Eine Einleitung zu Forex-Geschäften (FX)
IB bietet Marktplätze und Handelsplattformen an, die sich sowohl an Devisen-orientierte Trader als auch solche richtet, deren Devisenaktivitäten aus Aktien- und oder Derivat-Transaktionen aus mehreren Währungen entstanden sind. Im folgenden Artikel werden grundsätzliche Aspekte zu Devisen vorgestellt und wie Sie solche Orders in der TWS-Plattform eingehen können. Darüber hinaus werden Kursnotierungskonventionen sowie Positionsberichte (nach Ausführungen) erläutert.
Bei einer Devisentransaktion (FX) wird eine Währung gekauft und gleichzeitig eine andere Verkauft. Diese Kombination wird im Allgemeinen als "Cross Pair" bezeichnet. In den nachstehenden Beispielen wird anhand eines EUR.USD-Cross-Pairs gezeigt, dass es sich bei der ersten Währung (EUR) um die Transaktionswährung, die man entweder kaufen oder verkaufen möchte und die zweite Währung (USD) wird Abwicklungswährung genannt.
Zu einem spezifischen Abschnitt springen:
- Devisenkursnotierungen
- Erstellung einer Kurszeile
- Erstellung einer Order
- Pip-Wert
- Meldung von Positionen (nach Ausführung)
Devisenkursnotierungen
Bei einem Währungspaar handelt es sich um die Kursnotierung des relativen Werts einer Währungseinheit gegenüber der Einheit einer anderen Währung am Devisenmarkt. Die Währung, die als Referenz verwendet wird, wird Kursnotierungswährung genannt, während die Währung, die im Vergleich dazu notiert wird, Basiswährung genannt wird. In der TWS bieten wir ein Tickersymbol pro Währungspaar an. Mit dem FXTrader können Sie die Kursnotierung umkehren. Trader kaufen oder verkaufen die Basiswährung und kaufen oder verkaufen die Kursnotierungswährung. Beispiel: Bei dem Währungspaar EUR/USD lautet das Tickersymbol:
EUR.USD
wobei:
- EUR die Basiswährung ist
- USD die Kursnotierung ist
Der Preis des vorstehenden Währungspaares stellt dar, wie viele Einheiten von USD (Kursnotierungswährung) erforderlich sind, um eine Einheit von EUR (Basiswährung) handeln zu können. In anderen Worten: Der Preis von 1 EUR notiert in USD.
Bei einer Kauforder von EUR.USD wird EUR gekauft und ein äquivalenter Betrag in USD, basierend auf dem Handelskurs, verkauft.
Erstellung einer Kurszeile
Nachstehend erhalten Sie Anweisungen, wie Sie eine Kursnotierungszeile in der TWS hinzufügen können:
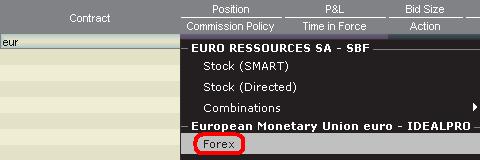
1. Geben Sie die Transaktionswährung (Beispiel: EUR) ein und drücken Sie auf die Enter-Taste.
2. Wählen Sie den Produkttypen aus: Forex
3. Wählen Sie die Abwicklungswährung (Beispiel: USD) aus und wählen Sie den Forex-Handelsplatz aus.
.jpg)
Hinweise:
IDEALFX bietet direkten Zugang zu Interbank-Devisenkursen für Orders, die die Mindestmengenanforderungen von IDEALFX überschreiten (im Allgemeinen 25,000 USD). An IDEALFX weitergeleitete Orders, die nicht die Mindestmengenanforderungen erfüllen, werden automatisch an einen kleineren Orderplatz für Devisen-Umwandlungen weitergeleitet. Klicken Sie HIER für Informationen zu Mindest- und Höchstmengen bei IDEALFX.
Währungsdealer notieren FX-Paare in eine bestimmte Richtung. Dadurch ist es möglich, dass Trader das Währungssymbol, das eingegeben wird, anpassen müssen, um das gewünschte Währungspaar zu finden. Beispiel: Wenn das Währungssymbol CAD verwendet wird, werden Trader sehen, dass die Abwicklungswährung USD nicht im Kontraktauswahlfenster gefunden werden kann. Der Grund hierfür ist, dass das Paar als USD.CAD notiert ist und Sie nur dann darauf zugreifen können, indem Sie das zugrunde liegende Symbol als USD eingeben und danach Forex auswählen.
Erstellung einer Order
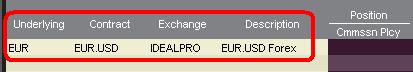
In Abhängigkeit davon, wie die Titel angezeigt werden, werden die Währungspaare folgendermaßen angezeigt:
Die Kontrakt- und Beschreibungsspalten zeigen das Paar im Format "Transaktionswährung.Abwicklungswährung" an (Beispiel: EUR.USD). Die Basiswertspalte zeigt ausschließlich die Transaktionswährung an.
Klicken Sie HIER für Informationen darüber, wie Sie die angezeigten Spaltenüberschriften ändern können.
1. Klicken Sie entweder auf den Geld- oder Briefkurs, um eine Order einzugehen.
2. Geben Sie Handelswährungsmenge ein, die Sie kaufen bzw. verkaufen möchten. Die Menge der Order wird in der Basiswährung angegeben. Dies ist die erste Währung des Paares in der TWS.
Interactive Brokers bietet kein Kontraktkonzept an, bei dem ein festgelegter Betrag einer Basiswährung am Devisenmarkt reflektiert wird. Stattdessen spiegelt Ihre Handelsgröße den erforderlichen Betrag in der Basiswährung dar.
Beispiel: Bei einer Kauforder von 100,000 EUR.USD werden 100,000 EUR gekauft und die äquivalente Anzahl an USD wird basierend auf dem angezeigten Wechselkurs verkauft.
3. Geben Sie den gewünschten Ordertypen sowie Wechselkurs (Preis) an und übermitteln Sie die Order.
Hinweis: Orders können in ganzen Währungseinheiten platziert werden. Es gibt keine Mindestkontrakt- bzw. Lotgrößen, die berücksichtigt werden müssen, mit Ausnahme von Marktplatz-Mindestanforderungen (wie oben beschrieben).
Allgemeine Frage: Wie platziert man eine Order mit dem FX Trader?
Pip-Wert
Bei einem Pip handelt es sich um die gemessene Veränderung in einem Währungspaar, das bei den meisten Paaren für die kleinste Veränderung steht, obwohl für andere Änderungen in Pip-Bruchteilen auch erlaubt sind.
Beispiel: Bei EUR.USD beträgt 1 Pip 0.0001, während bei USD.JPY 1 Pip 0.01 beträgt.
Mit der folgenden Formel kann 1 Pip-Wert in Kurswährungseinheiten berechnet werden:
(Nennbetrag) x (1 Pip)
Beispiele:
- Tickersymbol = EUR.USD
- Betrag = 100,000 EUR
- 1 Pip = 0.0001
1 Pipwert = 100’000 x 0.0001 = 10 USD
- Tickersymbol = USD.JPY
- Betrag = 100’000 USD
- 1 Pip = 0.01
1 Pipwert = 100’000 x (0.01) = 1000 JPY
Mit der folgenden Formal kann 1 Pip-Wert in Basiswährungseinheiten berechnet werden:
(Nennbetrag) x (1 Pip/Wechselkurs)
Beispiele:
- Tickersymbol = EUR.USD
- Betrag = 100’000 EUR
- 1 Pip = 0.0001
- Wechselkurs = 1.3884
1 Pipwert = 100’000 x (0.0001/1.3884) = 7.20 EUR
- Tickersymbol = USD.JPY
- Betrag = 100’000 USD
- 1 Pip = 0.01
- Wechselkurs = 101.63
1 Pipwert = 100’000 x (0.01/101.63) = 9.84 USD
Meldung von Positionen (nach Ausführung)
Informationen zu FX-Positionen sind ein wichtiger Aspekt im Zuge von Transaktionen bei IB, die Sie verstehen sollten, bevor Sie Handelsgeschäfte in einem Live-Konto durchführen. Die Handelssoftware von IB gibt FX-Positionen an zwei verschiedenen Orten an, die jeweils im Kontofenster angezeigt werden.
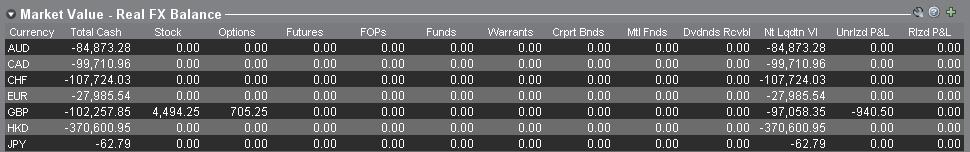
1. Marktwert
Der Abschnitt zum Marktwert innerhalb des Kontofensters zeigt Währungspositionen in Echtzeit und für jede einzelne Währung an (nicht als Währungspaar).
Der Marktwert-Abschnitt im Kontofenster ist der einzige Ort, an dem Trader Informationen zu FX-Positionen in Echtzeit sehen können. Trader, die mehrere Währungspositionen halten, sind nicht verpflichtet, diese mit demselben Paar zu schließen, mit dem sie sie die eröffnet haben. Beispiel: Ein Trader, der EUR.USD kaufte (Kauf von EUR und Verkauf von USD) und zudem USD.JPY kaufte (Kauf von USD und Verkauf von JPY), kann die sich daraus ergebende Position schließen, indem er EUR.JPY handelt (Verkauf von EUR und Kauf von JPY).
Hinweise:
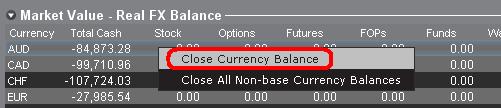
Der Abschnitt mit dem Marktwert kann beliebig aus- und eingeklappt werden. Trader sollten das Symbol überprüfen, das oberhalb der Spalte mit dem Nettoliquidierungswert angezeigt wird, um sicherzustellen, dass ein grünes Minus angezeigt wird. Wenn Sie ein grünes Plus sehen, ist es möglich, dass einige aktive Positionen verborgen sind.
Trader können im Marktwert-Abschnitt Schließtransaktionen veranlassen, indem sie auf die Währung klicken, die sie schließen möchten und "Devisenposition schließen" oder "Alle Salden in anderen Währungen als der Basiswährung auflösen" auswählen.
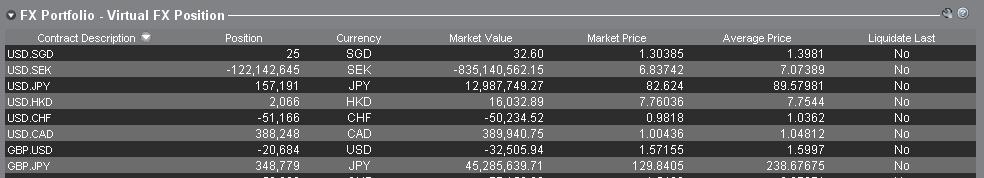
2. FX Portfolio
Der FX-Portfolio-Abschnitt im Kontofenster bietet Informationen zu Ihren virtuellen Positionen und zeigt Positionsinformationen in Bezug auf Währungspaare anstelle von einzelnen Währungen wie im Marktwert-Abschnitt an. Dieses besondere Anzeigeformat dient zur Anwendung einer für institutionelle Devisen-Trader gebräuchlichen Konvention und kann grundsätzlich von Retail- oder gelegentlichen Devisen-Tradern außer Acht gelassen werden. Die im FX-Portfolio angezeigten Positionsmengen reflektieren nicht alle FX-Aktivitäten, jedoch haben Trader die Möglichkeit, Positionsmengen und Durchschnittskosten, die in diesem Abschnitt angezeigt werden, zu ändern. Die Möglichkeit, Informationen zu Positionen und Durchschnittskosten zu ändern, ohne eine Transaktion durchzuführen, kann für Trader nützlich sein, die Währungstransaktionen häufig durchführen und darüber hinaus Währungsprodukte nicht in der eigenen Basiswährung handeln. Auf diese Weise können Trader automatische Umwandlungen (die automatisch passieren, wenn man Währungsprodukte nicht in der eigenen Basiswährung handelt) von direkten FX-Trading-Aktivitäten trennen.
Im FX-Portfolio-Abschnitt sind FX-Positionen und Gewinn- und Verlust-Informationen in allen anderen Handelsfenstern angeführt. Dies kann manchmal Verwirrung sorgen, da nicht klar ist, welche Positionsinformationen real und in Echtzeit sind. Um diese etwaige Verwirrung zu umgehen, können Trader Folgendes unternehmen:
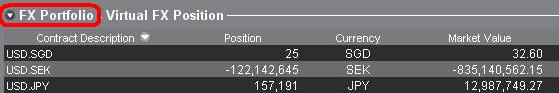
a. FX-Portfolio-Bildschirm einklappen
Wenn Trader auf den Pfeil links vom Wort "FX-Portfolio" klicken, können sie den FX-Portfolio-Abschnitt einklappen. Durch das Einklappen dieses Bereichs werden Informationen zu virtuellen Positionen nicht mehr auf allen Handelsseiten angezeigt. (Hinweis: Dadurch werden keine Marktwert-Informationen angezeigt, es werden lediglich FX-Portfolio-Informationen nicht mehr angezeigt.)
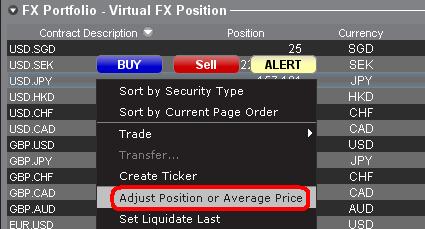
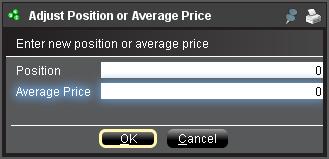
b. Position bzw. Durchschnittskurs anzeigen
Wenn Sie einen Rechtsklick auf den FX-Portfolio-Abschnitt im Kontofenster machen, können Trader entweder Positionen oder den Durchschnittskurs anpassen. Sobald Trader alle Währungspositionen geschlossen haben, die nicht auf ihre Basiswährung lauten, und bestätigen haben, dass der Marktwert-Abschnitt alle Positionen in Währungen, die nicht auf die Basiswährung lauten, als geschlossen bestätigt, können Trader die Positions- und Durchschnittskursfelder auf 0 zurücksetzen. Dadurch wird die im FX-Portfolio-Abschnitt angezeigte Positionsmenge zurückgesetzt und Trader sollten in der Lage sein, genauere Informationen zu ihren Positionen sowie Gewinnen und Verlusten auf den Handelsbildschirmen sehen. (Hinweis: Hierbei handelt es sich um einen manuellen Prozess und müsste jedes Mal, wenn Währungspositionen glattgestellt werden, durchgeführt werden. Trader sollten Positionsinformationen im Marktwert-Abschnitt immer bestätigen, um sicherzustellen, dass ihre übermittelten Orders das erwünschte Ergebnis einer Positionsschließung bzw. -eröffnung erzielen.
Wir empfehlen Tradern, sich mit FX-Trading mittels eines Paper-Trading-Kontos oder eines DEMO-Kontos vertraut zu machen, bevor sie Transaktionen in ihrem Live-Konto eingehen. Kontaktieren Sie IB für zusätzliche Details zu den vorstehenden Informationen.
Weitere allgemeine Fragen:
How to update the US Social Security Number (SSN) or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) on your account
If you have been informed or believe that your account profile contains an incorrect US SSN/ITIN, you may simply log into your Account Management to update this information. Depending on your taxpayer status, you can update your US SSN/ITIN by modifying one of the following documents:
1) IRS Form W9 (if you are a US tax resident and/or US citizen holding a US SSN/ITIN)
2) IRS Form W-8BEN (if you are a Non-US tax resident holding a US SSN/ITIN)
Please note, if your SSN/ITIN has already been verified with the IRS you will be unable to update the information. If however the IRS has not yet verified the ID, you will have the ability to update through Account Management.
How to Modify Your W9/W8
1) To submit this information change request, first login to Account Management
2) Click on the Settings section followed by Account Settings
3) Find the Profile(s) section. Locate the User you wish to update and click on the Info button (the "i" icon) to the left of the User's name
.png)
4) Scroll down to the bottom where you will see the words Tax Forms. Next to it will be a link with the current tax form we have for the account. Click on this tax form to open it

5) Review the form. If your US SSN/ITIN is incorrect, click on the UPDATE button at the bottom of the page
6) Make the requisite changes and click the CONTINUE button to submit your request.

7) If supporting documentation is required to approve your information change request, you will receive a message. Otherwise, your information change request should be approved within 24-48 hours.
IRA: Required Minimum Distributions
IRA owners may be required to to withdraw funds beginning at age 73, and every year thereafter. Determining your Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) is significant while retaining an IRA, considering both your life expectancy and the IRA's fair market value.
The required amount for each eligible person is based on the December 31 IRA account value of the previous year and the IRA owners date of birth. Your spouse's date of birth may also be a factor if your spouse is at least 10 years younger than you. Interactive Brokers LLC provides several information resources to understand and calculate your RMD, including access to the online FINRA RMD Calculator.
Requesting Your RMD Withdrawal
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires the IRA plan custodian to notify IRA owners about the RMD requirements by January 31 each year. If you turn 73 this year, you are required to begin taking RMDs before April 1 of the following year.
Eligible IRA owners must begin receiving withdrawals by December 31 of the year they reach age 73. The first RMD withdrawal, however, may be delayed until April 1 of the following year.
If you elect to delay the withdrawal, then please observe the following considerations:
(1) Two RMD withdrawals will be required the following year, the undistributed initial RMD and the new RMD.
(2) The new RMD will be slightly larger due to the December 31 market value's inclusion of the undistributed initial RMD.
Subsequent RMD withdrawals from your IRA must be distributed by December 31 to avoid a penalty tax.
Note: Roth IRAs are exempt from the RMD rules during the IRA owner's lifetime.
Requesting Your RMD Withdrawal
You may request a withdrawal of funds through the Transfer & Pay and then Transfer Funds menu options within Client Portal. The IRS deadline for taking RMDs is December 31 each year. Keep in mind that the year end withdrawal cut off for processing withdrawals from your Interactive Brokers account may occur before December 31.
Please note that you can elect to transfer your funds to your bank account or to an Interactive Brokers non-IRA account. To transfer funds to an Interactive Brokers non-IRA account, log into Client Portal, select Transfer & Pay, Transfer Funds then select Transfer Funds Between Accounts.
Your RMD is determined by dividing the account balance on December 31 of last year by your life expectancy factor. Your life expectancy factor is taken from the Life Expectancy Tables contained in IRS Publication 590. Your IRA beneficiary election may play an important role in determining your RMD, as well.
You must calculate your RMD separately for each qualifying IRA custodied at Interactive Brokers and any other financial institution. The RMD, however, may be satisfied from any single one or combination of your IRAs. The IRA Required Minimum Distribution Worksheets may provide additional assistance with the calculation of your RMD.
Click here to return to the Retirement Account Resource page.
Disclaimer: IB does not provide tax advice. These statements are provided for information purposes only, are not intended to constitute tax advice which may be relied upon to avoid penalties under any international, federal, state, local or other tax statutes or regulations, and do not resolve any tax issues in your favor. We recommend that you consult a qualified tax adviser or refer to the U.S. Internal Revenue Service.
IRA: Retirement Account Resource Center
IMPORTANT NOTE: This article has been customized for use by self-directed Individual Retirement Account (IRA) owners for information purposes only. Persons are encouraged to consult a qualified tax professional with the investments and elections within the IRA. IB does not provide tax advice. For detailed information regarding IRAs, you may consult the IRS Publication 590-A about IRA contributions and the IRS Publication 590-B about IRA distributions.
This resource center provides a central reference point for information concerning the various IRA account types offered by IB.
Important Notice - Select IRA Tax Reporting for key information with transaction and tax reporting in your IRA.
Account Management IRA Reference
Beneficiary Options
Recharacterizations from a Roth IRA
Required Minimum Distributions
IRS Circular 230 Notice: These statements are provided for information purposes only, are not intended to constitute tax advice which may be relied upon to avoid penalties under any federal, state, local or other tax statutes or regulations, and do not resolve any tax issues in your favor.
IRA: Rollover Rules & Conditions
This information is for general educational purposes only. Individuals should consult with their financial adviser or legal counsel to determine how rollover regulations affect their unique situations.
Generally, an IRA rollover is a tax-free distribution to you of cash or other assets from one retirement plan that you contribute to another retirement plan. The contribution to the second retirement plan is called a rollover contribution.
This article outlines the types of IRA rollover transactions, rules and conditions, IB's Rollover Certification form, and rollover transaction details. Select from list below for details:
Eligible Rollover Transactions
Rules & Conditions
Prior to completing an IRA Rollover transaction, we recommend that you review the rules and conditions surrounding eligibility. Interactive Brokers can accept as a tax-free transaction an eligible rollover distribution as defined under the Internal Revenue Code. Included in this article is information about eligible transactions, as well as the Interactive Brokers IRA Rollover Certification form.
IRA Rollover Certification
Before accepting an IRA rollover transaction into an Interactive Brokers LLC IRA, we require that you review your eligibility for the rollover and certify your understanding of the rollover rules and conditions. The IRA Rollover Form includes the IRA Rollover Certification.
The Transfer Funds page within the Client Portal lets you notify IB of an IRA Rollover deposit of funds into your account. From the Transfer & Pay menu select Transfer Funds and then Make a Deposit. Select one of the saved deposit instructions and follow the prompts on the screen or create a new deposit instruction by selecting the Currency of the deposit from the drop-down menu. Click Connect or Get Instructions for the method you will use to transfer funds. And finally follow the remaining instructions provided to initiate the transfer with your bank.
Rollover Transactions
Two types of IRA rollover transactions exist with different guidelines and delivery methods:
- Direct Rollover - a transfer of assets from an employer-sponsored retirement plan directly to an eligible IRA. If you choose to receive the distribution first, then you may roll over the funds to the IRA within 60 days.
- Indirect Rollover - a distribution from an IRA paid to you, followed by a rollover into another IRA within 60 days. The IRS allows an indirect rollover of each IRA's funds once during a twelve-month period.
(Note: A distributions directly from one IRA trustee to another IRA trustee is a Trustee-to-Trustee transfer. It is not affected by the twelve-month waiting period.)
For additional information about rollovers, visit Understanding Rollovers. See also IRS Publication 590-A, Contributions to Individual Retirement Arrangements (IRAs) for more specific guidelines on moving retirement plan assets.
Eligible Rollover Transactions
Almost any distribution from a qualified plan can be rolled over to an IRA. Your retirement account may be eligible for one of the following eligible rollover transactions.
Traditional IRA or SIMPLE IRA to Traditional IRA Rollover
- Funds or property deposited less than 60 days of receipt by the IRA owner from the previous IRA
- During the preceding 12 months, no other distributions from the distributing IRA were rolled over
- The assets involved in the transaction have not been rolled over in the past 12 months
- Required Minimum Distribution satisfied (if over 73)
- For SIMPLE IRAs, after two years from the first contribution
Roth IRA to Roth IRA Rollover
- Funds or property deposited less than 60 days of receipt by the IRA owner from the previous IRA
- During the preceding 12 months, no other distributions from the distributing IRA were rolled over
- The assets involved in the transaction have not been rolled over in the past 12 months
Rollover or Direct Rollover from Qualified Plan into a Traditional IRA
- Eligible participant (participant, spouse beneficiary, or former spouse due to divorce)
- Funds or property deposited less than 60 days of receipt by the participant from the previous plan
- Funds received from an eligible qualified retirement plan
- Required Minimum Distribution satisfied (if over 73)
- Consists of funds, property, or proceeds from the sale of property distributed from the qualified plan
- All of the funds are eligible to be rolled over
Roth IRA to Roth IRA Rollover
- Funds or property deposited less than 60 days of receipt by the IRA owner from the previous IRA
- Required Minimum Distribution satisfied (if over 73)
Ineligible Rollover Transactions
Some funds distributed from a retirement plan are not eligible for rollover into an IRA. The following transactions are not eligible rollover transactions.
- Any portion of a distribution from a retirement plan not rolled over
- Required Minimum Distributions
- Distribution of excess contributions and related earnings
- Retirement plan loan treated as a distribution
- Hardship distributions
- Distributions part of substantially equal payments (73-t)
- Dividends on employer securities
- Non-spousal death benefit distributions
- The cost of life insurance coverage
Click here to return to the Retirement Account Resource page.
Disclaimer: IB does not provide tax advice. These statements are provided for information purposes only, are not intended to constitute tax advice which may be relied upon to avoid penalties under any international, federal, state, local or other tax statutes or regulations, and do not resolve any tax issues in your favor. We recommend that you consult a qualified tax adviser or refer to the U.S. Internal Revenue Service.
IRA: Charitable Donations from IRAs
Charitable Distributions
What is a Qualified Charitable Distribution (QCD)?
How to determine if a charity can receive the QCD
Where can an IRA owner find additional information on QCDs?
Withdrawal Processing
When can I submit my withdrawal?
Can IBKR customers submit a QCD withdrawal online?
What amount may be withdrawn? Why?
Where are the funds disbursed?
Does the distribution count towards the Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) amount?
Eligible IRA Accounts
Is the Charitable Distribution allowed from all IRAs held at IBKR?
Are the QCDs allowed from other IRA and retirement plans not held at IBKR?
QCD Tax Reporting
How is the QCD reported to the IRS?
Can any taxes be withheld from the distribution?
Do federal taxes have to be paid on the distribution?
Does a state or municipal tax have to be paid on the distribution?
Charitable Distributions
What is a Qualified Charitable Distribution (QCD)?
An otherwise taxable distribution from an eligible IRA owned by an individual 72 or older paid to an IRS qualified charity.
How to determine if a charity can receive the QCD?
The IRS Exempt Organizations Select Check allows users to "Search for Charities" among a list of organizations eligible to receive tax-deductible charitable contributions.
Where can an IRA owner find additional information on QCDs?
Visit Charitable Donations for IRAs for additional information on qualified charitable distributions. See also IRS Publication 590-b.
Withdrawal Processing
Can IBKR customers submit a QCD withdrawal online?
What amount may be withdrawn? Why?
IBKR will process the withdrawal for any amount, as long as the account has sufficient available funds. Why? Although the QCD donations to the charity must not exceed $100,000 per year to retain QCD status, charitable gifts may exceed this limit.
Where are the funds disbursed?
Funds are made payable to the IRS qualified charity and mailed direct to the charity. Only funds disbursed to the charity can be designated from your IRA as a QCD.
Does the distribution count towards the Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) amount?
Yes
Eligible IRA Accounts
Is the Charitable Distribution allowed from all IRAs held at IBKR?
No, see the list below. IRA owners should contact a qualified tax advisor about how to preserve QCD tax benefits. Not all distributions are created equal. A tax advisor will be able to assess an IRA owner’s best choice.
Traditional IRA > YES
Rollover IRA > YES
Roth IRA > YES
Inherited IRA > YES, if the beneficiary is at least age 70 1/2
SEP IRA > NO
Education IRA > NO
Are the Charitable Distributions allowed from other IRA and retirement plans not held at IBKR?
No, not directly. Retirement plans, employer sponsored SEP IRAs, and Simple IRAs (account classifications not held at IBKR) are not eligible for a QCD election. IRA owners may be eligible to rollover assets from these plans into a traditional, rollover, or Roth IRA to request a charitable distribution. IRA owners should contact a qualified tax advisor or their retirement plan administrator.
QCD Tax Reporting
How is the QCD reported to the IRS?
IBKR will report the charitable distributions on Form 1099-R when issued. See Reports and Dates for 1099 availability dates.
Can any taxes be withheld from the distribution?
No.
Do federal taxes have to be paid on the distribution?
Generally, federal taxes are not paid with QCDs. But distributions in excess of the IRS limit may be subject to income tax. IBKR recommends that customers contact a qualified tax advisor.
Does a state or municipal tax have to be paid on the distribution?
Contact your tax advisor or local tax authority on state and municipal requirements for the distributed amount.
Disclaimer: IBKR does not provide tax advice. These statements are provided for information purposes only, are not intended to constitute tax advice which may be relied upon to avoid penalties under any international, federal, state, local or other tax statutes or regulations, and do not resolve any tax issues in your favor. We recommend that you consult a qualified tax advisor or refer to the U.S. Internal Revenue Service.
ACATS Transfer Guide (US brokerage account transfers)
ACATS Transfer Guide
Introduction
Understanding the basic facts about transferring accounts between US brokerage firms can be help to avoid delays. Through this article and other Knowledge Database resources, Interactive Brokers seeks to assist with your incoming and outgoing ACATS requests.
US brokerage firms utilize a standardized system to transfer customer accounts from one firm to another. Known as the Automated Customer Account Transfer Service or ACATS, the process allows assets to move seamlessly between brokerage firms in a unified time frame. ACATS transfers are facilitated by a third party, the National Securities Clearing Corporation (NSCC), to assist participating members with timely asset transfers.
ACATS Transfer Benefits
The majority of assets may be transferred between US brokerage firms and some banks through ACATS. This standardized system includes stocks, US corporate bonds, listed options, unit investment trusts, mutual funds, and cash. Information on assets eligible for transfer is provided at "Assets Eligible..." Though impacted by multiple factors and time constraints, the accepted or rejected transfers finalize within 10 business days in most cases.
Navigating The Process
4 simple steps of the ACATS process will help you understand the flow and minimize delays. Familiarizing yourself with the transfer process helps to ensure a successful transition.
1. Incoming or Outgoing
Incoming ACATS Transfers
The financial institution that is receiving your assets and account transfer is known as the "receiving firm." Investors always work with and through the "receiving firm" to move full or partial account assets into a new broker.
Contact the "receiving firm" (Interactive Brokers) to review the firm's trading policies and requirements. You should verify that your assets are eligible for trading at the "receiving firm" before initiating the transfer request. Not all ACATS transferable assets are acceptable for trading at every brokerage firm.
Outgoing ACATS Transfers
All outgoing ACATS transfers, full or partial, must be approved by the "delivering firm." Investors, however, should work with and through the "receiving firm" in order to begin the the transfer process or to status the progress of the request.
2. Initiating Your Transfer
Investors must always begin the ACATS transfer with the "receiving firm." An ACATS transfer form or Transfer Initiation Form (TIF) must be submitted. The "receiving firm" takes your reqeust and communicates with the "delivering firm" via ACATS. The process begins with this request for transfer of the account.
For your Interactive Brokers Account, the transfer is usually submitted online. Video instruction on submitting the transfer is provided at "How to deposit funds via a full ACATS/ATON Transfer." or through Step-by-step instructions.
Note: Outgoing account transfers from your IB account should be directed to the other broker. Your request will be submitted to IB from the other broker through the ACATS electronically.
3. What to Expect
Your Account
Brokers ensure the safety and security of transfer requests by only authorizing requests between open accounts that meet the following criteria:
- Same Account Title
- Same Tax ID Number
- Same Account Type
Transfer Approval
Ultimately responsible for validating the transfer, the "delivering firm" may accept information from the "receiving firm" correcting data originally entered. Approved or validated requests result in the delivery of positions to the "receiving firm" for their acceptance. Assets may not be accepted by the "receiving firm" for the following:
- Non-marginable or Margin (credit) violation
- Not Tradable
- DTC Chill
Note: The most common reasons for ACATS rejections are outlined by clicking here.
Processing Time-frame
The processing time for each transfer request is fixed. In general, approved transfers complete within 4 to 8 business days. Almost all transfers complete within 10 business days. Each firm is required to perform certain steps at specific intervals in the process. Feel free to review the Full ACATS transfer process flow.
Fees
While Interactive Brokers does not charge a fee to transfer your account via ACATS, some brokers do apply a fee for full and partial transfers. Prior to initiating your transfer, you should contact the "delivering firm" to verify any charge.
4. Who To Contact For Help
Interactive Brokers Customer Service stands poised to assist with your incoming ACATS transfer reqeust. Click here for Customer Service contact resources.
Note: Outgoing or ACATS transfers sending accounts to another broker should be directed to the "receiving firm." Their Account Transfer Group will work with Interactive Brokers directly to complete your outgoing request.
Year End Statement & Report Comparison
The Interactive Brokers Year End Reports provide an activity review for US persons and US entities. The various account statements provide the transaction details as the basis for each report. Each of the standard reports spans the time period from January 1 through December 31.
Some reports, such as the Gain/Loss Summary Worksheet, may consolidate transactions and calculations. For the sake of conserving volume, trade activity may be combined. The account statements include all activity. For your convenience and to assist with your reconcilation, customized statements permit activity displays suitable for your personal needs (see the tab "Customized Templates" for details).
All US tax reports include the total figures as required under the US tax laws.
Non-US Persons and Entities
Income paid from US sources to non-US persons and entities may find this comparison helpful. IB is required to withhold US taxes at a rate of 30% on payments of US source stock dividends and substitute payments in lieu. Both the withholding and the income is reported on the US tax Form 1042-S.
For additional information about how IB handles non-US persons and entities, select this Tax Information and Reporting link and choose the tab Non-US Persons and Entities.
Year End Reports (For Trading) Comparison shown below identifies the most common transaction types which appear on the year end reports. Not all activity is included on each report.
| Year End Reports | Stock | Bond | Equity & Index Option | Single Stock Futures | Futures | Forex |
| Form 1099 | Sell | Sell | - | - | Gain/Loss | - |
| Form 1042-S | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Annual Statement | Buy/Sell Gain/Loss | Buy/Sell Gain/Loss | Buy/Sell Gain/Loss |
Buy/Sell Gain/Loss |
Buy/Sell Gain/Loss |
Buy/Sell Gain/Loss |
| Gain/Loss Worksheet |
Cost/Sell Gain/Loss | Cost/Sell Gain/Loss | Cost/Sell1 Gain/Loss1 | Cost/Sell Gain/Loss | - | - |
| 1256 Worksheet |
- | - | Gain/Loss5 | - | Gain/Loss | - |
NOTES: (1) Only cash settled; (2) Gain/Loss Worksheet was first published by IB with tax year 2007. Worksheets for prior years are not available. IB did provide gain and loss data on the Annual Statements; (3) The 1256 Worksheet was first published by IB with tax year 2008; (4) Option transactions are not 1099 or 1042-S reportable transactions. In accordance with the IRS guidelines, IB excludes the activity from the tax reports; (5) Only broad-sed index options appear on the 1256 Worksheet
Year End Reports (For Income) Comparison shown below identifies the most common types of income which appear on the year end reports. Not all income is reportable on a 1099 or Dividend Summary.
| Year End Reports | Dividends | Credit Interest | Debit Interest | Accruals | Pay In Lieu Credit | Pay In Lieu Debits | Fees |
| Form 1099 | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Form 1042-S | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Annual Statement | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Dividend Summary | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Gain/Loss Worksheet | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| 1256 Worksheet | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
NOTES: (1) US Tax Form 1042-S is provided to non-US persons/entities, along with the Dividend Summary. The Tax Form reports interest, dividends, substitute payments in lieu, and US tax withholding from US securities; (2) For US persons/entities, the Dividend Summary may list dividends as potentially eligible for treatment as “Qualified” based on the holding period. IB does not report this on the 1099-DIV or to the Internal Revenue Service; (3) Debit transactions are not 1099 or 1042-S reportable transactions. In accordance with the IRS guidelines, IB excludes the activity from the tax reports; (4) Exchange, market data, and activity fees
Tax Reporting: When to expect Forms 1099-R and 5498
Forms 1099-R and 5498 are available by January 31 and May 31, respectively.
IRS Circular 230 Notice: The information contained in this FAQ is provided for information purposes only, is not intended to constitute tax advice which may be relied upon to avoid penalties under any federal, state, local or other tax statutes or regulations and does not resolve any tax issues in your favor. Refer to IRS Publication 590, Individual Retirement Accounts for additional information on IRAs in general and consult your tax advisor about your individual tax situation.
Can I contribute to an IRA if I already have a retirement plan through my employer?
Yes. You can contribute to a Roth IRA or Traditional IRA regardless of whether or not you have an employer-sponsored plan. While participation in a retirement plan does not change how much you can contribute to an IRA, it can affect whether or not you are eligible to deduct your Traditional IRA contributions on your tax return.
IRS Circular 230 Notice: The information contained in this FAQ is provided for information purposes only, is not intended to constitute tax advice which may be relied upon to avoid penalties under any federal, state, local or other tax statutes or regulations and does not resolve any tax issues in your favor. Refer to IRS Publication 590, Individual Retirement Accounts for additional information on IRAs in general and consult your tax advisor about your individual tax situation.