dividend obligation were all short calls assigned. As reflected on the table below, had the short option leg not been assigned, the maximum risk when the final contract settlement prices were determined on 3/15/13 would have remained at $100 per contract.
| Date | SPY Close | March '13 $146 Call | March '13 $147 Call |
| March 14, 2013 | $156.73 | $10.73 | $9.83 |
| March 15, 2013 | $155.83 | $9.73 | $8.83 |
Please note that if your account is subject to tax withholding requirements of the US Treasure rule 871(m), it may be beneficial to close a long option position before the ex-dividend date and re-open the position after ex-dividend.
For information regarding how to submit an early exercise notice please click here.
The above article is provided for information purposes only as is not intended as a recommendation, trading advice nor does it constitute a conclusion that early exercise will be successful or appropriate for all customers or trades. Account holders should consult with a tax specialist to determine what, if any, tax consequences may result from early exercise and should pay particular attention to the potential risks of substituting a long option position with a long stock position.
Why Do Commission Charges on U.S. Options Vary?
IBKR's option commission charge consists of two parts:
1. The execution fee which accrues to IBKR. For Smart Routed orders this fee is set at $0.65 per contract, reduced to as low as $0.15 per contract for orders in excess of 100,000 contracts in a given month (see website for costs on Direct Routed orders, reduced rates on low premium options and minimum order charges); and
2. Third party exchange, regulatory and/or transaction fees.
In the case of third party fees, certain U.S. option exchanges maintain a liquidity fee/rebate structure which, when aggregated with the IBKR execution fee and any other regulatory and/or transaction fees, may result in an overall per contract commission charge that varies from one order to another. This is attributable to the exchange portion of the calculation, the result of which may be a payment to the customer rather than a fee, and which depends upon a number of factors outside of IBKR's control including the customer's order attributes and the prevailing bid-ask quotes.
Exchanges which operate under this liquidity fee/rebate model charge a fee for orders which serve to remove liquidity (i.e., marketable orders) and provide a credit for orders which add liquidity (i.e., limit orders which are not marketable). Fees can vary by exchange, customer type (e.g., public, broker-dealer, firm, market maker, professional), and option underlying with public customer rebates (credits) generally ranging from $0.10 - $0.90 and public customer fees from $0.01 - $0.95.
IBKR is obligated to route marketable option orders to the exchange providing the best execution price and the Smart Router takes into consideration liquidity removal fees when determining which exchange to route the order to when the inside market is shared by multiple (i.e., will route the order to the exchange with the lowest or no fee). Accordingly, the Smart Router will only route a market order to an exchange which charges a higher fee if they can better the market by at least $0.01 (which, given the standard option multiplier of 100 would result in price improvement of $1.00 which is greater than the largest liquidity removal fee).
For additional information on the concept of adding/removing liquidity, including examples, please refer to KB201.
