Entity and FATCA Classification for Non-Financial Entities
Introduction
Interactive Brokers (“IB”, “we” or “us”) is required to collect certain documentation from clients (“you”) to comply with U.S. Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (“FATCA”) and other international exchange of information agreements.
This guide contains a series of flowcharts and accompanying notes that summarize IRS rules relating to:
1. The tax classification for purposes of determining which W-8 or W-9 tax form an entity is required to complete; and
2. The FATCA classification required of entities completing the W-8 tax form (Part I, Section 5).
![]() Note: The flowcharts and notes contained herein do not cover every possible scenario and other scenarios not presented here exist and may more closely align with your situation. You should consult a tax professional regarding your particular circumstances if you are still unsure of your U.S. entity and/or FATCA classification after reading this guide.
Note: The flowcharts and notes contained herein do not cover every possible scenario and other scenarios not presented here exist and may more closely align with your situation. You should consult a tax professional regarding your particular circumstances if you are still unsure of your U.S. entity and/or FATCA classification after reading this guide.
What is NOT Covered in this Guide
The guide is directed to non-U.S. entities that (i) are the beneficial owners of the payments made to the account and (ii) are not financial institutions. This guide does not apply to:
• Individuals (use W-9 or W-8BEN)
• U.S. entities (use W-9)
• Entities acting as an intermediary (such as a nominee, broker, custodian, investment advisor) on behalf of another person (use W-8IMY).
• Non-U.S. Tax-Exempt Organizations and Private Foundations
• Financial Institutions
![]() Note: The U.S. entered into bilateral agreements called Intergovernmental Agreements (IGAs) with many countries regarding the implementation of FATCA. In some cases, the provisions of an applicable IGA could modify the results described in this guide. Entities are covered by an IGA should refer to the IGA and/or consult a tax professional for their filing requirements.
Note: The U.S. entered into bilateral agreements called Intergovernmental Agreements (IGAs) with many countries regarding the implementation of FATCA. In some cases, the provisions of an applicable IGA could modify the results described in this guide. Entities are covered by an IGA should refer to the IGA and/or consult a tax professional for their filing requirements.
1. U.S. Tax Classification
Your U.S. income tax classification determines the tax form(s) required to document the account. The flow chart below may help you determine your tax classification and the tax form to be completed.
Important: The U.S. imposes income tax on its residents’ worldwide income. On the other hand, nonresidents are only subject to withholding tax on certain limited types of US source investment income (dividends from U.S. companies, etc.). Completion of a W-8 series tax form certifies you are NOT taxable as a U.S. resident. A W-8 form may also be used to claim a reduced rate of withholding tax under a U.S. income tax treaty.
Flowchart for Determining Tax Classification and Required Tax Form (Non-Trust Entities)
.png)
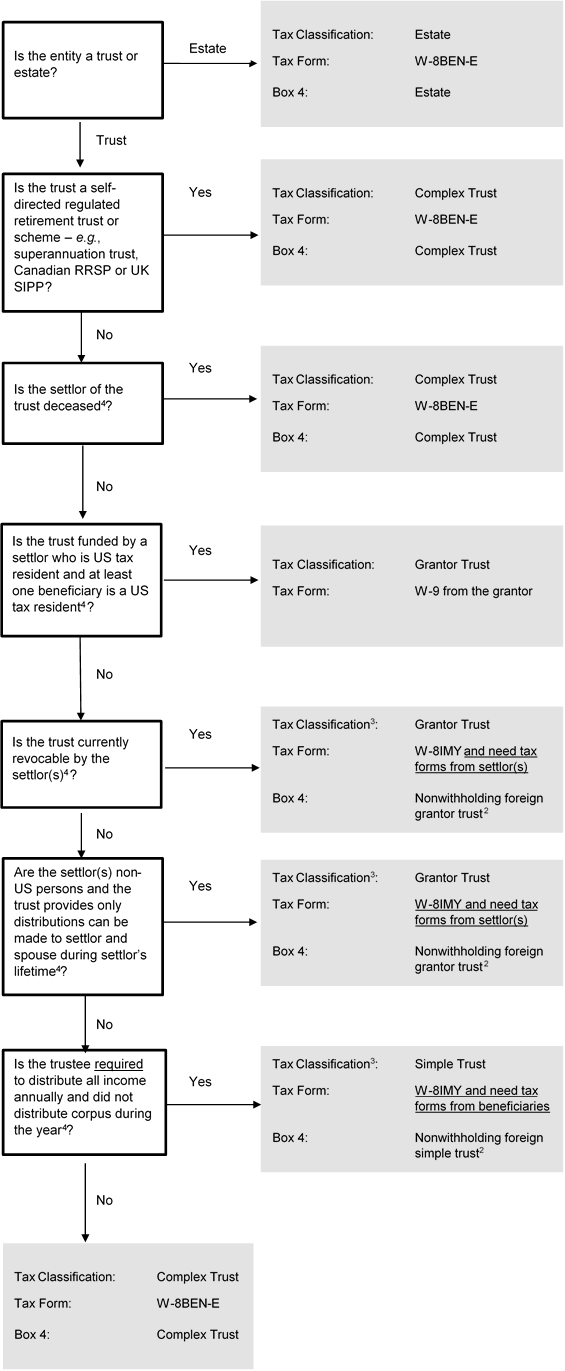
Flowchart for Determining Tax Classification and Required Tax Form (Trusts)
2. FATCA Classification
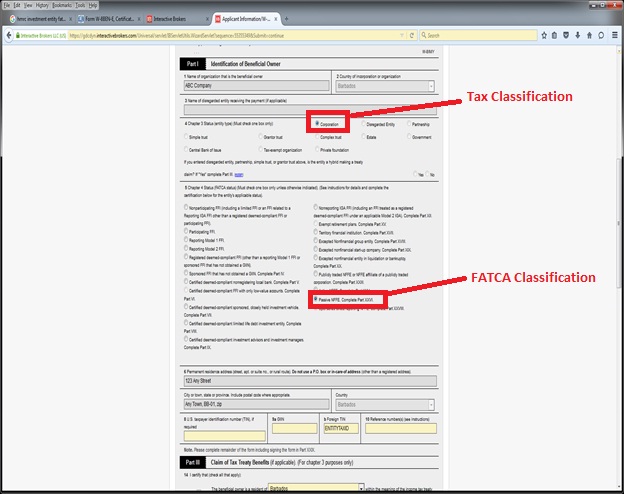
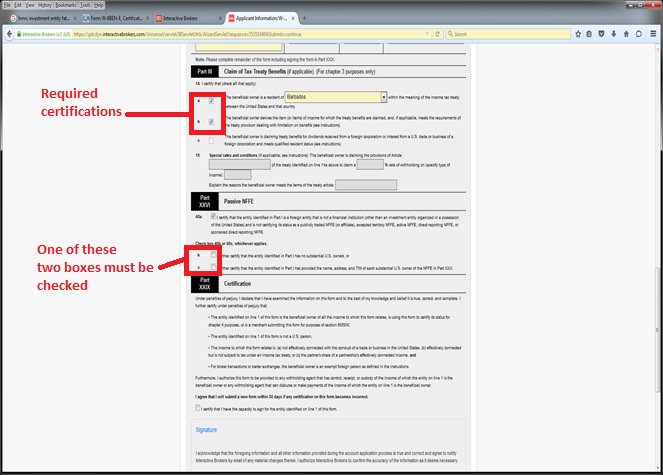
The W8 tax forms are also used to collect FATCA classifications. Many countries have executed “Intergovernmental Agreements (IGA)” with the U.S. requiring its local financial institutions to classify its customers for FATCA purposes. The classification rules under an IGA may not exactly match the classification rules established by the IRS. Other institutions have agreed with the IRS to become FATCA compliant and determine their customers’ FATCA classifications under the IRS rules. We are required to collect this information. The flowchart below applies the IRS default FATCA classification rules and is general in nature. The flowchart is accompanied by sample W-8BEN-E screenshots for a common account structure: a non-U.S. corporation classified for FATCA purposes as a Passive Non-Financial Foreign Entity (NFFE), which qualifies for treaty witholding rates.
![]() Note: It is important to recognize many organizations meet the qualifications for multiple FATCA types and you must select the most appropriate classification. Your specific situation may not fall within the general guidance. We recommend you seek your own independent advice as we are not in a position to make this determination for you and the rules are complex.
Note: It is important to recognize many organizations meet the qualifications for multiple FATCA types and you must select the most appropriate classification. Your specific situation may not fall within the general guidance. We recommend you seek your own independent advice as we are not in a position to make this determination for you and the rules are complex.
Flowchart for Determining FATCA Classification
.png)
Example: A corporation is a common form of entity ownership, involving two or more owners with none having any personal liability for the debts of entity. As outlined in the Tax Classification flowchart above, an entity of this type would be required to complete the W-8BEN-E. Assuming the corporation is not classified as a Foreign Financial Entity (e.g. bank, broker, investment manager, hedge fund, mutual fund, insurance company) as discussed in footnote 5 below, then its FATCA classification would be Passive NFFE. Screenshots of the W-8BEN-E for this sample entity are provided below.
Sample Screenshots - W-8BEN-E (Passive NFFE)
Footnotes
1 The US Internal Revenue Service (IRS) established rules for determining the tax classification of entities formed outside the United States. These rules apply regardless of how the entity is classified in its country of organization or residency.
Generally corporate entities are treated as the beneficial owners of an account and should complete a W-8BEN-E and select “corporation” unless they elect otherwise (discussed below).
IRS regulations assign a default classification to each entity type. This default classification may be overridden by making a filing with the IRS and obtaining an US employer identification number. Certain entities cannot change their classification and are treated as corporations in all events (e.g., Sociedad Anonima, Public Limited Company and Aktiengesellschaft). A complete list may be found at US Treasury Regulation Section 301.7701-2(b)(8).
The IRS default classification usually depends on (i) the number of owners and (ii) whether any owner is personally liable for the debts of the entity based on the organizing statute (i.e., bank guarantees or other contractual agreements by owners are ignored). The following table summarizes the default rules:
|
|
Number of Owners
|
Owners have Limited Liability?
|
|
|||
|
|
Yes?
|
No?
|
|
|||
|
|
1 Owner
|
Corporation
|
Disregarded Entity
|
|
||
|
|
2+ Owners
|
Corporation
|
Partnership
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||||
Note: Since the entity tax classification of a disregarded entity is determined by its owner, a US disregarded entity may find the flowchart helpful if the owner is a non-US entity.
A fiscally transparent entity (such as a partnership, simple trust or grantor trust) using IRS Form W-8IMY must provide IRS tax forms for all of its beneficial owners (partners in a partnership, beneficiaries for a simple trust and settlors for a grantor trust) for the account to be documented for US tax purposes.
Certain unit investment trusts (generally where there is an ability to vary the investments) are not considered trusts for US tax purposes. These investment trusts are treated in the same manner as a traditional business entity under the rules discussed above (i.e., corporation, partnership or disregarded entity).
Finally, a trust (other than a unit investment trust treated as a business entity) is considered a non-US trust for US tax purposes if (1) a court outside the United States is able to exercise primary supervision over the administration of the trust, and (2) any non-US person has the ability to control (or veto) any “substantial decision” of the trust.
The flowchart assumes that the default entity classification rules apply and the entity is not a per se corporation.
2 A partnership or simple or grantor trust may enter into a withholding agreement with the IRS pursuant to which the partnership or simple or grantor trust agrees to withhold US taxes on the account. The flowchart assumes no withholding agreement was executed.
3 In general, US tax treaty benefits are granted to the beneficial owner of the income determined under US tax principles. For fiscally transparent entities (such as partnerships, simple or grantor trusts or disregarded entities), this means the owners of the entity, NOT THE ENTITY ITSELF, claim US tax treaty benefits. These benefits are claimed on the beneficial owners’ W8 tax forms. However in certain limited cases, an entity may be considered fiscally transparent for US tax purposes but not fiscally transparent by the country with which the US has an income tax treaty. This type of an entity is called a “hybrid entity.” In certain cases, a hybrid entity, not the owners, may claim US tax treaty benefits if the hybrid entity meets the so-called qualified resident test under the applicable tax treaty. A qualifying “hybrid entity” claims the benefits of a US tax treaty by providing a Form W-8BEN-E, in addition to the form required by the flowchart. Importantly, electing hybrid status does not eliminate the need to document all beneficial owners. We note it is unusual for a hybrid entity to claim treaty benefits. The more common scenario is the beneficial owners claim treaty benefits on their tax forms.
4 The rules for classifying trusts are difficult and complex. The flowchart applies generalized rules only. There are many nuances to be considered when classifying a trust which are not addressed in the flowchart. For example, simple trusts cannot have charitable beneficiaries.
5 What is a foreign financial institution for FATCA purpose?
The various FATCA classifications can be broken down into two major categories: foreign financial institutions (FFI) and non-financial foreign (NFFE). Very generally, a financial institution is an entity that is a:
• Depository Institution
• Custodial Institution
• Investment Entity
• Insurance Company that issues certain cash value insurance or annuity contracts.
An FFI typically is required to register with the IRS, obtain a Global Intermediary Identification Number and report on its customers / owners to the appropriate tax authorities. If the entity does not meet the definition of a Financial Institution, it is considered an NFFE and covered by this guide book.
Subject to variations under IRS regulations and intergovernmental agreements:
• a Depository Institution is an institution that accepts deposits in the ordinary course of a banking or similar business. This includes banks and credit unions.
• a Custodial Institution is an institution which holds financial assets for the account of others as a substantial portion of its business. This includes brokers, custodial banks, trust companies, clearing organizations, etc.
• an Investment Entity is any entity if either
(i) the entity generates 50%+ of its gross income from (i) trading in money market instruments, foreign currency, transferrable securities, interest rates, futures, etc.; (ii) portfolio management or (iii) otherwise investing, administering or managing funds or financial assets on behalf of other persons (generally, broker-dealers and investment managers);
or
(ii) 50%+ of the entity gross income is attributable to investing, reinvesting, or trading in financial assets AND it is managed by a Financial Institution (mutual funds, hedge funds, and collective investment vehicles are examples);
or
(iii) the entity holds itself out as an entity created to invest, reinvest, or trade invest in financial assets (mutual funds, hedge funds, and collective investment vehicles are examples).
An individual cannot be an FFI. Thus, an organization managed by a professional individual investment advisor (as opposed to an employee of an organization) would not be considered an Investment Entity under (ii) above because it is not managed by a financial institution.
Trusts, family investment companies and funds may fall within the definition of an Investment Entity when they are professionally managed by a financial institution – i.e. where a financial institution handles the day-to-day functions of the entity or has discretionary authority over the fund.
Example: Individual created a non-US Trust A and appoints X, a non-US bank or other financial institution, as the trustee. X, as trustee, is responsible for the management and administration of Trust A. Trust A is an Investment Entity and a Foreign Financial Institution because it is managed by a Foreign Financial Institution.
Example: Individual created a non-US Trust A and appoints Y, an individual professional manager, as the trustee. Y, as trustee, is responsible for the management and administration of Trust A. Trust A is not an Investment Entity or a Foreign Financial Institution because it is not managed by a Foreign Financial Institution. Individuals cannot be financial institutions.
6 The IRS has a list of countries with which it has executed intergovernmental agreements (IGAs) to authorize the implementation of FATCA in that jurisdiction. The list of IGAs can be found at https://www.treasury.gov/resource-center/tax-policy/treaties/Pages/FATCA....
7 See #4 for the definition of Financial Institution. An organization that is not considered a financial institution is considered a non-financial foreign entity (NFFE). There are 3 types of NFFEs; Excepted, Active and Passive. An Active NFFE is an operating business where less than 50% of (i) its gross income is considered passive income and (ii) its average assets are held for the production of passive income. Any NFFE that is not Excepted or Active is a Passive NFFE and must provide us with a certification of its substantial US owners (if any) – generally 10%+ direct or indirect ownership. Some IGAs modify the means of substantial US owners and refer to them as Controlling Persons.
8 Other possible choices include nonfinancial group entity, excepted nonfinancial start-up company, excepted non-financial entity in liquidation or bankruptcy, publicly traded NFFE or sponsored NFFE. See the instructions to the W-8 for further information.
Disclaimer
This guide does not constitute tax or legal advice and Interactive Brokers cannot advise you on how to complete IRS Forms W-8. Examples included in this guide are for illustration only and do not address all possible scenarios. Please consult your tax professional if you are unsure how to complete IRS Forms W-8.
