How do I know if I am eligible to contribute to an IRA?
You are eligible to contribute to a Traditional IRA if you received taxable compensation during the year and you are under the age of 70½ by the end of the year. Traditional IRA contributions are not subject to income limits. You can contribute to a Roth IRA after age 70½ as long as you have taxable compensation. Roth IRA contributions are subject to income limits. If you are not employed but have a spouse who is, your spouse may be able to make a contribution on your behalf. You can open an IRA account even if you are covered by another retirement plan.
IRS Circular 230 Notice: The information contained in this FAQ is provided for information purposes only, is not intended to constitute tax advice which may be relied upon to avoid penalties under any federal, state, local or other tax statutes or regulations and does not resolve any tax issues in your favor. Refer to IRS Publication 590, Individual Retirement Accounts for additional information on IRAs in general and consult your tax advisor about your individual tax situation.
Tax: What is an excess contribution?
An excess contribution is a contribution to a Traditional or Roth IRA that is not permitted or that is larger than is permitted. For example, if the total amount of your contributions to one or more Roth and Traditional IRAs exceeds the annual limitation, if your total annual contributions exceed your taxable compensation income for the year or if your permitted Roth contribution was reduced or eliminated because of the size of your modified adjusted gross income. Other factors may also result in an excess contribution. Refer to IRS Publication 590 and consult your tax advisor.
IRS Circular 230 Notice: The information contained in this FAQ is provided for information purposes only, is not intended to constitute tax advice which may be relied upon to avoid penalties under any federal, state, local or other tax statutes or regulations and does not resolve any tax issues in your favor. Refer to IRS Publication 590, Individual Retirement Accounts for additional information on IRAs in general and consult your tax advisor about your individual tax situation.
Are annual contributions to my IRA required and is there a minimum contribution amount?
No, you are not required to contribute to your IRA every tax year and there is no minimum contribution amount.
IRS Circular 230 Notice: The information contained in this FAQ is provided for information purposes only, is not intended to constitute tax advice which may be relied upon to avoid penalties under any federal, state, local or other tax statutes or regulations and does not resolve any tax issues in your favor. Refer to IRS Publication 590, Individual Retirement Accounts for additional information on IRAs in general and consult your tax advisor about your individual tax situation.
Can I make a contribution for the prior tax year?
Yes, a contribution made between January 1 and April 15 may apply to the prior tax year. After your tax filing due date however, you can only make a current-year contribution.
IRS Circular 230 Notice: The information contained in this FAQ is provided for information purposes only, is not intended to constitute tax advice which may be relied upon to avoid penalties under any federal, state, local or other tax statutes or regulations and does not resolve any tax issues in your favor. Refer to IRS Publication 590, Individual Retirement Accounts for additional information on IRAs in general and consult your tax advisor about your individual tax situation.
Are there limits on IRA contributions?
Yes, there are annual limits on the amount of your IRA contribution each year and income limits based on your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI), which may reduce or even phase-out the allowable amount of your contribution. Traditional IRAs are not subject to income limits; however Roth IRA contributions are subject to limits based on income. Refer to IRS Publication 590 and consult your tax advisor about your individual tax situation.
IRS Circular 230 Notice: The information contained in this FAQ is provided for information purposes only, is not intended to constitute tax advice which may be relied upon to avoid penalties under any federal, state, local or other tax statutes or regulations and does not resolve any tax issues in your favor. Refer to IRS Publication 590, Individual Retirement Accounts for additional information on IRAs in general and consult your tax advisor about your individual tax situation.
An Introduction to Forex (FX)
IB offers market venues and trading platforms which are directed towards both forex-centric traders as well as traders whose occasional forex activity originates from multi-currency stock and/or derivative transactions. The following article outlines the basics of forex order entry on the TWS platform and considerations relating to quoting conventions and position (post-trade) reporting.
A forex (FX) trade involves a simultaneous purchase of one currency and the sale of another, the combination of which is commonly referred to as a cross pair. In the examples below the EUR.USD cross pair will be considered whereby the the first currency in the pair (EUR) is known as the transaction currency that one wishes to buy or sell and the second currency (USD) the settlement currency.
Jump to a specific topic in this article;
- Forex Price Quotes
- Creating a quote line
- Creating an order
- Pip Value
- Position (Post-Trade) Reporting
Forex Price Quotes
A currency pair is the quotation of the relative value of a currency unit against the unit of another currency in the foreign exchange market. The currency that is used as reference is called quote currency, while the currency that is quoted in relation is called base currency. In TWS we offer one ticker symbol per each currency pair. You could use FXTrader to reverse the quoting. Traders buy or sell the base currency and sell or buy the quote currency. For ex. the EUR/USD currency pair’s ticker symbol is:
EUR.USD
where:
- EUR is the base currency
- USD is the quote currency
The price of the currency pair above represents how many units of USD (quote currency) are required to trade one unit of EUR (base currency). Said in other words, the price of 1 EUR quoted in USD.
A buy order on EUR.USD will buy EUR and sell an equivalent amount of USD, based on the trade price.
Creating a quote line
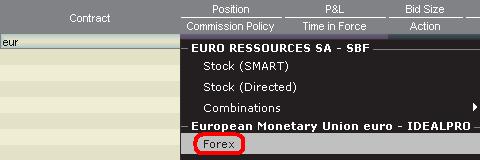
The steps for adding a currency quote line on the TWS are as follows:
1. Enter the transaction currency (example: EUR) and press enter.
2. Choose the product type forex
3. Select the settlement currency (example: USD) and choose the forex trading venue.
.jpg)
Notes:
The IDEALFX venue provides direct access to interbank forex quotes for orders that exceed the IDEALFX minimum quantity requirement (generally 25,000 USD). Orders directed to IDEALFX that do not meet the minimum size requirement will be automatically rerouted to a small order venue principally for forex conversions. Click HERE for information regarding IDEALFX minimum and maximum quantities.
Currency dealers quote the FX pairs in a specific direction. As a result, traders may have to adjust the currency symbol being entered in order to find the desired currency pair. For example, if the currency symbol CAD is used, traders will see that the settlement currency USD cannot be found in the contract selection window. This is because this pair is quoted as USD.CAD and can only be accessed by entering the underlying symbol as USD and then choosing Forex.
Creating an order
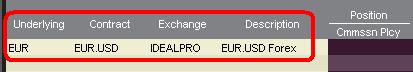
Depending on the headers that are shown, the currency pair will be displayed as follows;
The Contract and Description columns will display the pair in the format Transaction Currency.Settlement Currency (example: EUR.USD). The Underlying column will display only the Transaction Currency.
Click HERE for information regarding how to change the shown column headers.
1. To enter an order, left click on the bid (to sell) or the ask (to buy).
2. Specify the quantity of the trading currency you wish to buy or sell. The quantity of the order is expressed in base currency, that is the first currency of the pair in TWS.
Interactive Brokers does not know the concept of contracts that represent a fixed amount of base currency in Foreign exchange, rather your trade size is the required amount in base currency.
For example, an order to buy 100,000 EUR.USD will serve to buy 100,000 EUR and sell the equivalent number of USD based on the displayed exchange rate.
3. Specify the desired order type, exchange rate (price) and transmit the order.
Note: Orders may be placed in terms of any whole currency unit and there are no minimum contract or lot sizes to consider aside from the market venue minimums as specified above.
Common Question: How is an order entered using the FX Trader?
Pip Value
A pip is measure of change in a currency pair, which for most pairs represents the smallest change, although for others changes in fractional pips are allowed.
For ex. in EUR.USD 1 pip is 0.0001, while in USD.JPY 1 pip is 0.01.
To calculate 1 pip value in units of quote currency the following formula can be applied:
(notional amount) x (1 pip)
Examples:
- Ticker symbol = EUR.USD
- Amount = 100,000 EUR
- 1 pip = 0.0001
1 pip value = 100’000 x 0.0001= 10 USD
- Ticker symbol = USD.JPY
- Amount = 100’000 USD
- 1 pip = 0.01
1 pip value = 100’000 x (0.01)= JPY 1000
To calculate 1 pip value in units of base currency the following formula can be applied:
(notional amount) x (1 pip/exchange rate)
Examples:
- Ticker symbol = EUR.USD
- Amount = 100’000 EUR
- 1 pip = 0.0001
- Exchange rate = 1.3884
1 pip value = 100’000 x (0.0001/1.3884)= 7.20 EUR
- Ticker symbol = USD.JPY
- Amount = 100’000 USD
- 1 pip = 0.01
- Exchange rate = 101.63
1 pip value = 100’000 x (0.01/101.63)= 9.84 USD
Position (Post-Trade) Reporting
FX position information is an important aspect of trading with IB that should be understood prior to executing transactions in a live account. IB's trading software reflects FX positions in two different places both of which can be seen in the account window.
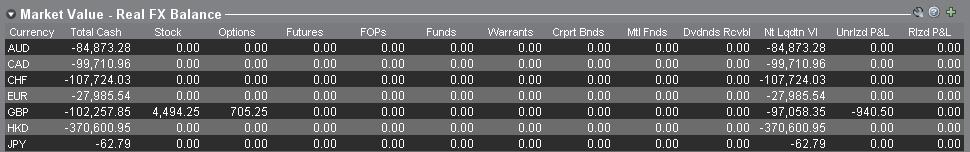
1. Market Value
The Market Value section of the Account Window reflects currency positions in real time stated in terms of each individual currency (not as a currency pair).
The Market Value section of the Account view is the only place that traders can see FX position information reflected in real time. Traders holding multiple currency positions are not required to close them using the same pair used to open the position. For example, a trader that bought EUR.USD (buying EUR and selling USD) and also bought USD.JPY (buying USD and selling JPY) may close the resulting position by trading EUR.JPY (selling EUR and buying JPY).
Notes:
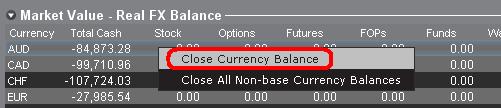
The Market Value section is expandable/collapsible. Traders should check the symbol that appears just above the Net Liquidation Value Column to ensure that a green minus sign is shown. If there is a green plus symbol, some active positions may be concealed.
Traders can initiate closing transactions from the Market Value section by right clicking on the currency that they wish to close and choosing "close currency balance" or "close all non-base currency balances".
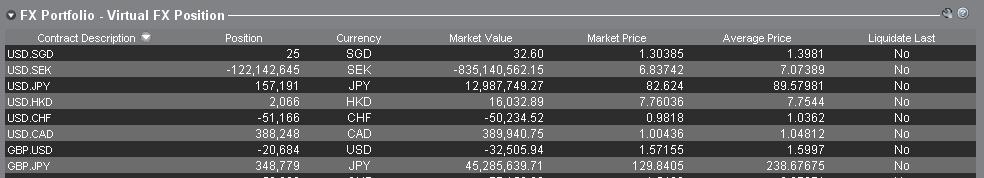
2. FX Portfolio
The FX Portfolio section of the account window provides an indication of Virtual Positions and displays position information in terms of currency pairs instead of individual currencies as the Market Value section does. This particular display format is intended to accommodate a convention which is common to institutional forex traders and can generally be disregarded by the retail or occasional forex trader. FX Portfolio position quantities do not reflect all FX activity, however, traders have the ability to modify the position quantities and average costs that appear in this section. The ability to manipulate position and average cost information without executing a transaction may be useful for traders involved in currency trading in addition to trading non-base currency products. This will allow traders to manually segregate automated conversions (which occur automatically when trading non base currency products) from outright FX trading activity.
The FX portfolio section drives the FX position & profit and loss information displayed on all other trading windows. This has a tendency to cause some confusion with respect to determining actual, real time position information. In order to reduce or eliminate this confusion, traders may do one of the following;
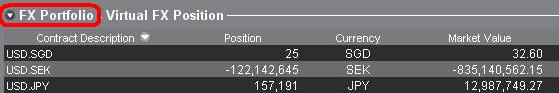
a. Collapse the FX Portfolio section
By clicking the arrow to the left of the word FX Portfolio, traders can collapse the FX Portfolio section. Collapsing this section will eliminate the Virtual Position information from being displayed on all of the trading pages. (Note: this will not cause the Market Value information to be displayed it will only prevent FX Portfolio information from being shown.)
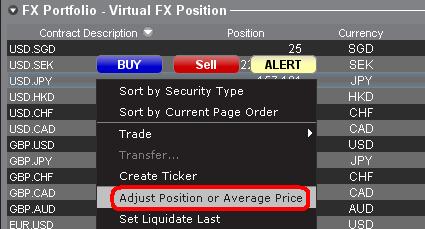
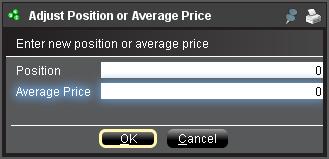
b. Adjust Position or Average Price
By right clicking in the FX portfolio section of the account window, traders have the option to Adjust Position or Average Price. Once traders have closed all non base currency positions and confirmed that the market value section reflects all non base currency positions as closed, traders can reset the Position and Average Price fields to 0. This will reset the position quantity reflected in the FX portfolio section and should allow traders to see a more accurate position and profit and loss information on the trading screens. (Note: this is a manual process and would have to be done each time currency positions are closed out. Traders should always confirm position information in the Market Value section to ensure that transmitted orders are achieving the desired result of opening or closing a position.
We encourage traders to become familiar with FX trading in a paper trade or DEMO account prior to executing transactions in their live account. Please feel free to Contact IB for additional clarification on the above information.
Other common questions:
Tax Reporting: When does IB send the 1099-R information to the IRS?
The information will be provided to the IRS by March 31 of the year following the year in which the IRA distribution takes place.
Tax Treaty Benefits
Income payments (dividends and payment in lieu) from U.S. sources into your IB account may have U.S. tax withheld. Generally, a 30% rate is applied to non-U.S. accounts. Exemption from the withholding or a lower rate may apply if your home country has a tax treaty with the U.S. Complete the applicable Form W-8 to find out your status.
Tax Treaties*
U.S. tax treaties with some countries have different benefits. Legal tax residents of the following countries may be eligible for the treaty benefits. Below is a list of the tax treaty countries. Benefits vary by country.
| Australia | Czech Republic | India | Lithuania | Sweden |
| Austria | Denmark | Indonesia | Poland | Switzerland |
| Bangladesh | Egypt | Ireland | Portugal | Thailand |
| Barbados | Estonia | Israel | Romania | Trinidad & Tobago |
| Belgium | Finland | Italy | Russia | Tunisia |
| Bulgaria | France | Jamaica | Slovak Republic | Turkey |
| Canada | Germany | Japan | Slovenia | Ukraine |
| China, People's Rep. Of | Greece | Kazakhstan | South Africa | United Kingdom |
| Commonwealth of Ind. States | Hungary | Korea, Rep. of | Spain | Venezuela |
| Cyprus | Iceland | Latvia | Sri Lanka |
*Country list as of April 2009
Refer to IRS Publication 901 for details on withholding rates for your tax residence country and your eligible benefits.
How and When to Use a Direct Rollover
This information is for general educational purposes only. Individuals should consult with their financial adviser or legal counsel to determine how rollover regulations affect their unique situations.
Generally, an investor changing jobs or leaving the workforce may utilize either a Direct Rollover election to continue their retirement savings outside of their employer-sponsored retirement plan. Assets distributed directly to your IRA from the retirement plan may qualify as a Direct Rollover.
What is a Direct Rollover?
The Direct Rollover is a tax-free distribution to you of cash or other assets from one retirement plan that you contribute to another retirement plan, including an IRA. The contribution to the IRA is called a rollover contribution. The Direct Rollover method transfers the assets directly from the retirement plan (and not to the IRA owner) into the investor's IRA, avoiding the 20% mandatory IRS withholding. This option to transfer retirement assets has no age limitations.
Eligible retirement plans include:
- Employer's qualified pension, profit -sharing, or stock bonus plan
- Annuity plan
- Tax sheltered annuity plan (section 403(b) plan)
- Governmental deferred compensation plan (section 457 plan)
Who do you contact first?
Contact your retirement plan administrator or the human resources office for eligibility and requirements. The plan administrator is required to provide a reasonable direct method of asset transfer. Completion of an IRA Rollover Form provided by the administrator may be required, in some cases. In other cases, the plan accepts an IRA Rollover Form supplied by your IRA's broker. Therefore, it is important to check with the plan administrator.
Initiating your Direct Rollover through IB
For those transfers that require a broker-supplied IRA Rollover Form, Interactive Brokers provides a convenient IRA Rollover Form. Interactive Brokers will forward the request to the plan administrator or broker for processing. Funds may be transferred by either wire transfer or check directly to Interactive Brokers.
Before accepting an IRA rollover transaction into an IRA, we require that you review your eligibility for the rollover and certify your understanding of the rollover rules and conditions. The IRA Rollover Form includes the Rollover Form and an IRA Rollover Certification Form.
The Fund Transfers page within the Account Management lets you notify IB of an IRA Rollover deposit of funds into your account. Select the Funding tab in the header link and choose Deposit Funds in the Transaction list. In the Method list, select Direct Rollover. Complete, sign, and return both forms to the Interactive Brokers address on the form.
Contact Customer Service with any additional questions.
In compliance with Treasury Department Circular 230, unless stated to the contrary, any information contained in this article was not intended or written to be used and cannot be used for the purpose of avoiding tax penalties that may be imposed on any taxpayer.
IRA: Roth Conversions
Traditional and SEP IRA owners may process a full conversion of cash or securities into a Roth IRA that has identical trading capabilities at Interactive Brokers.
An IRA Roth Conversion is a transfer of Traditional, SEP, or SIMPLE IRA assets into a Roth IRA as a rollover or conversion.
While Interactive Brokers is unable to re-designate a Traditional or SEP IRA as a Roth IRA (e.g. change the same Traditional IRA into a Roth IRA), you may still complete a Roth conversion without sending funds to another brokerage firm. See below for methods to convert your IRA funds into a Roth IRA.
Internal Full Conversion Between IB Accounts
Conversion By Rollover Deposit
Click Conversions and Recharacterizations for additional information.
Converting Your Funds
The IRS permits eligible IRA owners to contribute funds to a Roth IRA from a Traditional or SEP IRA. Regardless of the conversion method used, the entire transaction is treated as a conversion. There are three (3) conversion methods available for converting into an IB Roth IRA account:
(1) Internal Full Conversion (Cash & Securities)
(2) Rollover Deposit (Cash only)
(3) Trustee-to-Trustee Transfer (Cash only)
- Internal Full Conversion: You may open a Roth IRA at IB and then request a Full (all assets) conversion of a Traditional or SEP IRA through Account Management. All assets will be internally transferred into the Roth IRA. Internally processed Roth conversions submitted by 8:00 PM EST are processed the next business day.
[In Funds Management of the Traditional or SEP IRA, choose: IRA Conversion to Roth Account. Or, click Position Transfers, then select IRA Conversion - Transfer Assets to Roth Account.]
Note: Select the funding option IRA Conversion or Re-characterization in the Funding section of the account application to perform a full conversion. For step-by-step instructions, click here. See Partial IRA Conversions to perform a partial conversion.
- Rollover Deposit: You can receive a distribution from an IRA (Traditional, SEP, or SIMPLE) or qualified plan held outside of Interactive Brokers and roll the funds over (contribute it) to a Roth IRA within 60 days after the distribution.
[In Funds Management of the Roth IRA, choose the following deposit method: Cash Transfers. In the Transaction List, select Deposit Cash. In the Method List, select Check, Wire, Automated Clearing House (A.C.H.), or Direct Rollover. Choose Rollover as the IRA Deposit Type.]
Note: Selecting Rollover designates the deposit as a "conversion contribution," provided funds originate from an IRA or qualified plan. Select Cash Deposit instructions for step-by-step deposit instructions.
- Trustee-to-Trustee Transfer: You can direct the trustee of an IRA (Traditional, SEP, or SIMPLE) or qualified plan held outside of Interactive Brokers to transfer a cash amount into the Roth IRA account at IB. Use the IRA Transfer-In Authorization form to initiate your request.
[In Funds Management of the Roth IRA, choose the following deposit method: Cash Transfers. In the Transaction List, select Deposit Cash. In the Method List, select Trustee-to-Trustee.]
Important Note: IB is not responsible for the tax reporting of any funds distributed from the Traditional or SEP IRA held at another firm. Customers should speak with a tax advisor before requesting an IRA distribution as withholding tax may apply. Customers must contact the other firm to ensure that the IRA distribution is appropriately designated.
IRS Tax Reporting
The deposit of funds into the Roth IRA is treated by the IRS as a rollover contribution, regardless of the conversion method, and reported to the IRS on Form 5498. Form 5498 is available by May 31 for the prior year's contributions.
The disbursement of funds from the Traditional or SEP IRA is treated by the IRS as a distribution and reported by IB on the Form 1099-R (report of the distribution). This tax form is available by January 31 for the prior year's distributions.
For additional information on Forms 5498 and 1099-R, see US Year End Tax Forms.
Click here to return to the Retirement Account Resource page.
Disclaimer: IB does not provide tax advice. These statements are provided for information purposes only, are not intended to constitute tax advice which may be relied upon to avoid penalties under any international, federal, state, local or other tax statutes or regulations, and do not resolve any tax issues in your favor. We recommend that you consult a qualified tax adviser.