延時市場數據的延遲時間
市場數據供應商提供的交易所數據通常分爲兩類,即實時數據和延時數據。實時市場數據是只要信息一公開便會立刻發布。而延時市場數據則相對于實時報價會有一定延遲,通常會晚10到20分鐘。
某些交易所允許免費顯示延時數據,不收取任何市場數據訂閱費用。下方表格列出了我們可以無需正式請求(即在交易平臺輸入産品代碼便會顯示相應的延時數據)、免費提供延時數據的交易所。該表格還包含的對應的實時數據訂閱信息,詳細費用請參見IBKR的網站。
請注意:
- 根據監管要求,IBKR不再向Interactive Brokers LLC的客戶提供美國股票的延時報價信息。
- 延時報價應作爲指示參考使用,不一定可用于交易。延遲的時間可能會在無事先通知的情况下進一步延長。
美洲
| 外部交易所名稱 | IB交易所名稱 | 延遲時間 | 實時訂閱 |
| CBOT | CBOT | 10分鐘 | CBOT Real-Time |
| CBOE Futures Exchange | CFE | 10分鐘 | CFE Enhanced |
| Market Data Express (MDX) | CBOE | 10分鐘 | CBOE Market Data Express Indices |
| CME | CME | 10分鐘 | CME Real-Time |
| COMEX | COMEX | 10分鐘 | COMEX Real-Time |
| ICE US | NYBOT | 10分鐘 | ICE Futures U.S. (NYBOT) |
| Mexican Derivatives Exchange | MEXDER | 15分鐘 | Mexican Derivatives Exchange |
| Mexican Stock Exchange | MEXI | 20分鐘 | Mexican Stock Exchange |
| Montreal Exchange | CDE | 15分鐘 | Montreal Exchange |
| NYMEX | NYMEX | 10分鐘 | NYMEX Real-Time |
| NYSE GIF | NYSE | 15分鐘 | NYSE Global Index Feed |
| One Chicago | ONE | 10分鐘 | OneChicago |
| OPRA | OPRA | 15分鐘 | OPRA Top of Book (L1) (US Option Exchanges) |
| OTC Markets | PINK | 15分鐘 | OTC Markets |
| Toronto Stock Exchange | TSE | 15分鐘 | Toronto Stock Exchange |
| Venture Exchange | VENTURE | 15分鐘 | TSX Venture Exchange |
歐洲
| 外部交易所名稱 | IB交易所名稱 | 延遲時間 | 實時訂閱 |
| BATS Europe | BATE/CHIX | 15分鐘 | European (BATS/Chi-X) Equities |
| Boerse Stuttgart | SWB | 15分鐘 | Stuttgart Boerse incl. Euwax (SWB) |
| Bolsa de Madrid | BM | 15分鐘 | Bolsa de Madrid |
| Borsa Italiana | BVME/IDEM | 15分鐘 | Borsa Italiana (BVME stock / SEDEX / IDEM deriv) |
| Budapest Stock Exchange | BUX | 15分鐘 | Budapest Stock Exchange |
| Eurex | EUREX | 15分鐘 | Eurex Real-Time Information |
| Euronext | AEB/SBF/MATIF/BELFOX | 15分鐘 | Euronext Cash |
| Euronext | AEB/SBF/MATIF/BELFOX | 15分鐘 | Euronext Data Bundle |
| Frankfurt Stock Exchange and XETRA | FWB/IBIS/XETRA | 15分鐘 | Spot Market Germany (Frankfurt/Xetra) |
| ICE Futures Europe (Commodities) | IPE | 10分鐘 | ICE Futures E.U. - Commodities (IPE) |
| ICE Futures Europe (Financials) | ICEEU | 10分鐘 | ICE Futures E.U. – Financials (LIFFE) |
| LSE | LSE | 15分鐘 | LSE UK |
| LSEIOB | LSEIOB | 15分鐘 | LSE International |
| MEFF | MEFF | 15分鐘 | BME (MEFF) |
| NASDAQ OMX Nordic Derivatives | OMS | 15分鐘 | Nordic Derivatives |
| Prague Stock Exchange | PRA | 15分鐘 | Prague Stock Exchange Cash Market |
| SWISS Exchange | EBS/VIRTX | 15分鐘 | SIX Swiss Exchange |
| Tel Aviv Stock Exchange | TASE | 15分鐘 | Tel Aviv Stock Exchange |
| Turquoise ECN | TRQXCH/TRQXDE/TRQXEN | 15分鐘 | Turquoise ECNs |
| Warsaw Stock Exchange | WSE | 15分鐘 | Warsaw Stock Exchange |
亞洲
| 外部交易所名稱 | IB交易所名稱 | 延遲時間 | 實時訂閱 |
| Australian Stock Exchange | ASX | 20分鐘 | ASX Total |
| 恒生指數 | HKFE-IND | 15分鐘 | 恒生指數 |
| 香港期貨交易所 | HKFE | 15分鐘 | 香港衍生品(期貨&期權) |
| 香港聯合交易所 | SEHK | 15分鐘 | 香港證券交易所(股票、權證&債券) |
| Korea Stock Exchange | KSE | 20分鐘 | Korea Stock Exchange |
| National Stock Exchange of India | NSE | 15分鐘 | National Stock Exchange of India, Capital Market Segment |
| Osaka Securities Exchange | OSE.JPN | 20分鐘 | Osaka Exchange |
| SGX Derivatives | SGX | 10分鐘 | Singapore Exchange (SGX) - Derivatives |
| 上海證券交易所 | SEHKNTL | 15分鐘 | 上海證券交易所 |
| 上海證券交易所科創板 | SEHKSTAR | 15分鐘 | 上海證券交易所 |
| 深圳證券交易所 | SEHKSZSE | 15分鐘 | 深圳證券交易所 |
| Singapore Stock Exchange | SGX | 10分鐘 | Singapore Exchange (SGX) - Stocks |
| Sydney Futures Exchange | SNFE | 10分鐘 | ASX24 Commodities and Futures |
| Tokyo Stock Exchange | TSEJ | 20分鐘 | Tokyo Stock Exchange |
關于盈透證券價格限制通知的披露
監管部門期望經紀公司能采取控制措施防止將具有擾亂市場風險(如突然的價格波動)的委托單提交到市場中心。
爲此,盈透證券對客戶委托單設置了多項價格篩選條件。該等價格篩選條件某些情况下會對客戶委托單施以價格限制以避免對市場造成干擾,而該等價格限制通常是IB計算得出的參考價格基礎上的一個%浮動範圍(價格限制的範圍取决于金融産品的類型及其當前價格)。
儘管價格限制是爲了在追求交易確定性和最小化價格風險之間尋求平衡,但其可能會導致交易延遲或無法成交。更多信息請參見盈透證券的委托單傳遞和定單流收入披露。
如果客戶的委托單被IB的系統施加了價格限制,則客戶會 (i) 在TWS中或通過API或FIX標簽58(對于FIX用戶)收到價格限制的實時通知;幷/或 (ii) 收到每日FYI消息,其中會列出前一日被施加了價格限制的前10筆委托單,包括該等委托單的初步價格限制(如有)和進一步價格限制的限制範圍。
客戶可以點擊FYI消息中的退訂鏈接選擇不再接受此類FYI消息。選擇退訂此類FYI消息即表示客戶:
- 同意不再接收盈透證券發出的任何關于對客戶委托單應用了價格限制的通知;幷且
- 確認客戶已經瞭解,客戶的委托單未來可能會被施加價格限制,但客戶不想再就其委托單被施加了價格限制收到任何通知。
Interaction between TWS and MacOS 12 (Monterey)
The present article addresses performance on the Trader Workstation (TWS) under MacOS Monterey (version: 12), as experienced by several clients. The TWS may experience freezes or may shut down unexpectedly (crash) when running on MacOS 12. This can happen immediately during the TWS start up phase or may occur at a later time point, after some minutes or even hours.
Fix Implementation
A fix has been released in the TWS Beta, available for download here
This process included an extensive amount of testing, in order to see which of the alternative Java platforms was the best fit for the Trader Workstation and as well to avoid introducing new issues while solving the current one.
We sincerely thank you for your patience.
TWS Account Window for Retail Clients of IBKR Ireland and Central Europe
This article describes the information provided in the TWS account window for IBKRs EU based entities.
|
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 61% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with IBKR. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money. |
Retail clients who are residents of the EEA and therefore maintain an account with one of IBKR’s European brokers, IBIE or IBCE, are subject to EU regulations which introduce leverage and other restrictions applicable to CFD transactions.
Notably the regulations require the use of free cash to satisfy CFD margin requirements and prohibit retail clients from using securities in the account as collateral to borrow funds to initiate or maintain a CFD position. Please see Overview of ESMA CFD Rules Implementation for Retail Clients at IBIE and IBCE for full details.
The accounts of IBKRs EU entities are universal accounts in which clients can trade all asset classes available on IBKRs platform, but unlike IBKRs US and UK entities, there are no separately funded segments.
Working examples of how this restriction is applied, along with details as to how clients can monitor free cash available for CFD transactions, are outlined below.
Account Window
IBKR enforces the restriction relating to free cash by calculating the funds available for CFD trading on a real-time basis, rejecting new orders and liquidating existing positions when the available free cash is insufficient to cover CFD initial and maintenance margin requirements.
IBKR offers clients the ability to monitor free cash available for CFD transactions via an enhancement to the TWS Account Window which displays the level of free cash in the account. Importantly, the funds shown as available for CFD trading do not imply that cash is held in a separate segment. It simply indicates what proportion of total account balances is available for CFD trading.
For example, assume that an account has EUR 9,705 in cash and no positions. All the cash is available to open CFD positions, or positions in any other asset class:
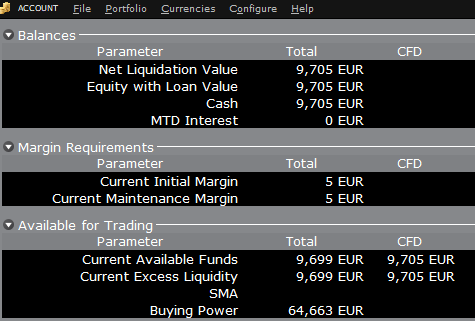
If the account now purchases 10 shares of AAPL stock for an aggregate value of USD 1,383 the cash in the account is reduced by a corresponding amount in EUR, and the funds available for CFD trading are reduced by the
same amount:
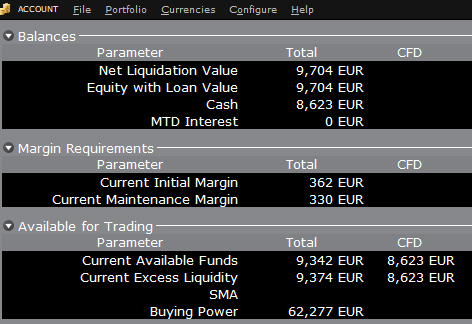
Note that Total available funds are reduced by a smaller amount, corresponding to the stock margin requirement.
If, instead of buying AAPL stock, the account buys 10 AAPL CFDs the impact will be different. As the transaction involves a derivative contract rather than the purchase of the underlying asset itself, there’s no reduction in cash but the funds available for CFDs are reduced by the CFD margin requirement to secure performance on the contract:
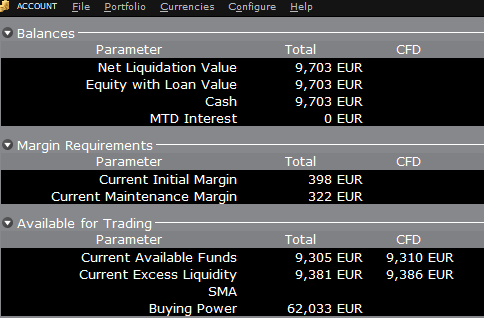
In this case Total available funds and CFD available funds are reduced by an equal amount; the CFD margin requirement.
Funding
As noted above, EU-based accounts do not have segments and therefore there is no need for internal transfers. Funds are available for trades in all asset classes in the amounts indicated in the account window, without the need for sweeps or transfers.
Note also that should an account have a margin loan, i.e. negative cash, it will not be possible to open CFD positions since the CFD margin requirement must be satisfied by free, positive cash. Should you have a margin loan and wish to trade CFDs you must first either close margin positions to eliminate the loan, or add cash to the account in an amount that covers the margin loan and creates a cash buffer sufficient for the necessary CFD margin.
Portfolio Restrictions
Residents of Luxembourg (LU): IB Luxembourg (“IB-LUX”) cannot support Commodity-Metals (London Gold Certificates).
Residents of Central-Eastern Europe (HU, CZ, PO, BG, RO, HR, SK, EE, LV, LT, CY, MT): IB Central Europe (“IB-CE”) cannot support commodity metals. Furthermore, IBCE currently only supports for the following currencies: EUR, USD, CZK, HUF, PLN. GBP and CHF are expected in the near future.
If you hold any of these currencies in your portfolio, you must close the positions as soon as possible in order to facilitate transfer of your account. Short cash positions (borrowing) do not have to be close immediately, just long positions.
Disclosure Regarding Interactive Brokers Price Cap Notices
Regulators expect brokerage firms to maintain controls designed to prevent the firm from submitting orders to market centers that create a risk of disruptive trading (e.g., the risk of sudden, transient price moves).
To comply with these expectations, Interactive Brokers implements various price filters on customer orders. Those price filters may, in certain circumstances, price cap customer orders in order to avoid market disruption, and those Price Caps will generally be in a % range from a reference price range calculated by IB. (The range of the Price Cap varies depending on the type of instrument and the current price.)
Although the price caps are intended to balance the objectives of trade certainty and minimized price risk, a trade may be delayed or may not take place as a result of price capping. More information is available in Interactive Broker’s Order Routing and Payment for Order Flow Disclosure.
If a customer’s order(s) are price capped by IB’s systems, that customer will either receive (i) real-time notification of those price cap(s) in Trader Workstation or via the API or FIX tag 58 (for FIX users); and/or (ii) a daily FYI message containing a digest of the first 10 order(s) that were price capped the prior day, the initial price cap(s) for those order(s) (if applicable), and the Price Cap Range(s) for further Price Cap(s) of those order(s).
Customers may opt out from receiving future FYI Messages by clicking the relevant opt-out link within an FYI Message. By opting out from receiving these future FYI Messages, a customer:
- Agrees to waive any further notifications from Interactive Brokers about the application of the firm’s Price Caps to that customer’s order(s); and
- Acknowledges that he or she understands that his or her orders may be price-capped in the future, but that the customer does not wish to be notified again about the application of any Price Caps to any of his or her orders.
Possible Alerts during the TWS installation or update
IBKR's Trader Workstation (TWS) is a global trading system enabling clients to use a suite of online trading tools. The TWS can be installed on Windows, Mac OS X and Linux, and it requires the presence of a Java Runtime Environment (JRE). Therefore, when you install the TWS, it also downloads the necessary Java files in order to run using a Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Sometimes, during the installation or update process of the TWS, software such as Antivirus applications will show an alert and prevent the process to complete. The warning and other messages in this case can safely be ignored, and you can complete the installation of the trading platform.
Table of content
Downloading the TWS installer and update patches
The TWS installers available in the download areas of ibkr.com or IBKR regional web sites are sealed and digitally signed using all the safety procedures required by the industry standards and do not contain any malicious code or process. The same industry standard practices have been used for the TWS update patches, which are automatically downloaded and installed when launching the TWS (if and only if there is an update available). Nevertheless, if you have received an alert, we recommend you to be cautious. Should you intend to keep the TWS installation file on your machine for future use, you should make sure that the same precautions for the protection of data from viruses and malware are applied to it.
Why do I receive a warning when I install the TWS or when the TWS automatic update runs?
You might see an alert (similar to Figure 1 but not limited to) and your security system would wait for your input on how to process the suspicious file. You usually have the option to quarantine the file, delete it, ignore it once or create a permanent exception for it.
Please note that your antivirus might autonomously quarantine or delete the TWS installer file or some of his components without asking for your confirmation and without showing you any warning. Nevertheless, this should only happen if you have preset your antivirus to specifically react in this way.
Figure 1.
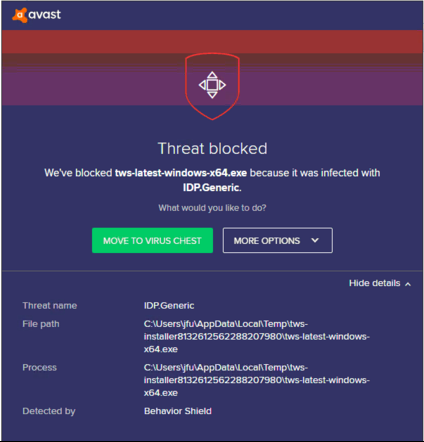
What should I do when I receive a warning?
In case you receive a warning during the TWS installation or update, we recommend the following steps:
1. Delete the TWS installer and download it again from the IBKR main or regional web site
a) Delete the TWS installer file already present on your computer and then delete it as well from your Trash (empty your Trash)
b) From the table below, click on the TWS download area correspondent to your location
| Location | TWS download area |
| US | https://www.ibkr.com |
| Asia / Oceania | https://www.interactivebrokers.com.hk |
| India | https://www.interactivebrokers.co.in |
| Europe | https://www.interactivebrokers.co.uk https://www.interactivebrokers.eu |
c) Check the website certificate. Most Internet browsers will immediately alert you in case the site certificate is invalid, compromised or expired. Nevertheless, if you want to check manually the validity of the site certificate, click on the padlock close to the address (URL) and make sure the Connection is reported as secure and no security warning are present (see Figure 2 below).
Figure 2.
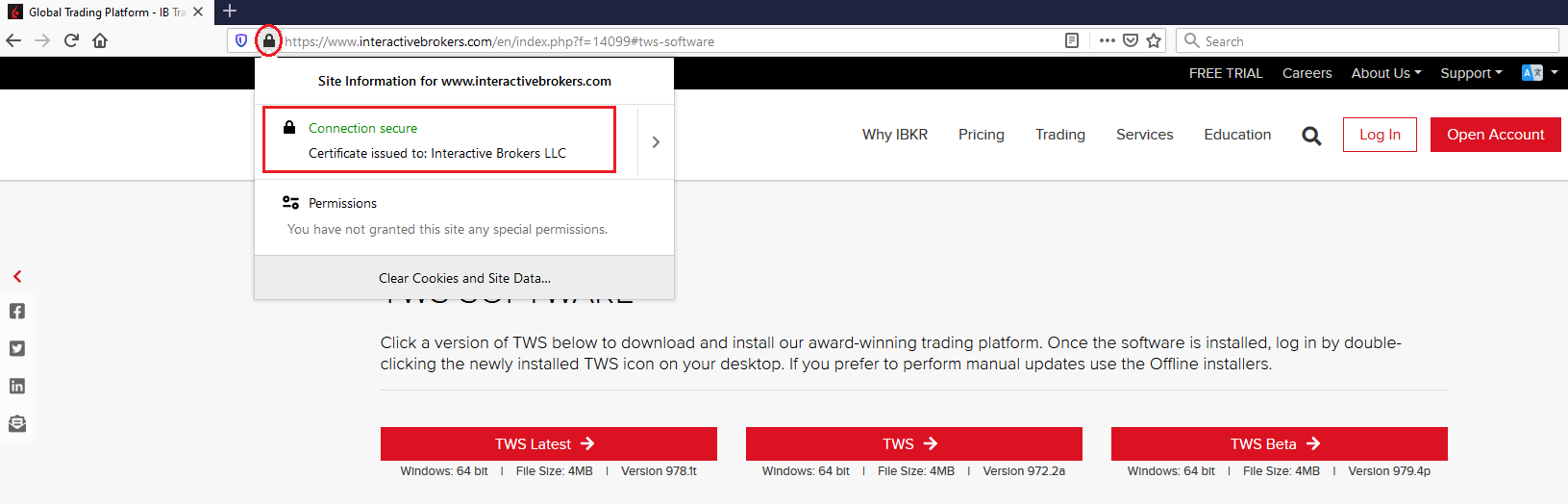
d) Click on the button labeled with the TWS version you wish to use and download again the TWS installer
2. Check the digital signature of the TWS installer file you have downloaded
Normally you will immediately receive a security warning in case the digital signature of a file is compromised. Nevertheless, if you wish to perform a manual check, proceed as follows, according to your Operating System:
For Windows
a) From the Windows file explorer, access your Downloads folder or the folder where you placed the TWS installer
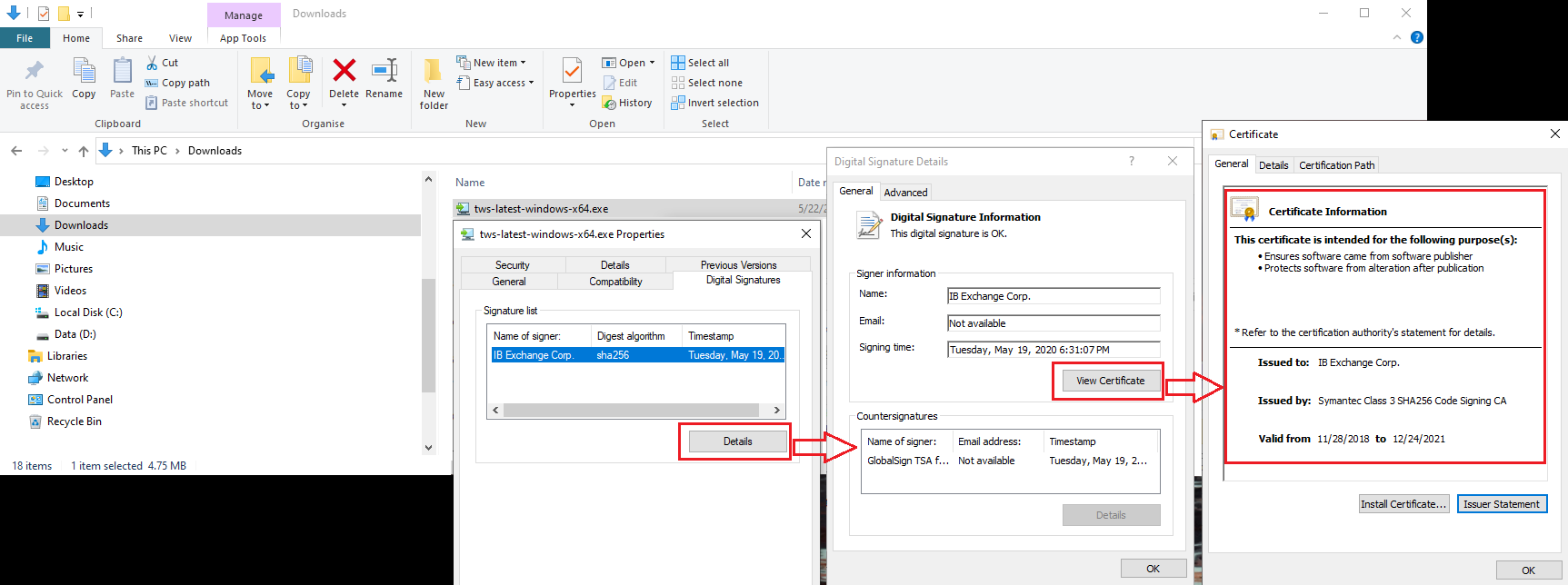
b) Right click on the TWS installer file, select Properties and then click on the tab "Digital Signatures"
c) Click on "Details" and on "View Certificate" to check the certificate status and signer. The legitimate signer is "IB Exchange Corp." (See Figure 3 below)
Figure 3.
For Mac OS X
a) Click on the magnifier glass (Spotlight Search) on the top right of your screen and type Terminal. From the search results, launch the Terminal app
b) Type cd Downloads and press Enter
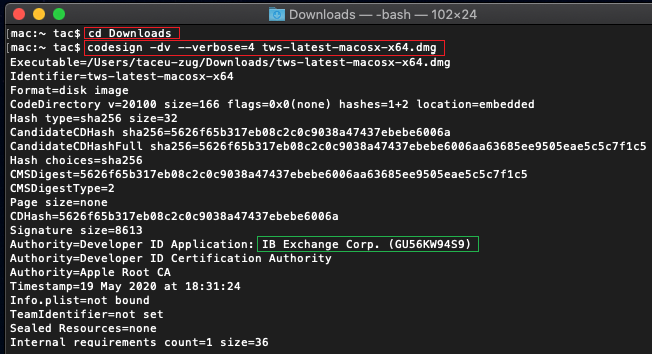
c) Type codesign -dv --verbose=4 tws-latest-macosx-x64.dmg and press Enter. Please notice that the name of the file (tws-latest-macosx-x64.dmg) may differ according to the TWS version you decided to download. If needed, replace the file name in the command with the appropriate one
d) Check the command output and make sure the "Developer ID Application" is "IB Exchange Corp." (see Figure 4 below)
Figure 4.
3. Run the TWS installer file you have downloaded
Once you have downloaded again the TWS installer and after you made sure the file is original (points 1. and 2. above), you can proceed with the installation. Should you still receive a warning from your antivirus, you can reasonably consider it as a false positive and ignore it. Should you need guidance on this step, please proceed directly to the next section.
How can I signal an Alert as false positive?
All modern security systems allow the creation of exceptions, precisely in order to address false positive cases. An exception is a rule forcing the antivirus engine not to scan a specific file or process. That specific file or process will hence be deemed safe and no further alerts will be raised for it.
The procedure for creating an exception may vary, according to the security software you are using. You may be able to create a temporary or permanent exception directly from the alert pop-up or you may have to create one manually from a specific section in the main configuration panel.
If you are unsure of the procedure, we recommend you to consult your antivirus documentation.
Once you have set an exception for the TWS installer file or for the TWS updater process, those will be no longer blocked and will be able to complete their respective tasks successfully.
What else can I do if I have doubts or if my system behaves abnormally?
If you have reasons to believe your machine may be compromised or infected, we recommend performing a full system scan. Usually you can right click on the antivirus icon present on the bottom taskbar (for Windows) or on the upper menu bar (for MacOS) and you will find the option to launch a full system scan. Alternatively, you may start that task from the main antivirus window. If you are unsure of the procedure, we recommend you to consult your antivirus documentation.
Technical Background
How does my security system scan the files I download from the Internet?
Modern antivirus and anti-malware engines base their threats recognition on:
Signature-based scanning: the antivirus scanner searches for a specific pattern of bytes that was previously catalogued as malicious or at least suspicious. The antivirus may check as well file signatures (called hash) against a database of known threats (called virus definitions).
Analysis of behavior: the antivirus engine detects specific actions which individually may not represent a threat but, when correlated together, resemble the usual activity of a malicious software (e.g. the ability of a code to replicate or hide itself, download additional files from the Internet, contact external hosts over the Internet, modify the Operating System registry) This type of scan is designed to detect previously unknown computer threats.
Heuristic detection: the scanner de-compiles the code or runs it within a virtual, restricted environment. It then classifies and weights the actions performed by the code against a predefined, behavior based, rule set.
Cloud-based protection and machine learning: those are relatively new techniques. The file that needs to be analyzed is sent to the antivirus / security system vendor cloud where sophisticated algorithms perform a deep analysis of the code authenticity and behavior.
Are those scan methods infallible?
Modern threats are very sophisticated and, like biological viruses, can mutate their code and their signatures. Moreover, new malwares and exploits are created every day and spread rapidly over the Internet. The threat recognition methods mentioned above are therefore not infallible but can guarantee a high percentage of malware recognition when combined together.
While signature based techniques are very successful in recognizing known threats and less prone to false positives, they are not so efficient in recognizing unknown malware or mutations of existing ones. In this area, the behavioral and heuristic methods perform much better although they are more prone to false positives since their detection is not based on bare code matching but on a certain degree of interpretation and hence uncertainty.
The term "false positive" is used when a security system classifies an innocuous file or process as malware.
Reference:
Alternative Streaming Quotes for US Equities
The SEC Vendor Display Rule requires that brokers give clients access to the NBBO at the point of order entry. In order to provide users with free live streaming market data, we cannot display this free stream when entering an order without the client subscribing to the paid NBBO. Please note, this does not apply to non-IBLLC clients.
Under the Rule 603(c) of Regulation NMS (Vendor Display Rule), when a broker is providing quotation information to clients that can be used to assess the current market or the quality of trade execution, reliance on non-consolidated market information as the source of that quotation would not be consistent with the Vendor Display Rule.
All clients (IBKR Lite and Pro) have access to streaming real-time US equity quotes from Cboe One and IEX at no charge. Since this data does not include all markets, we cannot show this quote when entering parameters for a US stock quote. Therefore and according to FINRA's enforcement of the SEC rule, IBKR provides IBLLC US clients a free default snapshot service, “US Snapshots VDR Required”. If clients do not sign up for an NBBO US equity data service and they are an IBLLC client, they will have access to free real-time snapshots when making trading decisions on US stocks. Order routing will not change based on what is shown on the screen. If one is subscribed to NBBO quotes or not, by default the trade will still take place with the assistance of the SMART order router designed to provide the best price for the order.
Please see the sample screenshots below from TWS Classic and TWS Mosaic for what occurs when placing an order without the NBBO streaming subscription for US equities.
TWS Classic:
1. Screenshot of quotes showing without order entry line item
2. Screenshot of quote going blank when putting in the order entry line item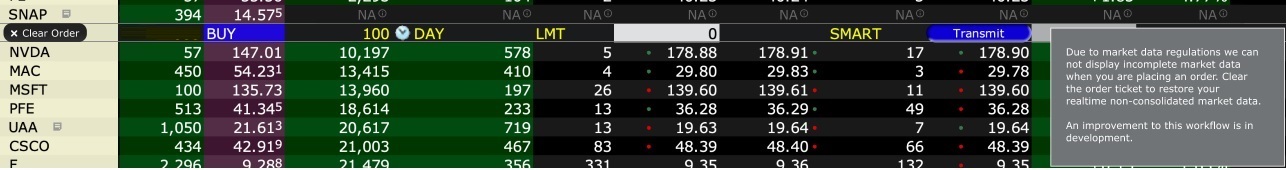
TWS Mosaic:
1. Screenshot of quotes showing without order entry line item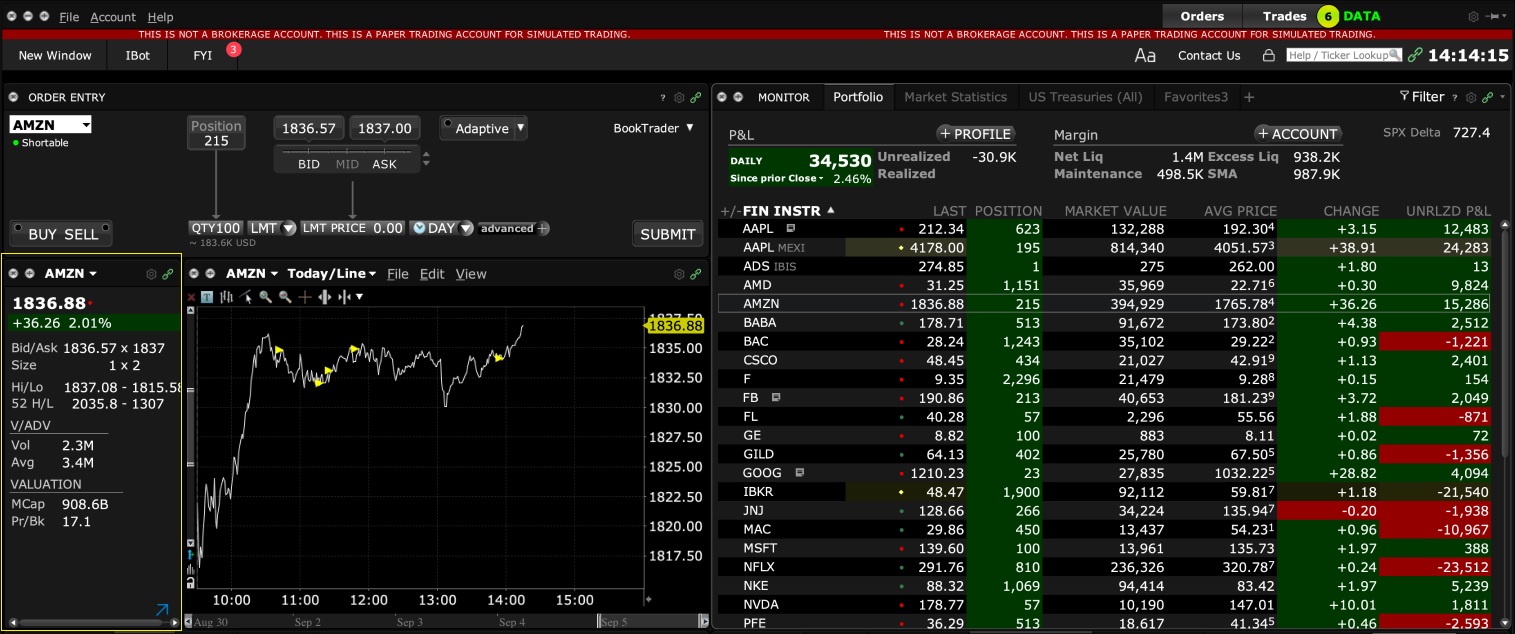
2. Screenshot of quote going blank when putting in the order entry line item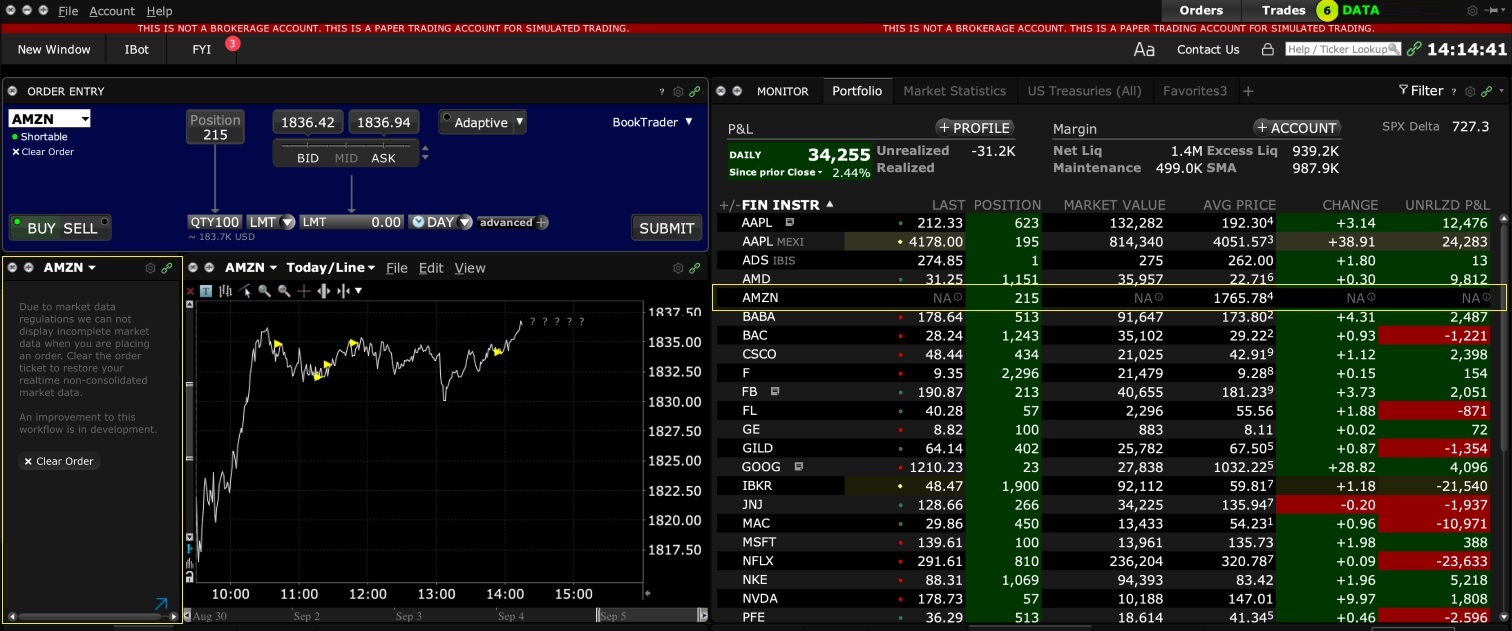
TWS / IB Gateway and their interaction with Proxy servers
Table of contents
Configuration instructions
- Can the TWS / IB Gateway operate through a Proxy server, and how?
- If I use a SOCKS Proxy server, do I need to configure the TWS / IB Gateway?
- If I use a SOCKS Proxy server, do I need to configure the client machines where TWS / IB Gateway runs?
- If I use a Web (HTTP) Proxy server, do I need to configure the TWS / IB Gateway?
- What alternatives do I have in case I cannot implement a proxy solution on my network?
Common issues
Technical Background
Configuration instructions
1. Can the TWS / IB Gateway operate through a Proxy?
Upon start-up and during the run-time, the TWS / IB Gateway must establish and maintain direct network connections to our gateways and market data servers1. Such connections are created from random local TCP ports (above 1024) and are directed to TCP ports 4000 and TCP 4001. Since those are not HTTP connections, they cannot be serviced by a Web (HTTP) Proxy. They can only be serviced by a SOCKS Proxy.
From within the TWS interface, you can access several external services, such as IBKR Client Portal, Statements, Contract details, Bond Search, etc. Those services, being web-based, can be accessed through a Web (HTTP) Proxy (see section 6 for details and configuration) or through a SOCKS Proxy (see sections 4. and 5. for details and configuration).
2. If I use a SOCKS Proxy server, do I need to configure the TWS / IB Gateway?
The TWS / IB Gateway does not contemplate an option for SOCKS proxy forwarding. Therefore, it does not have a place where an explicit SOCKS Proxy host/port can be configured. This does not mean that the TWS / IB Gateway cannot work with a Proxy. It simply means that the TWS / IB Gateway is unaware of the underlying SOCKS proxy setup (proxy-agnostic).
Important Note: While it is impossible for us to determine whether a Proxy is enabled on your network, we assure you that all IBKR platforms, including the TWS, do not impact nor influence your network configuration.
3. If I use a SOCKS Proxy server, do I need to configure the client machines where TWS / IB Gateway runs?
The connections started by the TWS / IB Gateway can be redirected to a SOCKS (Application) Proxy through a specific client machine setup. We mention some of them below. Please note that the final decision is yours and none of the below suggestions can be recommended by us as best adapted to your setup and requirements.
3a. Using a Proxy Client software installed on the client machine where TWS / IB Gateway is running
With this setup, the Proxy client will intercept the connections (not only HTTP but for other ports as well) initiated by the TWS / IB Gateway and redirect them to a SOCKS proxy server. The typical benefits of a transparent proxy include a standard enterprise configuration where all clients routed to the Internet will always be filtered and protected no matter what the end users do, or change, on their machines and the added benefit of reduction in typical user’s client-proxy configuration troubleshooting.
3b. Using a so-called Proxifier
This configuration is very similar to the one at point 5a with the only difference that the Proxifier software can be set to redirect to a Proxy all the requests started by a specific process (e.g., C:\Jts\tws.exe; C:\JTS\ibgateway\XYZ\ibgateway.exe), hence instating a process level packet forwarding instead of a port level forwarding. This setup allows handling environments where different proxy servers are used for different applications or where you would like to address a specific application requirement without modifying/disrupting the connectivity schema for other software installed. The advantage of this solution is minimal maintenance since the connectivity schema is bound to the process and not to the hosts/ports.
3c. Using specific network routing on a client machine
With this setup, you can modify the client machine standard network routes, adding new ones in order to forward packets with specific destinations (e.g., Order routing and Market Data servers1) to a different gateway.
This gateway will then be in charge of routing those requests to the destination hosts. This solution has as well the benefit of not modifying/disrupting the connectivity schema for other software installed but usually requires more maintenance on the gateway and on the client machine in case the IP of the destination servers are changed or in case new servers are added.
4. If I use a Web (HTTP) Proxy server, do I need to configure the TWS / IB Gateway?
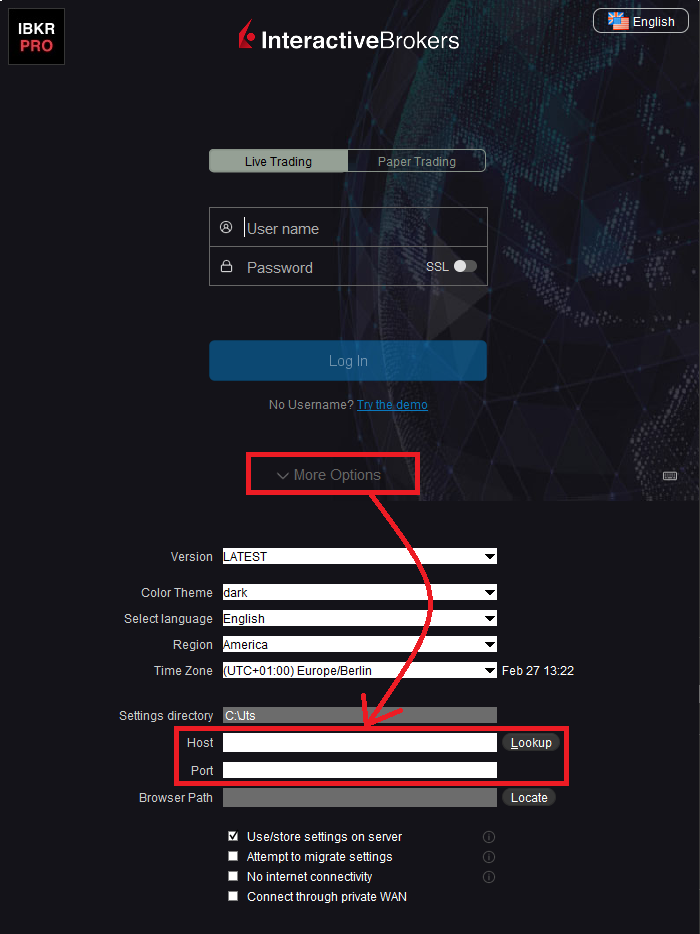
If the Workstations on your local network access the Web content through a Web (HTTP) Proxy, you need to specify the Web Proxy IP Address and port. To do this, click More Options at the bottom of the TWS Login Screen, and enter your Proxy server details in the fields Host and Port (see Figure 1 below). The same fields are present in the IB Gateway Login Screen.
Figure 1.
The Web Proxy you set there will ONLY be used to fetch the web content accessible from within the TWS (e.g., Client Portal, Statements, Product Details, etc.)
5. What alternatives do I have in case I cannot implement a proxy solution on my network?
In this case, you might orient yourself towards a different type of access to the IBKR infrastructure, which includes a special connection type and a FIX/CTCI engine setup. This setup would, on the other hand, have different requirements in terms of commissions2.
Common Issues
6. What happens if the proxy configuration on your computer is wrong or outdated?
Occasionally, third-party software, even if already uninstalled, may leave behind a SOCKS proxy configuration on your computer. This may also happen if your computer has been infected with malware. In such cases, the proxy server, although configured, is non-existent or not accessible on the network. In such scenarios, the TWS will show an error message (e.g., No Internet Connectivity) and/or start the "Connection attempt #" loop upon login. The same will happen if the Proxy server exists, but has not been correctly configured on the client machines.
6a. How can I correct the proxy configuration if wrong?
When applicable, we recommend you always consult the IT / Networking team of your company first and ask for guidance.
If you are autonomously managing your network, please follow the instructions below according to the Operating System of your machine/s:
Windows
W.1 Press CTRL+S to open the Windows search
W.2 Type Proxy Settings and press Enter
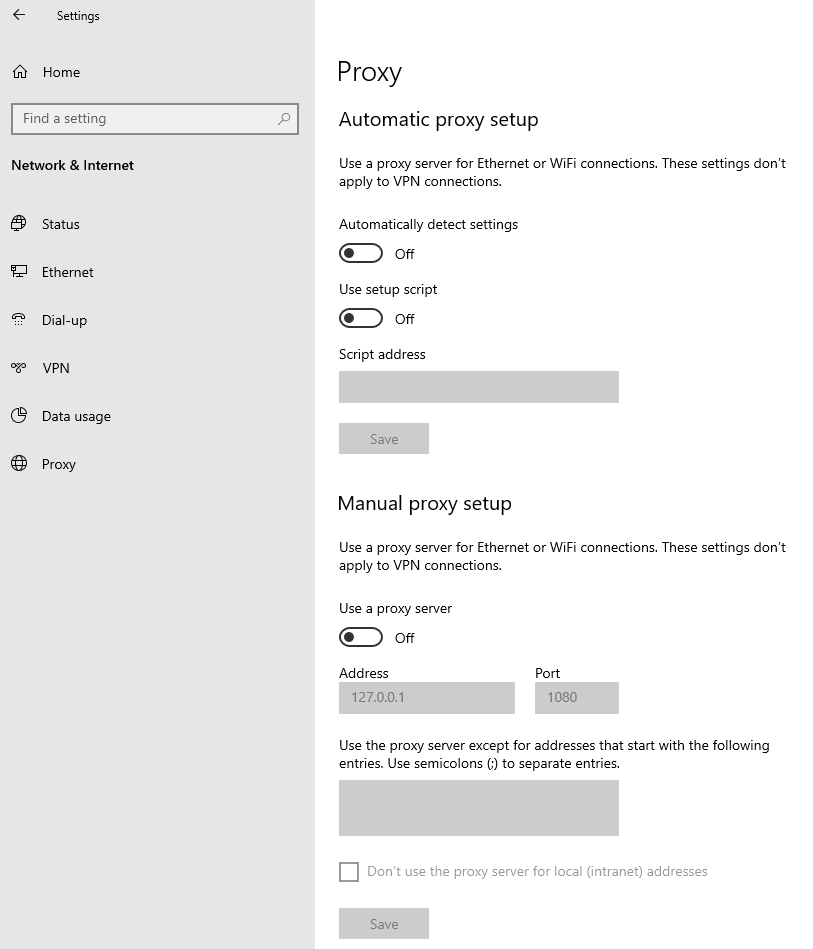
W.3 If no Proxy is present on your network, make sure the switch "Use a proxy server" is deactivated (see Figure 2 below). If a Proxy server is active on your network, make sure the Address (or hostname) and Port are correctly defined.
Figure 2.
Mac
M.1 Click on the Apple icon at the top left corner of the screen and select System Preferences
M.2 Click on Network
M.3 Select the Network connection you are using to access the Internet (e.g. Wi-Fi) and click on it
M.4 Click on the Advanced button and then on the Proxies tab
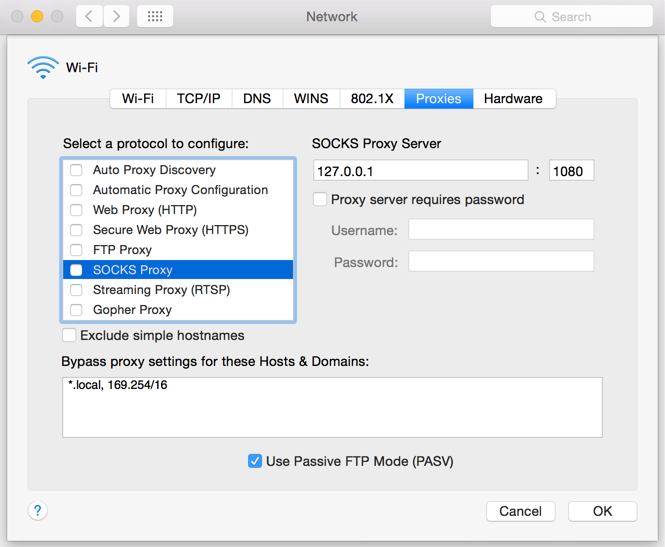
5. If no proxy is present on your network, make sure all the checkboxes (SOCKS Proxy, Web Proxy, Secure Web Proxy) are deactivated (see Figure 3 below). If a Proxy is present on your network, ensure the Protocol, Address (or hostname) and Port are correct.
Figure 3.
7. You are using Public proxies and proxy chains to hide your presence or identity
There are public proxy and proxy chain services purposed to disguise or hide the identity and the activity of the subscriber or to bypass regional restrictions. One of the most famous services is the "Tor" network.
While those services may not necessarily be used for criminal purposes, they render subscriber traceability very difficult when not impossible. Since IBKR is obliged by the financial industry regulators to maintain records of trading activities and trade initiators, we do not allow our clients to reach our systems while using an anonymizing service. If you are using such a service, your TWS connection attempts will be automatically rejected by our gateways.
Technical Background
A proxy server usually acts as a gateway and as a barrier between your local network and the Internet. The proxy listens for outgoing connection requests from the internal workstation/s and forwards them to the desired target host or service on the Internet. When the target replies to such requests, the proxy routes the incoming responses back to the internal workstation/s that initiated the process.
Being the proxy, the only machine of your network actually accessing the Internet, it prevents the other machines and the internal segment of your network (LAN) from being accessible by external actors and hence from being exposed to threats and intrusion attempts.
Additionally, a proxy server can offer a variety of other services, such as web content caching and filtering.
9. Which types of Proxy servers are commonly used and where?
Proxy servers are commonly found within enterprise-grade networks. In the vast majority of cases, proxies are not used by individuals since private broadband connections are established through consumer-grade routers that already offer built-in proxy/firewall solutions. An exception is represented by public proxy or proxy chains discussed in detail in the section You are using Public proxies and proxy chains to hide your presence or identity
There are two main types of Proxy servers:
The HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) defines the rules and the standards for fetching Web content from a Web server and rendering such content on your Web Browser.
A Web Proxy handles only the routing of HTTP requests and HTTP responses. Those requests are transparently generated and sent by your browser whenever you access a Web page. Such requests are normally sent using specific ports (TCP 80 and TCP 443). Hence a Web Proxy usually listens for outgoing HTTP requests coming from your internal network (LAN) only on the TCP ports mentioned above.
SOCKS (Socket Secure) Proxies are designed to handle any type of traffic (not only HTTP/S traffic), generated by any protocol or program (including Trader Workstation).
Notes
1. More information about the servers accessed by the TWS is available in IBKB2816.
2. For an overview of the different special connection options and related requirements, please click here.
For an overview of the FIX infrastructure, please click here.