Informationen zur Regelung von physischen Lieferungen
IB verfügt bei den meisten Produkten nicht über die erforderlichen Einrichtungen, um physische Lieferungen anzubieten. Daher können Kontoinhaber in Bezug auf Futures-Kontrakte, die durch physische Lieferung des zugrunde liegenden Rohstoffs abgewickelt werden (Futures mit physischer Lieferung), keine Lieferungen von Rohstoff-Basiswerten tätigen oder empfangen.
Es liegt in der Verantwortung jedes Kontoinhabers, sich über die Fristen zu informieren, innerhalb derer Positionen der jeweiligen Produkte geschlossen werden müssen. Falls ein Kontoinhaber eine Position eines Futures-Kontrakts mit physischer Lieferung nicht bis zur entsprechenden Liquidierungsfrist schließt, kann IB ohne weitere vorherige Benachrichtigung die Position des Kontoinhabers für den auslaufenden Kontrakt liquidieren. Bitte beachten Sie, dass Liquidierungen aktive Aufträge ansonsten nicht beeinflussen. Kontoinhaber müssen sicherstellen, dass offene Aufträge zur Schließung von Positionen auf die tatsächliche Position in Echtzeit angepasst werden.
Um Lieferungen bei auslaufenden Futures-Kontrakten zu umgehen, müssen Kontoinhaber Ihre Positionen vor Ablauf der Liquidierungsfrist entweder verlängern oder schließen.
Die nachstehende Tabelle bietet Ihnen einen Überblick über geltende Liquidierungsfristen für Futures-Kontrakte und Futures-Optionskontrakte. Die relevanten Informationen zum First Notice Date (Stichtag, nach dem Anleger über eine bevorstehende Zuteilung einer Lieferung benachrichtigt werden können), dem First Position Date (Stichtag, ab dem die Clearingstelle Lieferabsichtserklärungen von Anlegern entgegennimmt) und dem letzten Handelstag, an dem der Kontrakt gehandelt wird, können über die IBKR-Website abgerufen werden, indem Sie zur IBKR-Supportseite wechseln und Kontraktsuche auswählen. Sämtliche Datums-/Fristangaben werden nach bestem Wissen bereitgestellt und sollten durch Überprüfung der jeweiligen Kontrakt-Bedingungen, die auf der Website der entsprechenden Börse verfügbar sind, verifiziert werden.
Überblick über Vorgaben zur physischen Lieferung von Futures am
|
Kontrakt |
Lieferung zulässig |
Liquidierungsfrist |
|
ZB, ZN, ZF (CBOT) |
Nein |
2 Stunden vor Ende des Präsenzhandels am letzten Geschäftstag vor dem First Notice Day (Long-Positionen) oder am letzten Handelstag (Short-Positionen) |
|
ZT (CBOT) Futures, Futures auf japanische Staatsanleihen (JGB)) |
Nein |
Am Ende des vorletzten Geschäftstags vor dem First Position Day (Long-Positionen) oder am Ende des vorletzten Geschäftstags vor dem letzten Handelstag (Short-Positionen) |
|
EUREXUS-Futures |
Nein |
Am Ende des Geschäftstags vor dem First Position Day (Long-Positionen) oder am letzten Handelstag (Short-Positionen) |
|
EUREXUS Zwei-Jahres-Jumbo-Anleihen (FTN2) und Drei-Jahres-Bond-Futures (FTN3) |
Nein |
Am Ende des vorletzten Geschäftstags vor dem First Position Day (Long-Positionen) oder am letzten Handelstag (Short-Positionen) |
|
IPE-Kontrakte (GAS, NGS) |
Nein |
Am Ende des vorletzten Geschäftstags vor dem First Position Day (Long-Positionen) oder am Tag vor dem letzten Handelstag (Short-Positionen) |
|
GLOBEX LIVE CATTLE (LE) |
Nein |
Am Ende des vorletzten Geschäftstags vor dem First Intent Day, d. h. dem ersten Tag, an dem eine Lieferabsicht erklärt werden kann (Long-Positionen), oder am letzten Handelstag (Short-Positionen) |
|
GLOBEX NOK, SEK, PLZ, CZK, ILS, KRW und HUF, sowie korrespondierende Euro-Kurse |
Nein |
Handelsschluss fünf Geschäftstage vor dem Last Trading Day für Long- und Short-Positionen |
|
GBL, GBM, GBS, GBX (Eurex), CONF (Eurex) |
Nein |
2 Stunden vor Handelsschluss am letzten Handelstag |
|
GLOBEX-Währungsfutures (EUR, GBP, CHF, AUD, CAD, JPY, HKD) |
Ja* |
Nicht zutreffend* |
|
GLOBEX Ethanol-Futures (ET) |
Nein |
Handelsschluss fünf Geschäftstage vor dem First Position Day (Long-Positionen) oder am letzten Handelstag (Short-Positionen) |
| NG-Futures (NYMEX) | Nein | Am Ende des Geschäftstags vor dem First Position Day oder am letzten Handelstag (je nachdem welche Frist zuerst eintritt) (Long-Positionen) oder am Ende des Geschäftstags vor dem letzten Handelstag (Short-Positionen) |
|
Alle anderen Kontrakte |
Nein |
Am Ende des vorletzten Geschäftstags vor dem First Position Day oder dem letzten Handelstag, je nachdem welche Frist zuerst eintritt (Long-Positionen) oder am Ende des vorletzten Geschäftstags vor dem letzten Handelstag (Short-Positionen) |
*Da Cash- und IRA-Konten keine Fremdwährungspositionen halten können, gilt der vorstehend angegebene Liquidierungszeitplan für Alle anderen Kontrakte auch für Cash- und IRA-Konten dieser Fremdwährungsprodukte.
Überblick über Vorgaben zur physischen Lieferung von Futures-Opti
| Kontrakt | Lieferung zulässig | Liquidierungsfrist |
| Alle Kontrakte | Ja | Es ist zulässig, dass Optionen in Futures auslaufen (oder, falls sie „aus dem Geld“ liegen, wertlos verfallen), sofern das Verfallsdatum der Option vor dem First Position Day des zugrunde liegenden Futures liegt. Falls eine Futures-Position entsteht, gelten für diese anschließend die entsprechenden Liquidierungsfristen oben. |
Wissenswertes zur vorzeitigen Ausübung von Call-Optionen
EINFÜHRUNG
Die Ausübung einer Aktien-Call-Option vor Ende der Laufzeit bietet im Regelfall keine finanziellen Vorteile, denn:
- es bedeutet, das jeglicher verbleibende Zeitwert der Option verfällt;
- es erfordert einen höheren Kapitaleinsatz zur Zahlung oder Finanzierung der Bereitstellung der Aktien; und
- für den Inhaber der Option steigt unter Umständen das Risiko eines Verlustes an den Aktien im Verhältnis zur Optionsprämie.
Dennoch kann es für Depotinhaber, die über die Voraussetzungen verfügen, um erhöhte Kapital- oder Leihanforderungen zu erfüllen und das ggf. erhöhte Verlustrisiko tragen zu können, finanziell von Vorteil sein, die vorzeitige Ausübung einer amerikanischen Call-Option zu beantragen, um von einer bevorstehenden Dividendenausschüttung zu profitieren.
HINTERGRUND
Als Informationshintergrund sei erwähnt, der Inhaber einer Call-Option nicht berechtigt ist, eine Dividende auf die zugrunde liegende Aktie zu beziehen, da der Anspruch auf diese Dividende ausschließlich für den Inhaber der Dividende zum Dividendenstichtag entsteht. Bei ansonsten gleichen Bedingungen sollte der Kurs der Aktie um den Betrag sinken, der der Höhe der Dividende am Ex-Tag entspricht. Während die Optionspreistheorie davon ausgeht, dass der Call-Kurs den diskontierten Wert der erwarteten Dividendenausschüttungen über die Laufzeit hinweg abbildet, kann dieser jedoch auch am Ex-Tag fallen. Die folgenden Umstände machen den Eintritt dieses Szenarios besonders wahrscheinlich und die vorzeitige Ausübung der Option vorteilhaft:
1. Die Option steht tief im Geld und verfügt über einen Delta-Wert von 100.
2. Die Option verfügt lediglich über einen geringen oder keinen verbleibenden Zeitwert.
3. Der Dividendenbetrag ist relativ hoch und der Ex-Tag liegt vor dem Fälligkeitsdatum der Option.
BEISPIELE
Um die Auswirkungen dieser Umstände mit Blick auf die Entscheidung über eine vorzeitige Ausübung zu veranschaulichen, sei als Beispiel ein Depot gegeben, in dem sich Long-Cash-Guthaben in Höhe von $9,000 und eine Long-Call-Position auf eine fiktive Aktie „ABC“ mit einem Ausübungskurs von $90.00 und einer verbleibenden Laufzeit von 10 Tagen befindet. ABC wird aktuell zu einem Kurs von $100.00 gehandelt und es wurde eine Dividendenausschüttung in Höhe von $2.00 pro Aktie mit dem morgigen Tag als Ex-Tag angekündigt. Weiterhin sei angenommen, dass der Kurs der Option und der Aktienkurs sich ähnlich verhalten und am Ex-Tag um den Dividendenbetrag fallen.
Unter diesen Voraussetzungen werden wir die Ausübungsentscheidung unter der Absicht betrachten, die 100-Aktien-Delta-Position beizubehalten und das Gesamteigenkapital zu maximieren, indem wir zwei Optionskursannahmen verwenden: Im ersten Fall wird die Option bei Parität verkauft und im zweiten Fall über Parität.
SZENARIO 1: Optionskurs bei Parität - $10.00
Wird eine Option bei Parität gehandelt, ermöglicht die vorzeitige Ausübung die Erhaltung des Delta der Position und umgeht den Wertverlust in der Long-Option, wenn die Aktie ex-Dividende gehandelt wird. In diesem Fall werden die Barerträge vollständig eingesetzt, um die Aktien bei Ausübung zu kaufen. Die Optionsprämie verfällt und die Aktie (abzüglich des Dividendenbetrags) und die zahlbare Dividende werden dem Depot gutgeschrieben. Das gleiche Endergebnis kann durch den Verkauf der Option vor dem Ex-Tag und den Kauf der Aktie erzielt werden:
| SZENARIO 1 | ||||
|
Bestandteile des Depots |
Kontostand zu Beginn |
Vorzeitige Ausübung |
Keine Maßnahme |
Verkauf der Option & Kauf der Aktie |
| Barmittel | $9,000 | $0 | $9,000 | $0 |
| Optionen | $1,000 | $0 | $800 | $0 |
| Aktien | $0 | $9,800 | $0 | $9,800 |
| Zahlbare Dividende | $0 | $200 | $0 | $200 |
| Gesamteigenkapital | $10,000 | $10,000 | $9,800 | $10,000 |
SZENARIO 2: Optionskurs über Parität - $11.00
Wird eine Option oberhalb der Paritätsgrenze gehandelt, ist die vorzeitige Ausübung der Option zur Ausnutzung des Abschlags zwar besser als keinerlei Maßnahmen zu ergreifen, aber nicht unbedingt finanziell vorteilhaft. In diesem Szenario würde die vorzeitige Ausübung zu einem Verlust von $100 Optionszeitwert führen, während Untätigkeit einen Verlust der $200 Dividendenwert bedeuten würde. Die beste Vorgehensweise wäre hier der Verkauf der Option zur Gewinnung des Zeitwerts und der Kauf der Aktie, um die Dividende zu erhalten.
| SZENARIO 2 | ||||
|
Bestandteile des Depots |
Kontostand zu Beginn |
Vorzeitige Ausübung |
Keine Maßnahme |
Verkauf der Option & Kauf der Aktie |
| Barmittel | $9,000 | $0 | $9,000 | $100 |
| Optionen | $1,100 | $0 | $900 | $0 |
| Aktien | $0 | $9,800 | $0 | $9,800 |
| Zahlbare Dividende | $0 | $200 | $0 | $200 |
| Gesamteigenkapital | $10,100 | $10,000 | $9,900 | $10,100 |
![]() HINWEIS: Depotinhaber, die eine Long-Call-Position als Bestandteil eines Spreads halten, sollten insbesondere die Risiken einer Nicht-Ausübung der Long-Seite des Spreads in Anbetracht der Wahrscheinlichkeit einer Zuteilung für die Short-Seite des Spreads bedenken. Bitte beachten Sie, dass die Zuteilung eines Short-Calls zu einer Short-Position für die entsprechende Aktie führt und Inhaber von Short-Positionen einer Aktie zum Dividendenstichtag verpflichtet sind, die Dividende an den Verleiher der Aktien zu zahlen. Darüber hinaus erlaubt der Bearbeitungsprozess für Ausübungsanträge der Clearingstelle keine Einreichung von Ausübungsanträgen als Reaktion auf eine Zuteilung.
HINWEIS: Depotinhaber, die eine Long-Call-Position als Bestandteil eines Spreads halten, sollten insbesondere die Risiken einer Nicht-Ausübung der Long-Seite des Spreads in Anbetracht der Wahrscheinlichkeit einer Zuteilung für die Short-Seite des Spreads bedenken. Bitte beachten Sie, dass die Zuteilung eines Short-Calls zu einer Short-Position für die entsprechende Aktie führt und Inhaber von Short-Positionen einer Aktie zum Dividendenstichtag verpflichtet sind, die Dividende an den Verleiher der Aktien zu zahlen. Darüber hinaus erlaubt der Bearbeitungsprozess für Ausübungsanträge der Clearingstelle keine Einreichung von Ausübungsanträgen als Reaktion auf eine Zuteilung.
Nehmen wir als Beispiel einen Credit-Call-(Baisse-)Spread für den SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY), bestehend aus 100 Short-Kontrakten für März '13 $146 und 100 Long-Kontrakten für März '13 $147. Am 14. März 2013 kündigte der SPY Trust eine Dividende von $0.69372 pro Aktie mit Ausschüttung am 30. April 2013 für registrierte Aktieninhaber zum Stand vom 19. März 2013 als Stichtag an. Angesichts der Abwicklungsfrist von 3 Geschäftstagen für US-Aktien hätte der Kauf der Aktien oder die Ausübung der Call-Option spätestens am 14. März 2013 erfolgen müssen, um Anspruch auf die Dividende zu erhalten, da die Aktie ab dem folgenden Tag ex-Dividende gehandelt wurde.
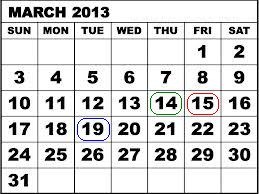
Am 14. März 2013, mit einem verbleibenden Handelstag bis zur Fälligkeit, wurden die beiden Optionskontrakte bei Parität gehandelt, was einem maximalen Risiko von 100 US-Dollar pro Kontrakt bzw. 10,000 US-Dollar für die Position von 100 Kontrakten entspricht. Jedoch wurde die Gelegenheit versäumt, die Long-Kontrakte auszuüben um die Dividende zu erhalten und sich für den wahrscheinlichen Fall einer Zuteilung für die Short-Kontrakte aufgrund anderer nach der Dividende strebender Anleger abzusichern. In der Folge entstand ein zusätzliches Risiko von $67.372 pro Kontrakt bzw. $6,737.20 für die Gesamtposition, was der Dividendenzahlungsverpflichtung im Falle einer Zuteilung aller Short-Calls entspricht. Wie sich der nachstehenden Tabelle entnehmen lässt, wäre das maximale Risiko bei Ermittlung der endgültigen Abwicklungskurse am 15. März 2013 bei $100 pro Kontrakt verblieben, wenn für die Short-Optionsseite keine Zuteilung erfolgt wäre.
| Datum | SPY Schlusskurs | März '13 $146 Call | März '13 $147 Call |
| 14. März 2013 | $156.73 | $10.73 | $9.83 |
| 15. März 2013 | $155.83 | $9.73 | $8.83 |
Weitere Informationen dazu, wie Sie einen Antrag auf vorzeitige Ausübung einreichen, erhalten Sie auf der IB-Website.
Der vorstehende Artikel wird ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bereitgestellt. Er stellt keine Empfehlung oder Handelsberatung dar und vertritt nicht die Einschätzung, dass die vorzeitige Ausübung von Optionen für alle Kunden und Transaktionen gewinnbringend oder angemessen ist. Depotinhaber sollten einen Steuerexperten konsultieren, um zu ermitteln, ob und in welcher Form eine vorzeitige Ausübung zu steuerlichen Konsequenzen führen kann, und sollten besonderes Augenmerk auf mögliche Risiken beim Ersatz einer Long-Optionsposition durch eine Long-Aktienposition richten.
Considerations for Exercising Call Options Prior to Expiration
INTRODUCTION
Exercising an equity call option prior to expiration ordinarily provides no economic benefit as:
- It results in a forfeiture of any remaining option time value;
- Requires a greater commitment of capital for the payment or financing of the stock delivery; and
- May expose the option holder to greater risk of loss on the stock relative to the option premium.
Nonetheless, for account holders who have the capacity to meet an increased capital or borrowing requirement and potentially greater downside market risk, it can be economically beneficial to request early exercise of an American Style call option in order to capture an upcoming dividend.
BACKGROUND
As background, the owner of a call option is not entitled to receive a dividend on the underlying stock as this dividend only accrues to the holders of stock as of its dividend Record Date. All other things being equal, the price of the stock should decline by an amount equal to the dividend on the Ex-Dividend date. While option pricing theory suggests that the call price will reflect the discounted value of expected dividends paid throughout its duration, it may decline as well on the Ex-Dividend date. The conditions which make this scenario most likely and the early exercise decision favorable are as follows:
1. The option is deep-in-the-money and has a delta of 100;
2. The option has little or no time value;
3. The dividend is relatively high and its Ex-Date precedes the option expiration date.
EXAMPLES
To illustrate the impact of these conditions upon the early exercise decision, consider an account maintaining a long cash balance of $9,000 and a long call position in hypothetical stock “ABC” having a strike price of $90.00 and time to expiration of 10 days. ABC, currently trading at $100.00, has declared a dividend of $2.00 per share with tomorrow being the Ex-Dividend date. Also assume that the option price and stock price behave similarly and decline by the dividend amount on the Ex-Date.
Here, we will review the exercise decision with the intent of maintaining the 100 share delta position and maximizing total equity using two option price assumptions, one in which the option is selling at parity and another above parity.
SCENARIO 1: Option Price At Parity - $10.00
In the case of an option trading at parity, early exercise will serve to maintain the position delta and avoid the loss of value in long option when the stock trades ex-dividend, to preserve equity. Here the cash proceeds are applied in their entirety to buy the stock at the strike, the option premium is forfeited and the stock (net of dividend) and dividend receivable are credited to the account. If you aim for the same end result by selling the option prior to the Ex-Dividend date and purchasing the stock, remember to factor in commissions/spreads:
| SCENARIO 1 | ||||
|
Account Components |
Beginning Balance |
Early Exercise |
No Action |
Sell Option & Buy Stock |
| Cash | $9,000 | $0 | $9,000 | $0 |
| Option | $1,000 | $0 | $800 | $0 |
| Stock | $0 | $9,800 | $0 | $9,800 |
| Dividend Receivable | $0 | $200 | $0 | $200 |
| Total Equity | $10,000 | $10,000 | $9,800 | $10,000 less commissions/spreads |
SCENARIO 2: Option Price Above Parity - $11.00
In the case of an option trading above parity, early exercise to capture the dividend may not be economically beneficial. In this scenario, early exercise would result in a loss of $100 in option time value, while selling the option and buying the stock, after commissions, may be less beneficial than taking no action. In this scenario, the preferable action would be No Action.
| SCENARIO 2 | ||||
|
Account Components |
Beginning Balance |
Early Exercise |
No Action |
Sell Option & Buy Stock |
| Cash | $9,000 | $0 | $9,000 | $100 |
| Option | $1,100 | $0 | $1,100 | $0 |
| Stock | $0 | $9,800 | $0 | $9,800 |
| Dividend Receivable | $0 | $200 | $0 | $200 |
| Total Equity | $10,100 | $10,000 | $10,100 | $10,100 less commissions/spreads |
![]() NOTE:
NOTE:
Options have two components that make up their total premium value - intrinsic value and time value. The intrinsic value is the amount by which the option is in-the-money, while the time value represents the possibility that the option could become even more profitable before expiration as the underlying asset price fluctuates while providing protection against adverse moves.
Many options are American-style, which means they can be exercised early, ahead of their expiration date. Early exercise of an option eliminates the remaining time value component from the option's premium, since the option holder loses protection against unfavorable movements in the underlying asset’s price.
This makes early exercise suboptimal in most situations, as the option holder is willingly forfeiting a portion of the option's value.
There are a few specific circumstances where early exercise could make sense, such as:
- For call options on a stock that will pay dividends soon, where the dividend amount exceeds the remaining time value (and only if the exercise will settle on or prior to the record date for the dividend).
- For deep in-the-money options where the time value is negligible compared to the intrinsic value, and the option is expected to drop in value due to interest rate effects (PUTS), or expected stock loan benefits (CALLS).
The first case, exercising an in the money call immediately ahead of a dividend payment, is the most common economically-sensible early exercise. In most cases, it is advisable to hold or sell the option instead of exercising it early, in order to capture the remaining time value. An option should only be exercised early after carefully considering all factors and determining that the benefits of early exercise outweigh the time value being surrendered.
Account holders holding a long call position as part of a spread should pay particular attention to the risks of not exercising the long leg given the likelihood of being assigned on the short leg. Note that the assignment of a short call results in a short stock position and holders of short stock positions as of a dividend Record Date are obligated to pay the dividend to the lender of the shares. In addition, the clearinghouse processing cycle for exercise notices does not accommodate submission of exercise notices in response to assignment.
As example, consider a credit call (bear) spread on the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY) consisting of 100 short contracts in the March '13 $146 strike and 100 long contracts in the March '13 $147 strike. On 3/14/13, with the SPY Trust declared a dividend of $0.69372 per share, payable 4/30/13 to shareholders of record as of 3/19/13. Given the 3 business day settlement time frame for U.S. stocks, one would have had to buy the stock or exercise the call no later than 3/14/13 in order receive the dividend, as the next day the stock began trading Ex-Dividend.

On 3/14/13, with one trading day left prior to expiration, the two option contracts traded at parity, suggesting maximum risk of $100 per contract or $10,000 on the 100 contract position. However, the failure to exercise the long contract in order to capture the dividend and protect against the likely assignment on the short contracts by others seeking the dividend created an additional risk of $67.372 per contract or $6,737.20 on the position representing the dividend obligation were all short calls assigned. As reflected on the table below, had the short option leg not been assigned, the maximum risk when the final contract settlement prices were determined on 3/15/13 would have remained at $100 per contract.
| Date | SPY Close | March '13 $146 Call | March '13 $147 Call |
| March 14, 2013 | $156.73 | $10.73 | $9.83 |
| March 15, 2013 | $155.83 | $9.73 | $8.83 |
Please note that if your account is subject to tax withholding requirements of the US Treasure rule 871(m), it may be beneficial to close a long option position before the ex-dividend date and re-open the position after ex-dividend.
For information regarding how to submit an early exercise notice please click here.
The above article is provided for information purposes only as is not intended as a recommendation, trading advice nor does it constitute a conclusion that early exercise will be successful or appropriate for all customers or trades. Account holders should consult with a tax specialist to determine what, if any, tax consequences may result from early exercise and should pay particular attention to the potential risks of substituting a long option position with a long stock position.
Expiration & Corporate Action Related Liquidations
In addition to the policy of force liquidating client positions in the event of a real-time margin deficiency, IBKR will also liquidate positions based upon certain expiration or corporate action related events which, after giving effect to, would create undue risk and/or operational concerns. Examples of such events are outlined below.
Option Exercise
IBKR reserves the right to prohibit the exercise of stock options and/or close short options if the effect of the exercise/assignment would be to place the account in margin deficit. While the purchase of an option generally requires no margin since the position is paid in full, once exercised the account holder is obligated to either pay for the ensuing long stock position in full (in the case of a call exercised in a cash account or stock subject to 100% margin) or finance the long/short stock position (in the case of a call/put exercised in a margin account). Accounts which do not have sufficient equity on hand prior to exercise introduce undue risk should an adverse price change in the underlying occur upon delivery. This uncollateralized risk can be especially pronounced and may far exceed any in-the-money value the long option may have held, particularly at expiration when clearinghouses automatically exercise options at in-the-money levels as low as $0.01 per share.
Take, for example, an account whose equity on Day 1 consists solely of 20 long $50 strike call options in hypothetical stock XYZ which have closed at expiration at $1 per contract with the underlying at $51. Assume under Scenario 1 that the options are all auto-exercised and XYZ opens at $51 on Day 2. Assume under Scenario 2 that the options are all auto-exercised and XYZ opens at $48 on Day 2.
| Account Balance | Pre-Expiration | Scenario 1 - XYZ Opens @ $51 | Scenario 2 - XYZ Opens @ $48 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cash | $0.00 | ($100,000.00) | ($100,000.00) |
| Long Stock | $0.00 | $102,000.00 | $96,000.00 |
|
Long Option* |
$2,000.00 | $0.00 | $0.00 |
| Net Liquidating Equity/(Deficit) | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | ($4,000.00) |
| Margin Requirement | $0.00 | $25,500.00 | $25,500.00 |
| Margin Excess/(Deficiency) | $0.00 | ($23,500.00) | ($29,500.00) |
*Long option has no loan value.
To protect against these scenarios as expiration nears, IBKR will simulate the effect of expiration assuming plausible underlying price scenarios and evaluating the exposure of each account assuming stock delivery. If the exposure is deemed excessive, IBKR reserves the right to either: 1) liquidate options prior to expiration; 2) allow the options to lapse; and/or 3) allow delivery and liquidate the underlying at any time. In addition, the account may be restricted from opening new positions to prevent an increase in exposure. IBKR determines the number of contracts that will be lapsed by IBKR/auto-exercised shortly after the end of trading on the date of expiration. The effect of any after hours trading you conduct on that day may not be taken into account in this exposure calculation.
While IBKR reserves the right to take these actions, account holders are solely responsible for managing the exercise/assignment risks associated with the positions in their accounts. IBKR is under no obligation to manage such risks for you.
IBKR also reserves the right to liquidate positions on the afternoon before settlement if IBKR’s systems project that the effect of settlement would result in a margin deficit. To protect against these scenarios as expiration nears, IBKR will simulate the effect of expiration assuming plausible underlying price scenarios and evaluating the exposure of each account after settlement. For instance, if IBKR projects that positions will be removed from the account as a result of settlement (e.g., if options will expire out of the money or cash-settled options will expire in the money), IBKR’s systems will evaluate the margin effect of those settlement events.
If IBKR determines the exposure is excessive, IBKR may liquidate positions in the account to resolve the projected margin deficiency. Account holders may monitor this expiration related margin exposure via the Account window located within the TWS. The projected margin excess will be displayed on the line titled “Post-Expiry Margin” (see below) which, if negative and highlighted in red indicates that your account may be subject to forced position liquidations. This exposure calculation is performed 3 days prior to the next expiration and is updated approximately every 15 minutes. Note that certain account types which employ a hierarchy structure (e.g., Separate Trading Limit account) will have this information presented only at the master account level where the computation is aggregated.
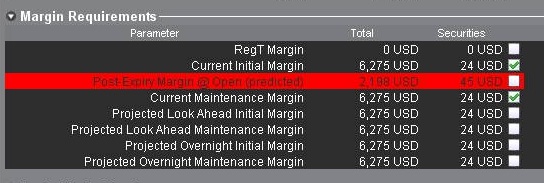
Note that IBKR generally initiates expiration related liquidations 2 hours prior to the close, but reserves the right to begin this process sooner or later should conditions warrant. In addition, liquidations are prioritized based upon a number of account-specific criteria including the Net Liquidating Value, projected post-expiration deficit, and the relationship between the option strike price and underlying.
Call Spreads in Advance of Ex-Dividend Date
In the event that you are holding a call spread (long and short calls having the same underlying) prior to an ex-dividend date in the underlying, and if you have not liquidated the spread or exercised the long call(s), IBKR reserves the right to: i) exercise some or all of the long call(s); and/or ii) liquidate (i.e., close out) some or all of the spreads - if IBKR, in its sole discretion, anticipates that: a) the short call(s) is (are) likely to be assigned; and b) your account would not ave sufficient equity to satisfy the liability to pay the dividend or to satisfy margin requirements generally. In the event that IBKR exercises the long call(s) in this scenario and you are not assigned on the short call(s), you could suffer losses. Likewise, if IBKR liquidates some or all of your spread position, you may suffer losses or incur an investment result that was not your objective.
In order to avoid this scenario, you should carefully review your option positions and your account equity prior to any ex-dividend date of the underlying and you should manage your risk and your account accordingly.
Physically Delivered Futures
With the exception of certain futures contracts having currencies or metals as their underlying, IBKR generally does not allow clients to make or receive delivery of the underlying for physically settled futures or futures option contracts. To avoid deliveries in an expiring contract, clients must either roll the contract forward or close the position prior to the Close-Out Deadline specific to that contract (a list of which is provided on the website).
Note that it is the client’s responsibility to be aware of the Close-Out Deadline and physically delivered contracts which are not closed out within the specified time frame may be liquidated by IBKR without prior notification.
Overview of SEC Fees
Under Section 31 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, U.S. national securities exchanges are obligated to pay transaction fees to the SEC based on the volume of securities that are sold on their markets. Exchange rules require their broker-dealer members to pay a share of these fees who, in turn, pass the responsibility of paying the fees to their customers.
This fee is intended to allow the SEC to recover costs associated with its supervision and regulation of the U.S. securities markets and securities professionals. It applies to stocks, options and single stock futures (on a round turn basis); however, IB does not pass on the fee in the case of single stock futures trades. Note that this fee is assessed only to the sale side of security transactions, thereby applying to the grantor of an option (fee based upon the option premium received at time of sale) and the exerciser of a put or call assignee (fee based upon option strike price).
For the fiscal year 2016 the fee was assessed at a rate of $0.0000218 per $1.00 of sales proceeds, however, the rate is subject to annual and,in some cases, mid-year adjustments should realized transaction volume generate fees sufficiently below or in excess of targeted funding levels.1
Examples of the transactions impacted by this fee and sample calculations are outlined in the table below.
|
Transaction |
Subject to Fee? |
Example |
Calculation |
|
Stock Purchase |
No |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Stock Sale (cost plus commission option) |
Yes |
Sell 1,000 shares MSFT@ $25.87 |
$0.0000218 * $25.87 * 1,000 = $0.563966 |
|
Call Purchase |
No |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Put Purchase |
No |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Call Sale |
Yes |
Sell 10 MSFT June ’11 $25 calls @ $1.17 |
$0.0000218 * $1.17 * 100 * 10 = $0.025506 |
|
Put Sale |
Yes |
Sell 10 MSFT June ’11 $25 puts @ $0.41 |
$0.0000218 * $0.41 * 100 * 10 = $0.008938 |
|
Call Exercise |
No |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Put Exercise |
Yes |
Exercise of 10 MSFT June ’11 $25 puts |
$0.0000218 * $25.00 * 100 * 10 = $0.545 |
|
Call Assignment |
Yes |
Assignment of 10 MSFT June ’11 $25 calls |
$0.0000218 * $25.00 * 100 * 10 = $0.545 |
|
Put Assignment |
No |
N/A |
N/A |
1Information regarding current Section 31 fees may be found on the SEC's Frequently Requested Documents page located at: http://www.sec.gov/divisions/marketreg/mrfreqreq.shtml#feerate
FAQs - U.S. Securities Option Expiration
The following page has been created in attempt to assist traders by providing answers to frequently asked questions related to US security option expiration, exercise, and assignment. Please feel free to contact us if your question is not addressed on this page or to request the addition of a question and answer.
Click on a question in the table of contents to jump to the question in this document.
Table Of Contents:
How do I provide exercise instructions?
Do I have to notify IBKR if I want my long option exercised?
What if I have a long option which I do not want exercised?
What can I do to prevent the assignment of a short option?
Is it possible for a short option which is in-the-money not to be assigned?
What happens if I have a spread position with an in-the-money option and an out-of-the-money option?
Am I charged a commission for exercise or assignments?
Q&A:
How do I provide exercise instructions?
Instructions are to be entered through the TWS Option Exercise window. Procedures for exercising an option using the IBKR Trader Workstation can be found in the TWS User's Guide.
![]() Important Note: In the event that an option exercise cannot be submitted via the TWS, an option exercise request with all pertinent details (including option symbol, account number and exact quantity), should be created in a ticket via the Account Management window. In the Account Management Message Center click on "Compose" followed by "New Ticket". The ticket should include the words "Option Exercise Request" in the subject line. Please provide a contact number and clearly state in your ticket why the TWS Option Exercise window was not available for use.
Important Note: In the event that an option exercise cannot be submitted via the TWS, an option exercise request with all pertinent details (including option symbol, account number and exact quantity), should be created in a ticket via the Account Management window. In the Account Management Message Center click on "Compose" followed by "New Ticket". The ticket should include the words "Option Exercise Request" in the subject line. Please provide a contact number and clearly state in your ticket why the TWS Option Exercise window was not available for use.
Do I have to notify IBKR if I want my long option exercised?
In the case of exchange listed U.S. securities options, the clearinghouse (OCC) will automatically exercise all cash and physically settled options which are in-the-money by at least $0.01 at expiration (e.g., a call option having a strike price of $25.00 will be automatically exercised if the stock price is $25.01 or more and a put option having a strike price of $25.00 will be automatically exercised if the stock price is $24.99 or less). In accordance with this process, referred to as exercise by exception, account holders are not required to provide IBKR with instructions to exercise any long options which are in-the-money by at least $0.01 at expiration.
![]() Important Note: in certain situations (e.g., underlying stock halt, corporate action), OCC may elect to remove a particular class of options from the exercise by exception process, thereby requiring the account holder to provide positive notice of their intent to exercise their long option contracts regardless of the extent they may be in-the-money. In these situations, IBKR will make every effort to provide advance notice to the account holder of their obligation to respond, however, account holders purchasing such options on the last day of trading are not likely to be afforded any notice.
Important Note: in certain situations (e.g., underlying stock halt, corporate action), OCC may elect to remove a particular class of options from the exercise by exception process, thereby requiring the account holder to provide positive notice of their intent to exercise their long option contracts regardless of the extent they may be in-the-money. In these situations, IBKR will make every effort to provide advance notice to the account holder of their obligation to respond, however, account holders purchasing such options on the last day of trading are not likely to be afforded any notice.
What if I have a long option which I do not want exercised?
If a long option is not in-the-money by at least $0.01 at expiration it will not be automatically exercised by OCC. If it is in-the-money by at least that amount and you do not wish to have it exercised, you would need to provide IBKR with contrary instructions to let the option lapse. These instructions would need to be entered through the TWS Option Exercise window prior to the deadline as stated on the IBKR website.
What can I do to prevent the assignment of a short option?
The only action one can take to prevent being assigned on a short option position is to buy back in the option prior to the close of trade on its last trading day (for equity options this is usually the Friday preceding the expiration date although there may also be weekly expiring options for certain classes). When you sell an option, you provided the purchaser with the right to exercise which they generally will do if the option is in-the-money at expiration.
Is it possible for a short option which is in-the-money not to be assigned?
While is unlikely that holders of in-the-money long options will elect to let the option lapse without exercising them, certain holders may do so due to transaction costs or risk considerations. In conjunction with its expiration processing, OCC will assign option exercises to short position holders via a random lottery process which, in turn, is applied by brokers to their customer accounts. It is possible through these random processes that short positions in your account be part of those which were not assigned.
What happens if I have a spread position with an in-the-money option and an out-of-the-money option?
Spread positions can have unique expiration risks associated with them. For example, an expiring spread where the long option is in-the-money by less than $0.01 and the short leg is in-the-money more than $0.01 may expire unhedged. Account holders are ultimately responsible for taking action on such positions and responsible for the risks associated with any unhedged spread leg expiring in-the-money.
Can IBKR exercise the out-of-the-money long leg of my spread position only if my in-the-money short leg is assigned?
No. There is no provision for issuing conditional exercise instructions to OCC. OCC determines the assignment of options based upon a random process which is initiated only after the deadline for submitting all exercise instructions has ended. In order to avoid the delivery of a long or short underlying stock position when only the short leg of an option spread is in-the-money at expiration, the account holder would need to either close out that short position or consider exercising an at-the-money long option.
What happens to my long stock position if a short option which is part of a covered write is assigned?
If the short call leg of a covered write position is assigned, the long stock position will be applied to satisfy the stock delivery obligation on the short call. The price at which that long stock position will be closed out is equal to the short call option strike price.
Am I charged a commission for exercise or assignments?
There is no commissions charged as the result of the delivery of a long or short position resulting from option exercise or assignment of a U.S. security option (note that this is not always the case for non-U.S. options).
What happens if I am unable to meet the margin requirement on a stock delivery resulting from an option exercise or assignment?
You should review your positions prior to expiration to determine whether you have adequate equity in your account to exercise your options. You should also determine whether you have adequate equity in the account if an in-the-money short option position is assigned to your account. You should also be aware that short options positions may be exercised against you by the long holder even if the option is out-of-the-money.
If you anticipate that you will be unable to meet the margin requirement on a stock delivery resulting from an option exercise or assignment, you should either close positions or deposit additional funds to your account to meet the anticipated post-delivery margin requirement.
IBKR reserves the right to prohibit the exercise of stock options and/or close short options if the effect of the exercise/assignment would be to place the account in margin deficit. To protect against these scenarios as expiration nears, IBKR will simulate the effect of expiration assuming plausible underlying price scenarios and evaluating the exposure of each account assuming stock delivery. If the exposure is deemed excessive, IBKR reserves the right to either:
- Liquidate options prior to expiration. Please note: While IBKR retains the right to liquidate at any time in such situations, liquidations involving US security positions will typically begin at approximately 9:40 AM ET as of the business day following expiration;
- Allow the options to lapse; and/or
- Allow delivery and liquidate the underlying at any time.
In addition, the account may be restricted from opening new positions to prevent an increase in exposure. IBKR determines the number of contracts that will be lapsed by IBKR/auto-exercised shortly after the end of trading on the date of expiration. The effect of any after hours trading you conduct on that day may not be taken into account in this exposure calculation.
While IBKR reserves the right to take these actions, account holders are solely responsible for managing the exercise/assignment risks associated with the positions in their accounts. IBKR is under no obligation to manage such risks for you.
For more information, please see Expiration & Corporate Action Related Liquidations
Overview of Fees
Clients and as well as prospective clients are encouraged to review our website where fees are outlined in detail.
An overview of the most common fees is provided below:
1. Commissions - vary by product type and listing exchange and whether you elect a bundled (all in) or unbundled plan. In the case of US stocks, for example, we charge $0.005 per share with a minimum per trade of $1.00.
2. Interest - interest is charged on margin debit balances and IBKR uses internationally recognized benchmarks on overnight deposits as a basis for determining interest rates. We then apply a spread around the benchmark interest rate (“BM”) in tiers, such that larger cash balances receive increasingly better rates, to determine an effective rate. For example, in the case of USD denominated loans, the benchmark rate is the Fed Funds effective rate and a spread of 1.5% is added to the benchmark for balances up to $100,000. In addition, individuals who short stock should be aware of special fees expressed in terms of daily interest where the stock borrowed to cover the short stock sale is considered 'hard-to-borrow'.
3. Exchange Fees - again vary by product type and exchange. For example, in the case of US securities options, certain exchanges charge a fee for removing liquidity (market order or marketable limit order) and provide payments for orders which add liquidity (limit order). In addition, many exchanges charge fees for orders which are canceled or modified.
4. Market Data - you are not required to subscribe to market data, but if you do you may incur a monthly fee which is dependent upon the vendor exchange and their subscription offering. We provide a Market Data Assistant tool which assists in selecting the appropriate market data subscription service available based upon the product you wish to trade. To access, log in to Portal click on the Support section and then the Market Data Assistant link.
5. Minimum Monthly Activity Fee - there is no monthly minimum activity requirement or inactivity fee in your IBKR account.
6. Miscellaneous - IBKR allows for one free withdrawal per month and charges a fee for each subsequent withdrawal. In addition, there are certain pass-through fees for trade bust requests, options and futures exercise & assignments and ADR custodian fees.
For additional information, we recommend visiting our website and selecting any of the options from the Pricing menu option.
Information Regarding Physical Delivery Rules
IBKR does not have the facilities necessary to accommodate physical delivery for most products. For futures contracts that are settled by actual physical delivery of the underlying commodity (physical delivery futures), account holders may not make or receive delivery of the underlying commodity.
It is the responsibility of the account holder to make themselves aware of the close-out deadline of each product. If an account holder has not closed out a position in a physical delivery futures contract by the close-out deadline, IBKR may, without additional prior notification, liquidate the account holder’s position in the expiring contract. Please note that liquidations will not otherwise impact working orders; account holders must ensure that open orders to close positions are adjusted for the actual real-time position.
To avoid deliveries in expiring futures contracts, account holders must roll forward or close out positions prior to the Close-Out Deadline.
Below provides an overview of the relevant close-out deadlines of futures and futures options contracts. The relevant First Notice Date, First Position Date and Last Trading Date information may be obtained through the IBKR website by navigating to the IBKR Support page and selecting Contract Search. Any date information provided is on a best-efforts basis and should be verified by reviewing the contract specifications available on the exchange's website.
Summary of Physical Delivery Futures Policies
|
Contract |
Delivery Permitted |
Close-Out Deadline |
|
ZB, ZN, ZF (CBOT) |
No |
2 hours before the end of open outcry trading on the business day prior to First Notice Day (longs) or Last Trading Day (shorts) |
|
ZT (CBOT) futures, Japanese Govt Bond Futures (JGB) |
No |
End of second business day prior to the First Position Day (longs) or end of second business day prior to Last Trading Day (shorts) |
|
EUREXUS futures |
No |
End of business day prior to the First Position Day (longs) or Last Trading Day (shorts) |
|
EUREXUS 2 yr Jumbo bond (FTN2) and 3 yr bond (FTN3) futures |
No |
End of the second business day prior to the First Position Day (longs) or Last Trading Day (shorts) |
|
IPE contracts (GAS, NGS) |
No |
End of the second business day prior to the First Position Day (longs) or day prior to Last Trading Day (shorts) |
|
CME LIVE CATTLE (LE) |
No |
End of the second business day prior to the First Intent Day (longs) or Last Trading Day (shorts) |
|
CME NOK, SEK, PLZ, CZK, ILS, KRW and HUF, and correspondent Euro rates |
No |
End of the fifth business day prior to the Last Trading Day for both longs and shorts |
|
GBL, GBM, GBS, GBX (Eurex), CONF (Eurex) |
No |
2 hours before the end of trading on the last trading day |
|
CME currency futures (EUR, GBP, CHF, AUD, CAD, JPY, HKD) |
Yes* |
Not applicable* |
|
CME Ethanol futures (ET) |
No |
End of the fifth business day prior to the First Position Day (longs) or Last Trading Day (shorts) |
| NG futures (NYMEX) | No | End of the business day prior to the First Position Day or last trading day (whichever comes first) (longs) or end of business day prior to Last Trading Day (shorts) |
|
All other contracts |
No |
End of the second business day prior to the sooner of First Position Day or Last Trading Day (longs) or end of the second business day prior to the Last Trading Day (shorts) |
*As Cash and IRA accounts are restricted from holding foreign currencies, the liquidation schedule outlined above for All other contracts will also apply to Cash and IRA accounts for these foreign currency products.
Summary of Physical Delivery Future Options Policies
| Contract | Delivery Permitted | Close-Out Deadline |
| All contracts | Yes | Options will be allowed to expire into futures (or, if out-of-the-money, expire worthless), if the options expiration date is prior to the underlying futures’ First Position Day. If there is a resulting futures position, it will then be subject to the respective Close-Out Deadlines, as detailed above. |
What happens to US security options if the underlying becomes the subject of a full cash merger?
In the case of any stock option associated with a merger in which the underlying security has been converted to 100% cash after December 31, 2007, the OCC will accelerate its expiration. The new expiration date for such options will be accelerated to the nearest standard equity expiration, unless the cash conversion takes place after the Tuesday within an expiration week, in which case the expiration date for all contracts not already expiring that week will be deferred until the following month’s expiration.
Note that this acceleration does not impact the automatic exercise threshold, through which all options having a strike price that is in-the-money by at least $0.01 will be automatically exercised by OCC. Nor does it impact the date of the cash settlement attributable to the exercise which remains at T+2.
Also note that this acceleration does not affect options which were converted to cash on or before December 31, 2007 which will remain valid series until their original expiration date has been reached.
Can I take delivery on my futures contract?
With the exception of certain currency futures contracts carried in an account eligible to hold foreign currency cash balances, IB does not allow customers to make or receive delivery of the commodity underlying a futures contract.
IB does not have the facilities necessary to accommodate physical delivery. For futures contracts that are settled by actual physical delivery of the underlying commodity (physical delivery futures), account holders may not make or receive delivery of the underlying commodity.
It is the responsibility of the account holder to make themselves aware of the close-out deadline of each product. If an account holder has not closed out a position in a physical delivery futures contract by the close-out deadline, IB may, without additional prior notification, liquidate the account holder’s position in the expiring contract. Please note that liquidations will not otherwise impact working orders; account holders must ensure that open orders to close positions are adjusted for the actual real-time position.
To avoid deliveries in expiring futures contracts, account holders must roll forward or close out positions prior to the Close-Out Deadline indicated on www.interactivebrokers.com. From the home page, choose the Trading menu, and then select Delivery, Exercise & Actions. From the Delivery, Exercise and Corporate Actions page, read the information governing Futures and Future Options Physical Delivery Liquidation Rules. Also listed are the few futures in which delivery can be taken, such as currency futures.
