Alternative Streaming Quotes for US Equities
The SEC Vendor Display Rule requires that brokers give clients access to the NBBO at the point of order entry. In order to provide users with free live streaming market data, we cannot display this free stream when entering an order without the client subscribing to the paid NBBO. Please note, this does not apply to non-IBLLC clients.
Under the Rule 603(c) of Regulation NMS (Vendor Display Rule), when a broker is providing quotation information to clients that can be used to assess the current market or the quality of trade execution, reliance on non-consolidated market information as the source of that quotation would not be consistent with the Vendor Display Rule.
All clients (IBKR Lite and Pro) have access to streaming real-time US equity quotes from Cboe One and IEX at no charge. Since this data does not include all markets, we cannot show this quote when entering parameters for a US stock quote. Therefore and according to FINRA's enforcement of the SEC rule, IBKR provides IBLLC US clients a free default snapshot service, “US Snapshots VDR Required”. If clients do not sign up for an NBBO US equity data service and they are an IBLLC client, they will have access to free real-time snapshots when making trading decisions on US stocks. Order routing will not change based on what is shown on the screen. If one is subscribed to NBBO quotes or not, by default the trade will still take place with the assistance of the SMART order router designed to provide the best price for the order.
Please see the sample screenshots below from TWS Classic and TWS Mosaic for what occurs when placing an order without the NBBO streaming subscription for US equities.
TWS Classic:
1. Screenshot of quotes showing without order entry line item
2. Screenshot of quote going blank when putting in the order entry line item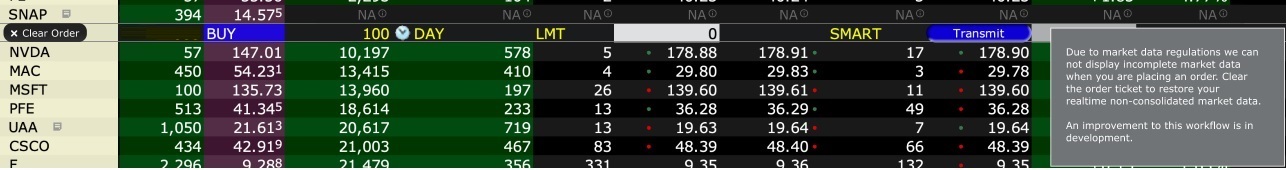
TWS Mosaic:
1. Screenshot of quotes showing without order entry line item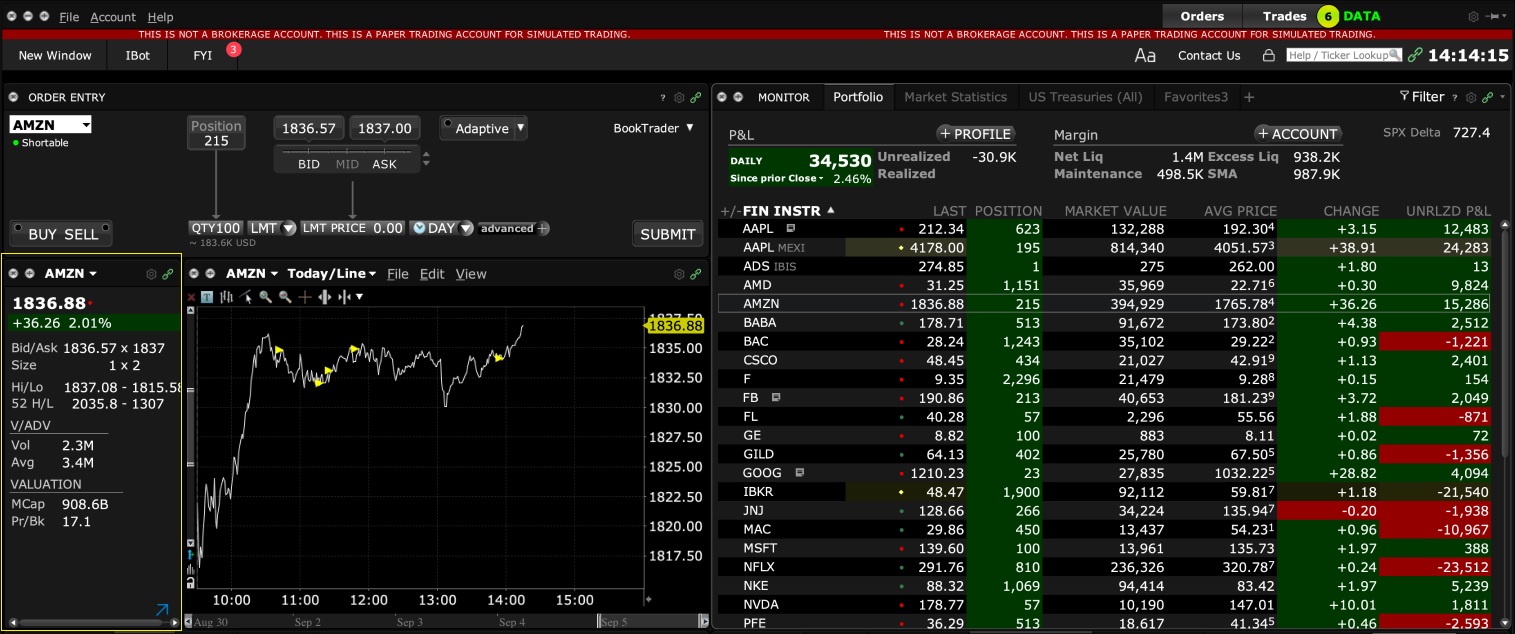
2. Screenshot of quote going blank when putting in the order entry line item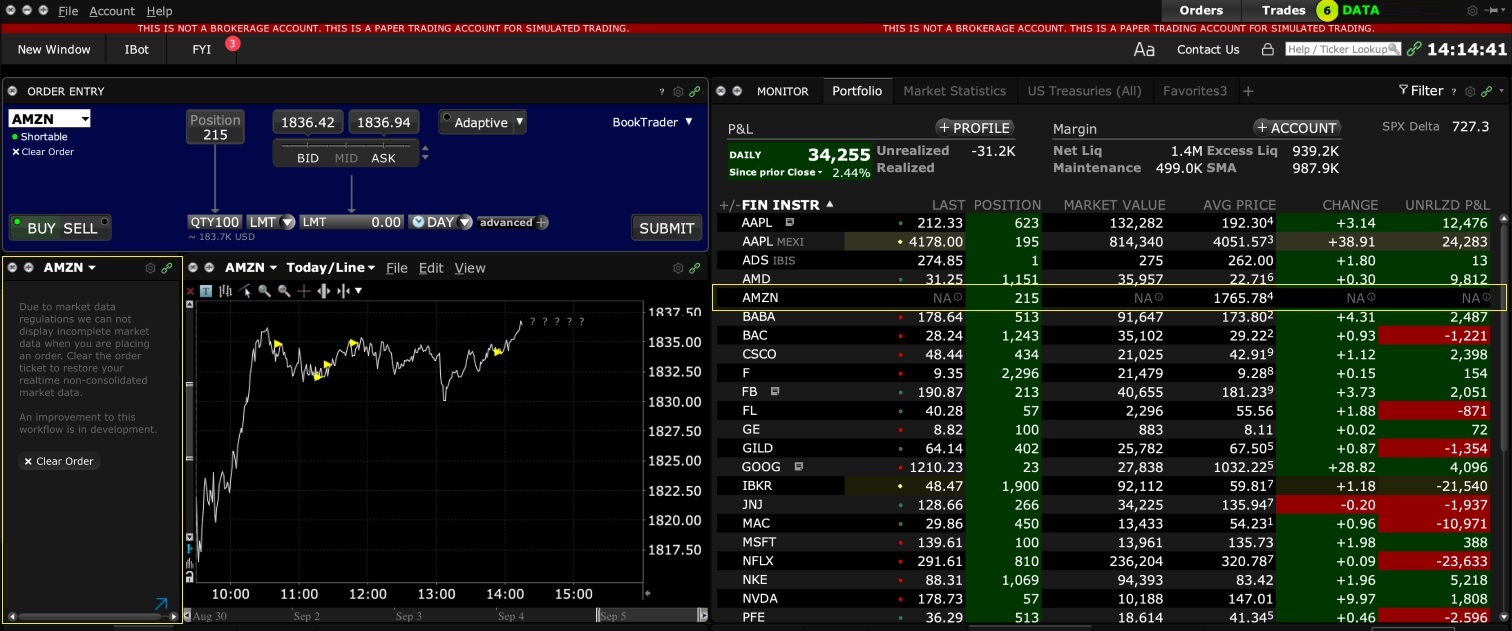
TWS / IB Gateway and their interaction with Proxy servers
Table of contents
Configuration instructions
- Can the TWS / IB Gateway operate through a Proxy server, and how?
- If I use a SOCKS Proxy server, do I need to configure the TWS / IB Gateway?
- If I use a SOCKS Proxy server, do I need to configure the client machines where TWS / IB Gateway runs?
- If I use a Web (HTTP) Proxy server, do I need to configure the TWS / IB Gateway?
- What alternatives do I have in case I cannot implement a proxy solution on my network?
Common issues
Technical Background
Configuration instructions
1. Can the TWS / IB Gateway operate through a Proxy?
Upon start-up and during the run-time, the TWS / IB Gateway must establish and maintain direct network connections to our gateways and market data servers1. Such connections are created from random local TCP ports (above 1024) and are directed to TCP ports 4000 and TCP 4001. Since those are not HTTP connections, they cannot be serviced by a Web (HTTP) Proxy. They can only be serviced by a SOCKS Proxy.
From within the TWS interface, you can access several external services, such as IBKR Client Portal, Statements, Contract details, Bond Search, etc. Those services, being web-based, can be accessed through a Web (HTTP) Proxy (see section 6 for details and configuration) or through a SOCKS Proxy (see sections 4. and 5. for details and configuration).
2. If I use a SOCKS Proxy server, do I need to configure the TWS / IB Gateway?
The TWS / IB Gateway does not contemplate an option for SOCKS proxy forwarding. Therefore, it does not have a place where an explicit SOCKS Proxy host/port can be configured. This does not mean that the TWS / IB Gateway cannot work with a Proxy. It simply means that the TWS / IB Gateway is unaware of the underlying SOCKS proxy setup (proxy-agnostic).
Important Note: While it is impossible for us to determine whether a Proxy is enabled on your network, we assure you that all IBKR platforms, including the TWS, do not impact nor influence your network configuration.
3. If I use a SOCKS Proxy server, do I need to configure the client machines where TWS / IB Gateway runs?
The connections started by the TWS / IB Gateway can be redirected to a SOCKS (Application) Proxy through a specific client machine setup. We mention some of them below. Please note that the final decision is yours and none of the below suggestions can be recommended by us as best adapted to your setup and requirements.
3a. Using a Proxy Client software installed on the client machine where TWS / IB Gateway is running
With this setup, the Proxy client will intercept the connections (not only HTTP but for other ports as well) initiated by the TWS / IB Gateway and redirect them to a SOCKS proxy server. The typical benefits of a transparent proxy include a standard enterprise configuration where all clients routed to the Internet will always be filtered and protected no matter what the end users do, or change, on their machines and the added benefit of reduction in typical user’s client-proxy configuration troubleshooting.
3b. Using a so-called Proxifier
This configuration is very similar to the one at point 5a with the only difference that the Proxifier software can be set to redirect to a Proxy all the requests started by a specific process (e.g., C:\Jts\tws.exe; C:\JTS\ibgateway\XYZ\ibgateway.exe), hence instating a process level packet forwarding instead of a port level forwarding. This setup allows handling environments where different proxy servers are used for different applications or where you would like to address a specific application requirement without modifying/disrupting the connectivity schema for other software installed. The advantage of this solution is minimal maintenance since the connectivity schema is bound to the process and not to the hosts/ports.
3c. Using specific network routing on a client machine
With this setup, you can modify the client machine standard network routes, adding new ones in order to forward packets with specific destinations (e.g., Order routing and Market Data servers1) to a different gateway.
This gateway will then be in charge of routing those requests to the destination hosts. This solution has as well the benefit of not modifying/disrupting the connectivity schema for other software installed but usually requires more maintenance on the gateway and on the client machine in case the IP of the destination servers are changed or in case new servers are added.
4. If I use a Web (HTTP) Proxy server, do I need to configure the TWS / IB Gateway?
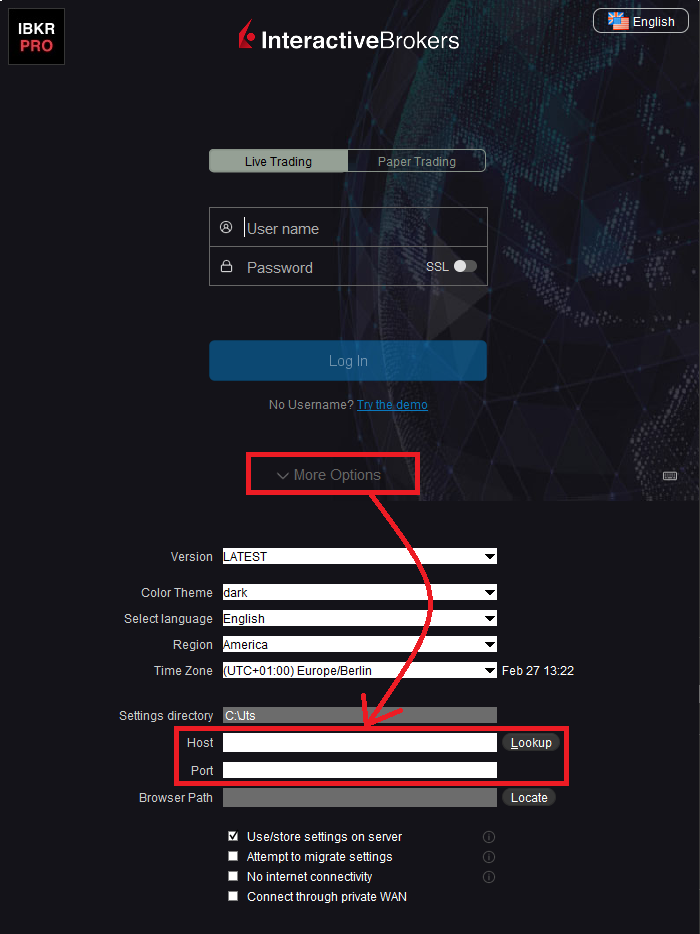
If the Workstations on your local network access the Web content through a Web (HTTP) Proxy, you need to specify the Web Proxy IP Address and port. To do this, click More Options at the bottom of the TWS Login Screen, and enter your Proxy server details in the fields Host and Port (see Figure 1 below). The same fields are present in the IB Gateway Login Screen.
Figure 1.
The Web Proxy you set there will ONLY be used to fetch the web content accessible from within the TWS (e.g., Client Portal, Statements, Product Details, etc.)
5. What alternatives do I have in case I cannot implement a proxy solution on my network?
In this case, you might orient yourself towards a different type of access to the IBKR infrastructure, which includes a special connection type and a FIX/CTCI engine setup. This setup would, on the other hand, have different requirements in terms of commissions2.
Common Issues
6. What happens if the proxy configuration on your computer is wrong or outdated?
Occasionally, third-party software, even if already uninstalled, may leave behind a SOCKS proxy configuration on your computer. This may also happen if your computer has been infected with malware. In such cases, the proxy server, although configured, is non-existent or not accessible on the network. In such scenarios, the TWS will show an error message (e.g., No Internet Connectivity) and/or start the "Connection attempt #" loop upon login. The same will happen if the Proxy server exists, but has not been correctly configured on the client machines.
6a. How can I correct the proxy configuration if wrong?
When applicable, we recommend you always consult the IT / Networking team of your company first and ask for guidance.
If you are autonomously managing your network, please follow the instructions below according to the Operating System of your machine/s:
Windows
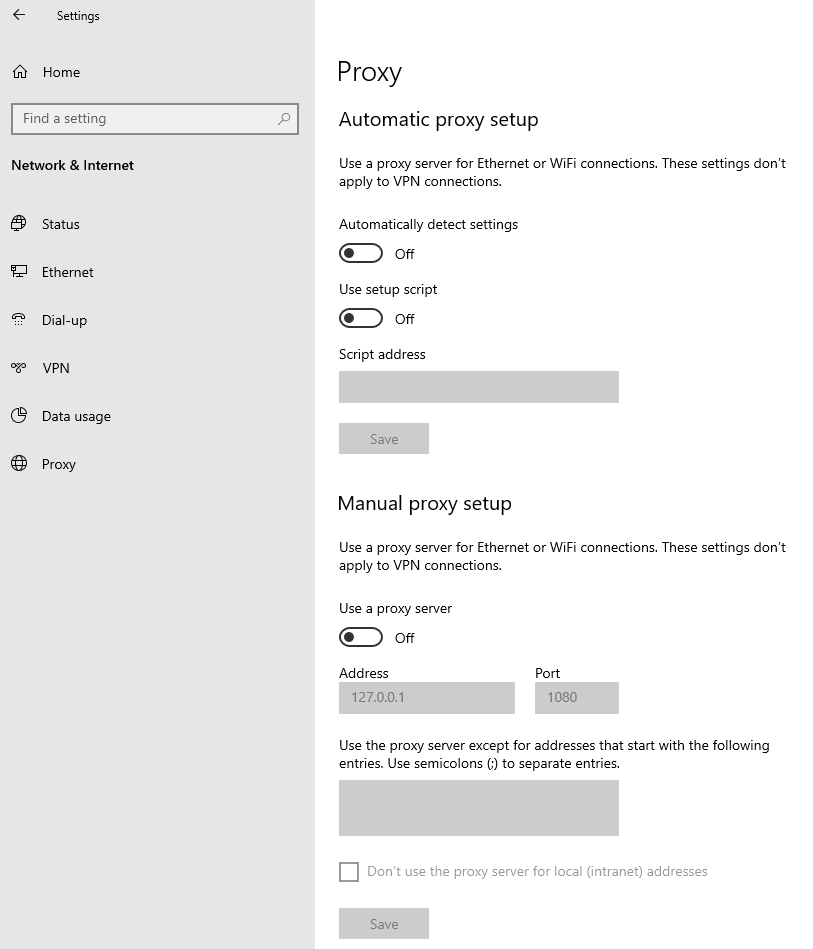
W.1 Press CTRL+S to open the Windows search
W.2 Type Proxy Settings and press Enter
W.3 If no Proxy is present on your network, make sure the switch "Use a proxy server" is deactivated (see Figure 2 below). If a Proxy server is active on your network, make sure the Address (or hostname) and Port are correctly defined.
Figure 2.
Mac
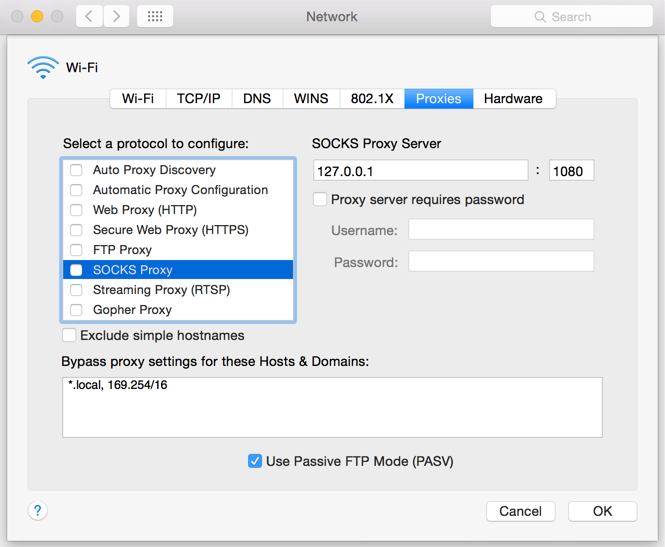
M.1 Click on the Apple icon at the top left corner of the screen and select System Preferences
M.2 Click on Network
M.3 Select the Network connection you are using to access the Internet (e.g. Wi-Fi) and click on it
M.4 Click on the Advanced button and then on the Proxies tab
5. If no proxy is present on your network, make sure all the checkboxes (SOCKS Proxy, Web Proxy, Secure Web Proxy) are deactivated (see Figure 3 below). If a Proxy is present on your network, ensure the Protocol, Address (or hostname) and Port are correct.
Figure 3.
7. You are using Public proxies and proxy chains to hide your presence or identity
There are public proxy and proxy chain services purposed to disguise or hide the identity and the activity of the subscriber or to bypass regional restrictions. One of the most famous services is the "Tor" network.
While those services may not necessarily be used for criminal purposes, they render subscriber traceability very difficult when not impossible. Since IBKR is obliged by the financial industry regulators to maintain records of trading activities and trade initiators, we do not allow our clients to reach our systems while using an anonymizing service. If you are using such a service, your TWS connection attempts will be automatically rejected by our gateways.
Technical Background
A proxy server usually acts as a gateway and as a barrier between your local network and the Internet. The proxy listens for outgoing connection requests from the internal workstation/s and forwards them to the desired target host or service on the Internet. When the target replies to such requests, the proxy routes the incoming responses back to the internal workstation/s that initiated the process.
Being the proxy, the only machine of your network actually accessing the Internet, it prevents the other machines and the internal segment of your network (LAN) from being accessible by external actors and hence from being exposed to threats and intrusion attempts.
Additionally, a proxy server can offer a variety of other services, such as web content caching and filtering.
9. Which types of Proxy servers are commonly used and where?
Proxy servers are commonly found within enterprise-grade networks. In the vast majority of cases, proxies are not used by individuals since private broadband connections are established through consumer-grade routers that already offer built-in proxy/firewall solutions. An exception is represented by public proxy or proxy chains discussed in detail in the section You are using Public proxies and proxy chains to hide your presence or identity
There are two main types of Proxy servers:
The HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) defines the rules and the standards for fetching Web content from a Web server and rendering such content on your Web Browser.
A Web Proxy handles only the routing of HTTP requests and HTTP responses. Those requests are transparently generated and sent by your browser whenever you access a Web page. Such requests are normally sent using specific ports (TCP 80 and TCP 443). Hence a Web Proxy usually listens for outgoing HTTP requests coming from your internal network (LAN) only on the TCP ports mentioned above.
SOCKS (Socket Secure) Proxies are designed to handle any type of traffic (not only HTTP/S traffic), generated by any protocol or program (including Trader Workstation).
Notes
1. More information about the servers accessed by the TWS is available in IBKB2816.
2. For an overview of the different special connection options and related requirements, please click here.
For an overview of the FIX infrastructure, please click here.
How to download and install the IBKR Mobile app from alternative app stores
As a consequence of the US Government Huawei ban, the owners of Huawei smartphones will be no longer able to access the Google Play Store and download app from there. If you are affected by this constraint, you will still be able to download and install the IBKR Mobile app from an alternative app store.
Please proceed as follows:
A) Allow your phone to install software from alternative app stores in this way:

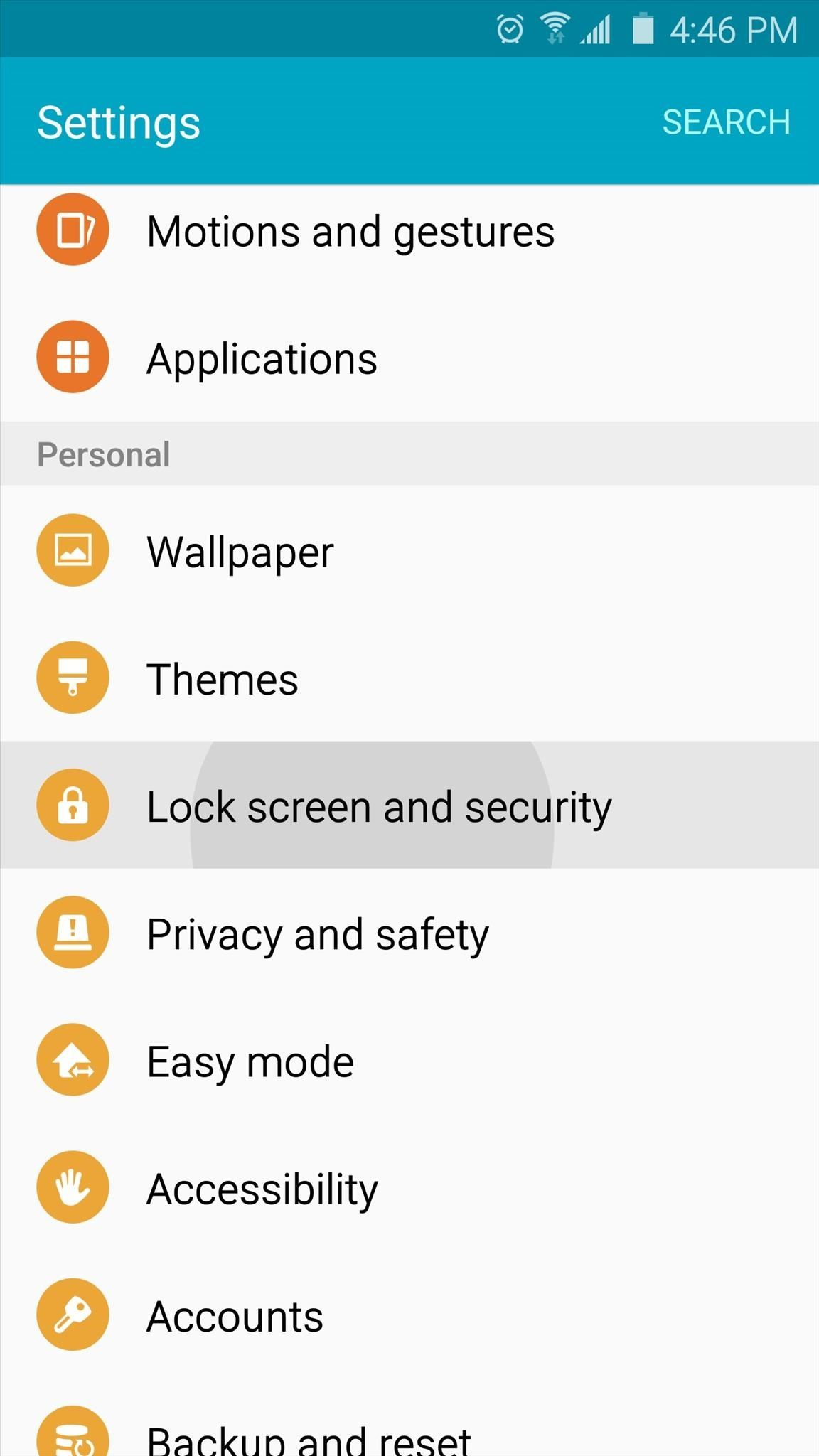
2) Under the section System you will find the item Security (it can be called Lock Screen and Security). Click on it
B) You can now download the IBKR Mobile by clicking on one of the links below, according to the alternative store you want to use:
360.cn
.png)
Baidu
Why do I receive a message stating market data is over the limit?
When you open an account with IBKR, you are initially set to receive a minimum of 100 concurrent lines of market data. This means that, either on IBKR Trading Platforms (TWS, IBKR Mobile, Client Portal trading facility) or on API/third party interface, you can simultaneously feed 100 tickers with market data. As explained here, after the first month of trading, your allowance might be increased either automatically (based on your account equity/commission) or manually (by the purchase of Quote Booster packs.)
Note: The same market data allowance is set for all the users of the same account, since it is based on account-wise parameters such as commissions and equities.
Table of contents
Why some financial instruments show question marks instead of data?
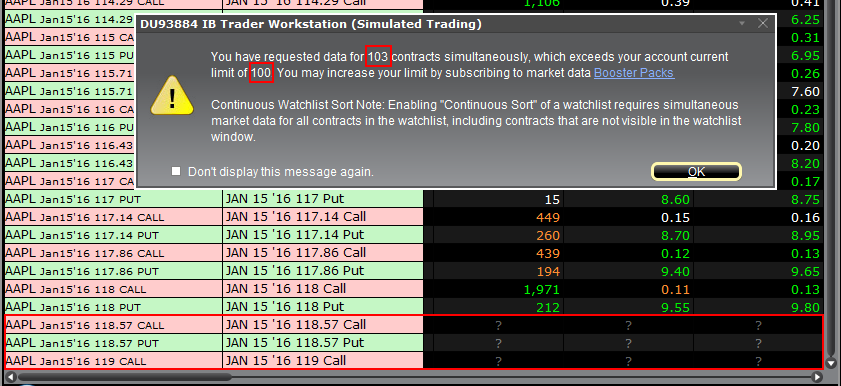
There are various functions and tools in TWS using market data: watchlists, charts, trading or analytical tools, alarms. In general, any foreground window which actively uses market data for display or for calculations, will increase the total number of market data channels currently opened. Once you have exceeded the maximum Market Data allowance for your account, you will be prevented from receiving additional market data. In this case, one or more tickers will show a "?" instead of actual quotes and your TWS will display the following warning message:
"You have requested data for XXX contracts simultaneously, which exceeds your account current limit of YYY. You may increase your limit by subscribing to market data Booster Packs."
Note: If you have decided to hide the warning by ticking the checkbox "Don't display this message again", you will not see it again next times you exceed the market data limit. Nevertheless you will still see "?" for one or more tickers instead of the actual quotes.
Where can I check the current market data allowance?
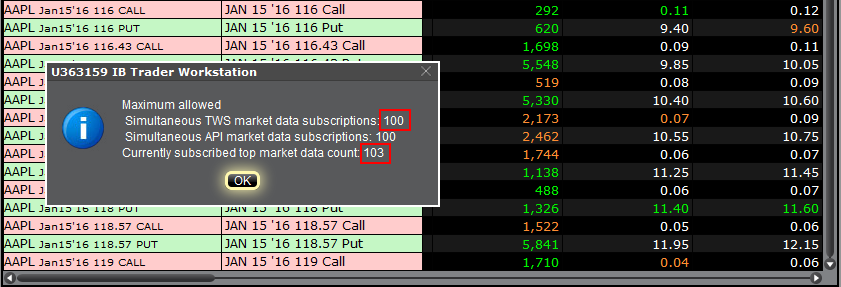
Within TWS, you can check how much of your total market data allowance you are currently consuming in the "Maximum Allowed" window. While in TWS, press the keys Ctrl + Alt + = (on a MAC click: Control + Option + =) and you will see the Maximum allowed pop-up indicating the market data allowance (the value close to "Simultaneous TWS market data subscriptions") and the market data lines currently used (the value close to "Currently subscribed top market data count".)
Which solutions are available to me?
-
Reduce the number of financial instruments displayed within your trading platform
To overcome an excessive market data usage, the easiest solution is to reduce the amount of financial instruments present within your trading platform. Here below are some ways to accomplish that:
a. Delete some tickers from your watchlist(s). There might be old tickers you are no longer interested in or there may be expired contracts. Deleting those will reduce the overall market data usage.
b. Minimize or hide one or more watchlist or other tools consuming market data. Only the TWS windows which are active and in the foreground contribute to market data count. If you have floating watchlists/charts and you minimize them or send them to the background, you will actually decrease the overall market data usage by the number of tickers present on those watchlists/charts
c. Use more restrictive filters within Option Trader / Option Chains / Strategy Builder. Those tools often become top market data consumers due to the high number of option contracts they display. All those tools provide filtering based on strike / expiry / trading class. By acting on those filters you can reduce the number of option contracts displayed
Note: Some derivatives contracts (Futures, Options, Future Options) will often consume two market data channel, one for the contract himself and one for the underlying, since the underlying contract is used for Greeks / Volatility calculations
-
Purchase Quote Booster pack(s)
Each Quote Booster pack will cost you 30 USD monthly and will entitle you to 100 additional market data lines (on the top of your current allotment). The maximum number of Quote Booster packs you can purchase for your account is 10.
How to fix the "Cannot create ... file" error during TWS installation on MacOS
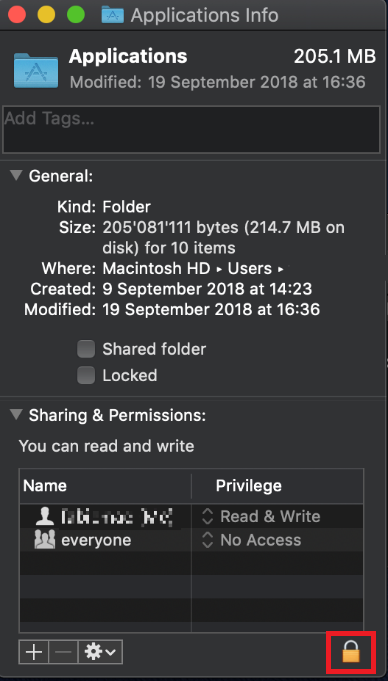
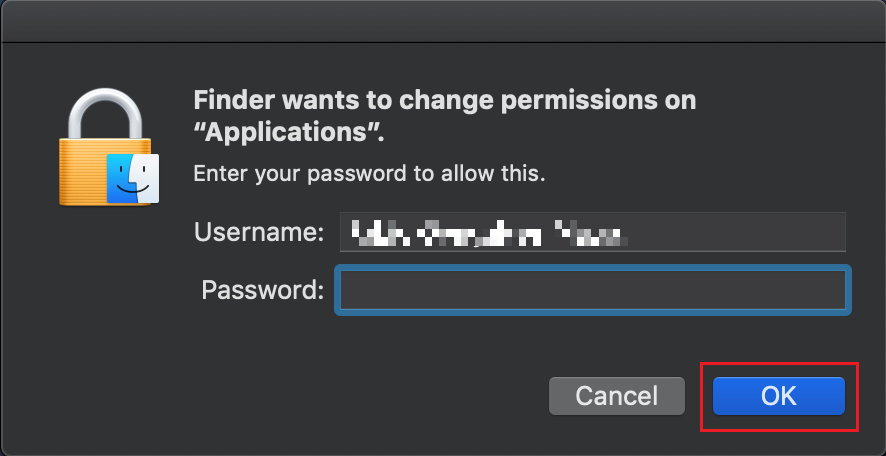
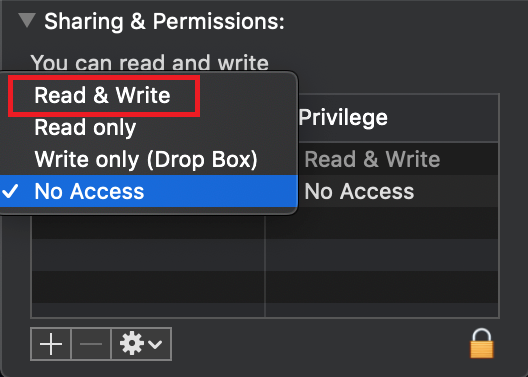
The filesystem permissions are controlled by your machines operating system. One of their functions is to secure your files, preventing unauthorized access or undesired modifications to the system and to your personal data.
Some software on your computer may modify or override the permissions assigned by the operating system. Under certain circumstances, this prevents the TWS installer from accessing the folder where the application core files have to be created (/users/youruser/home/Applications). In such cases, the TWS installation usually displays the error "Cannot create ... file. Shall I try again?"
Procedure:

.png)
.png)
.png)
7. Once the installation has completed successfully, repeat the previous steps from 1. to 5. setting back the permissions of “everyone” to “Read Only” to revert your changes to the initial status
Complex Position Size
For complex, multi-leg options positions comprising two or more legs, TWS might not track all changes to this position, e.g. a vertical spread where the short leg is assigned and the user re-writes the same leg the next day, or if the user creates a the position over multiple trades, or if the order is not filled as a native combination at the exchange.
How to overcome the "Downloading settings from server failed" error
Store settings on server allows clients the ability to store their Trader Workstation (TWS) settings/configuration on the cloud and retrieve them at anytime from another computer. This feature allows you to use the layout of a specific user on two or more machines.
In some specific circumstances, the operation which stores/downloads the settings to/from the cloud may fail and the following error message may appear shortly after the TWS has loaded on the screen:
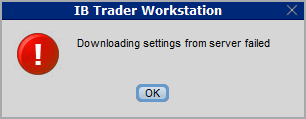
How to overcome this error message?
The underlying causes of this message are usually the following:
- ACCESS TO THE LOCAL MACHINE IS BLOCKED: A security setup, such as a firewall or antivirus, prevents the access of this computer to the cloud storage. This prevents TWS from accessing the remote server, thus disallowing the settings file upload or download. Recommended workaround: set up an exception on the firewall or antivirus in order to exclude the TWS executable file (c:\Jts\tws.exe) or the entire TWS folder (C:\Jts) from the real time security scan. The procedure to set an exclusion may vary, according to the software you are using, therefore we recommend consulting the user guide or the on-line documentation of your specific security program.
- ACCESS TO THE REMOTE SERVER IS BLOCKED: A firewall or proxy service blocks the communication with the cloud storage through the network on which this computer is. In this scenario, you (or your IT / Networking departments, in case you do not have the rights for such an operation) can modify the firewall or proxy settings to allow the computer to communicate with the cloud server s3.amazonaws.com on the TCP port 443. For additional details about the hosts/ports which needs to be allowed for the proper TWS operation, please see as well the section "DESKTOP TWS" of KB2816. Please refer to the documentation of your specific software in order to create specific rules for your firewall or proxy system.
Why is my chart delayed, showing question marks or only partially populated?
What are SMART Charts and how are they generated?
The SMART charting mechanism analyzes and compares the market data coming from all venues a given contract is traded on and graphically displays the most favorable quotes.
When all the data streams are live, the data points are available for all sources and for each time point, thus they can be fully compared. The resulting SMART chart will be up to date and fully populated, moreover it will constantly and automatically update1.
The comparison between non synchronized market data streams (some live and some delayed) is just partially possible, since the delayed feeds are lacking data points for the last 15 or 20 minutes. Therefore, within that time frame, the SMART chart will usually display a series of yellow question marks to indicate unavailability of source data. In this case the SMART Chart will not update automatically.
When the lack of data points is more extensive or when the Exchange does not distribute delayed data for a given contract, the correspondent SMART Chart may be completely blank.
What should I do to obtain a fully populated, up-to-date chart?
If your trading method is based on SMART charts, you would need to activate the live market data subscriptions for all the marketplaces your financial instruments are traded on2. For additional details, please see KB1201
If your trading method does not require SMART charts, you can decide to use Direct chart routing as a workaround.
A Directed Chart will allow you to graphically represent the market data coming from a single, specific Exchange. When possible, we suggest to select the primary marketplace for the product for this purpose, since this is usually the one offering the highest liquidity and trade volume, hence normally providing the most favorable quotes. If you have subscribed the market data for that venue, the resulting Directed Chart will be fully populated, up to date and it will update automatically1.
How do I set up a Directed Chart?
1. Within a watchlist, type the contract symbol and press Enter on your keyboard.
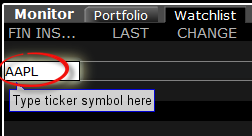
2. When then contract selection menu appears, select the item Stock (Directed). If you do not see this item, click on the small down arrow at the bottom of the menu to reveal the hidden menu items.
.png)
3. The Exchange selection screen will appear. You can now select the main Exchange for the product or the Exchange for which you have an active live market data subscription. Once done, click OK.
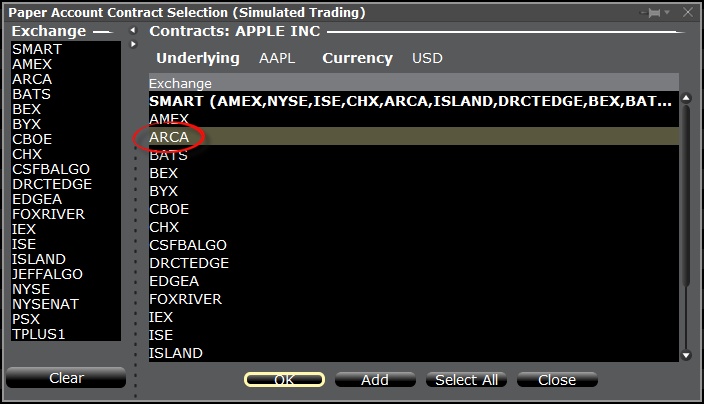
4. Within your watchlist you will see a newly created Directed Ticker line. It will contain the contract symbol and, preceded by the @ sign, the Exchange you selected at the previous step. Right click on that directed ticker line and select Chart > New Chart
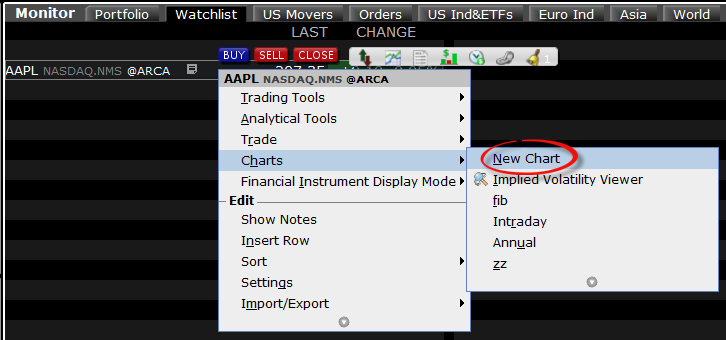
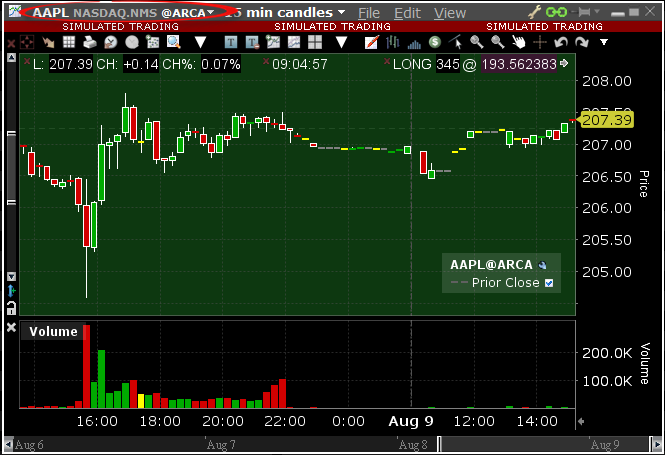
Delayed Market Data Timing
Market data vendors typically offer exchange data in two categories, real-time and delayed. Real-time market data is disseminated as soon as the information is publicly available. Delayed market data is on a time lag that is usually 10-20 minutes behind real-time quotes.
Some exchanges allow delayed data to be displayed without any market data subscription, free of charge. A list of the exchanges we provide delayed data for at no cost and without formal request (i.e., the delayed data will be displayed upon entry of the product symbol on the trading platform) are outlined in the table below. The table also includes the corresponding real-time subscription, the fees for which are posted on IBKR's public website.
Please Note:
- In accordance with regulatory requirements, IBKR no longer offers delayed quotation information on U.S. equities to Interactive Brokers LLC clients.
- Delayed quotes should be used for indicative purposes and not necessarily for trading. The times mentioned may be subject to further delays without notice.
The Americas
| External Exchange Name | IB Exchange Name | Delay Period | Real Time Subscription |
| CBOT | CBOT | 10 minutes | CBOT Real-Time |
| CBOE Futures Exchange | CFE | 10 minutes | CFE Enhanced |
| Market Data Express (MDX) | CBOE | 10 minutes | CBOE Market Data Express Indices |
| CME | CME | 10 minutes | CME Real-Time |
| COMEX | COMEX | 10 minutes | COMEX Real-Time |
| ICE US | NYBOT | 10 minutes | ICE Futures U.S. (NYBOT) |
| Mexican Derivatives Exchange | MEXDER | 15 minutes | Mexican Derivatives Exchange |
| Mexican Stock Exchange | MEXI | 20 minutes | Mexican Stock Exchange |
| Montreal Exchange | CDE | 15 minutes | Montreal Exchange |
| NYMEX | NYMEX | 10 minutes | NYMEX Real-Time |
| NYSE GIF | NYSE | 15 minutes | NYSE Global Index Feed |
| One Chicago | ONE | 10 minutes | OneChicago |
| OPRA | OPRA | 15 minutes | OPRA Top of Book (L1) (US Option Exchanges) |
| OTC Markets | PINK | 15 minutes | OTC Markets |
| Toronto Stock Exchange | TSE | 15 minutes | Toronto Stock Exchange |
| Venture Exchange | VENTURE | 15 minutes | TSX Venture Exchange |
Europe
| External Exchange Name | IB Exchange Name | Delay Period | Real Time Subscription |
| BATS Europe | BATE/CHIX | 15 minutes | European (BATS/Chi-X) Equities |
| Boerse Stuttgart | SWB | 15 minutes | Stuttgart Boerse incl. Euwax (SWB) |
| Bolsa de Madrid | BM | 15 minutes | Bolsa de Madrid |
| Borsa Italiana | BVME/IDEM | 15 minutes | Borsa Italiana (BVME stock / SEDEX / IDEM deriv) |
| Budapest Stock Exchange | BUX | 15 minutes | Budapest Stock Exchange |
| Eurex | EUREX | 15 minutes | Eurex Real-Time Information |
| Euronext | AEB/SBF/MATIF/BELFOX | 15 minutes | Euronext Cash |
| Euronext | AEB/SBF/MATIF/BELFOX | 15 minutes | Euronext Data Bundle |
| Frankfurt Stock Exchange and XETRA | FWB/IBIS/XETRA | 15 minutes | Spot Market Germany (Frankfurt/Xetra) |
| ICE Futures Europe (Commodities) | IPE | 10 minutes | ICE Futures E.U. - Commodities (IPE) |
| ICE Futures Europe (Financials) | ICEEU | 10 minutes | ICE Futures E.U. – Financials (LIFFE) |
| LSE | LSE | 15 minutes | LSE UK |
| LSEIOB | LSEIOB | 15 minutes | LSE International |
| MEFF | MEFF | 15 minutes | BME (MEFF) |
| NASDAQ OMX Nordic Derivatives | OMS | 15 minutes | Nordic Derivatives |
| Prague Stock Exchange | PRA | 15 minutes | Prague Stock Exchange Cash Market |
| SWISS Exchange | EBS/VIRTX | 15 minutes | SIX Swiss Exchange |
| Tel Aviv Stock Exchange | TASE | 15 minutes | Tel Aviv Stock Exchange |
| Turquoise ECN | TRQXCH/TRQXDE/TRQXEN | 15 minutes | Turquoise ECNs |
| Warsaw Stock Exchange | WSE | 15 minutes | Warsaw Stock Exchange |
Asia
| External Exchange Name | IB Exchange Name | Delay Period | Real Time Subscription |
| Australian Stock Exchange | ASX | 20 minutes | ASX Total |
| Hang Seng Indices | HKFE-IND | 15 minutes | Hang Seng Indexes |
| Hong Kong Futures Exchange | HKFE | 15 minutes | Hong Kong Derivatives (Fut & Opt) |
| Hong Kong Stock Exchange | SEHK | 15 minutes | Hong Kong Securities Exchange (Stocks, Warrants & Bonds) |
| Korea Stock Exchange | KSE | 20 minutes | Korea Stock Exchange |
| National Stock Exchange of India | NSE | 15 minutes | National Stock Exchange of India, Capital Market Segment |
| Osaka Securities Exchange | OSE.JPN | 20 minutes | Osaka Exchange |
| SGX Derivatives | SGX | 10 minutes | Singapore Exchange (SGX) - Derivatives |
| Shanghai Stock Exchange | SEHKNTL | 15 minutes | Shanghai Stock Exchange |
| Shanghai Stock Exchange STAR Market | SEHKSTAR | 15 minutes | Shanghai Stock Exchange |
| Shenzhen Stock Exchange | SEHKSZSE | 15 minutes | Shenzhen Stock Exchange |
| Singapore Stock Exchange | SGX | 10 minutes | Singapore Exchange (SGX) - Stocks |
| Australia Securities Exchange | ASX24 | 10 minutes | ASX24 Commodities and Futures |
| Taiwan Stock Exchange | TWSE | 20 minutes | Taiwan Stock Exchange |
| Tokyo Stock Exchange | TSEJ | 20 minutes | Tokyo Stock Exchange |
Risk Navigator: Alternative Margin Calculator
IB routinely reviews margin levels and will implement changes which serve to increase requirements above statutory minimums as market conditions warrant. To assist clients with understanding the effects of such changes on their portfolio, a feature referred to as the "Alternative Margin Calculator" is provided within the Risk Navigator application. Outlined below are the steps for creating a “what-if” portfolio for the purpose of determining the impact of such margin changes.
Step 1: Open a new “What-if” portfolio
From the Classic TWS trading platform, select the Analytical Tools, Risk Navigator, and then Open New What-If menu options (Exhibit1).
Exhibit 1
.png)
From the Mosaic TWS trading platform, select New Window, Risk Navigator, and then Open New What-If menu options.
Step 2: Define starting portfolio
A pop-up window will appear (Exhibit 2) from which you will be prompted to define whether you would like to create a hypothetical portfolio starting from your current portfolio or a newly created portfolio. Clicking on the "yes" button will serve to download existing positions to the new “What-If” portfolio.
Exhibit 2
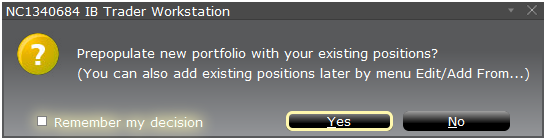
Clicking on the "No" button will open up the “What – If” Portfolio with no positions.
Risk Dashboard
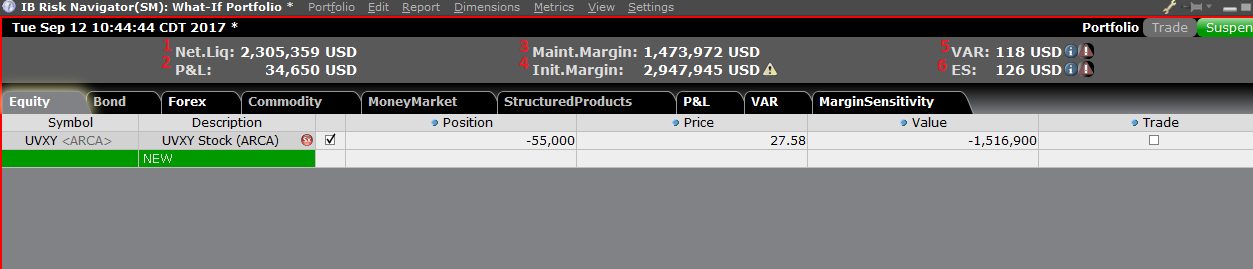
The Risk Dashboard is pinned along the top of the product tab-sets, and is and is available for what-if as well as active portfolios. The values are calculated on demand for what-if portfolios. The dashboard provides at-a-glance account information including:
1) Net Liquidation Value: The total Net Liquidation Value for the account
2) P&L: The total daily P&L for the entire portfolio
3) Maintenance Margin: Total current maintenance margin
4) Initial Margin: Total initial margin requirements
5) VAR: Shows the Value at risk for the entire portfolio
6) Expected Shortfall (ES): Expected Shortfall (average value at risk) is expected return of the portfolio in the worst case
Alternative Margin Calculator
The Alternative Margin Calculator, accessed from the Margin menu and clicking on the Margin Mode (Exhibit 3), shows how the margin change will affect the overall margin requirement, once fully implemented.
Exhibit 3
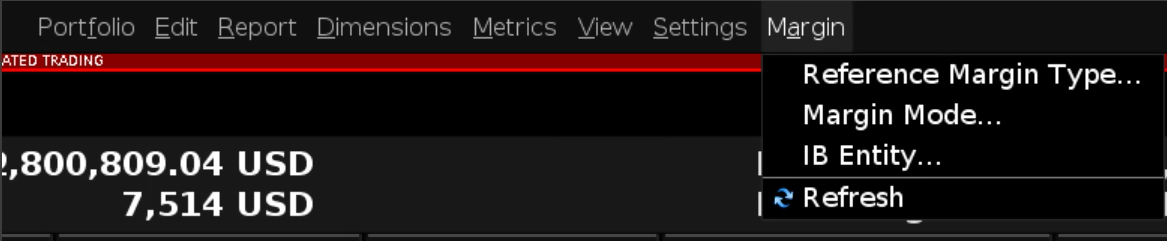
Step 3: Selecting Margin Mode Settings
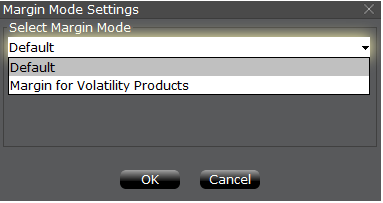
A pop-up window will appear (Exhibit 4) entitled Margin Mode Setting. You can use the drop-down menu in that window to change the margin calculations from Default (being the current policy) to the new title of the new Margin Setting (being the new margin policy). Once you have made a selection click on the OK button in that window.
Exhibit 4
Once the new margin mode setting is specified, the Risk Navigator Dashboard will automatically update to reflect your choice. You can toggle back and forth between the Margin Mode settings. Note that the current Margin Mode will be shown in the lower left hand corner of the Risk Navigator window (Exhibit 5).
Exhibit 5
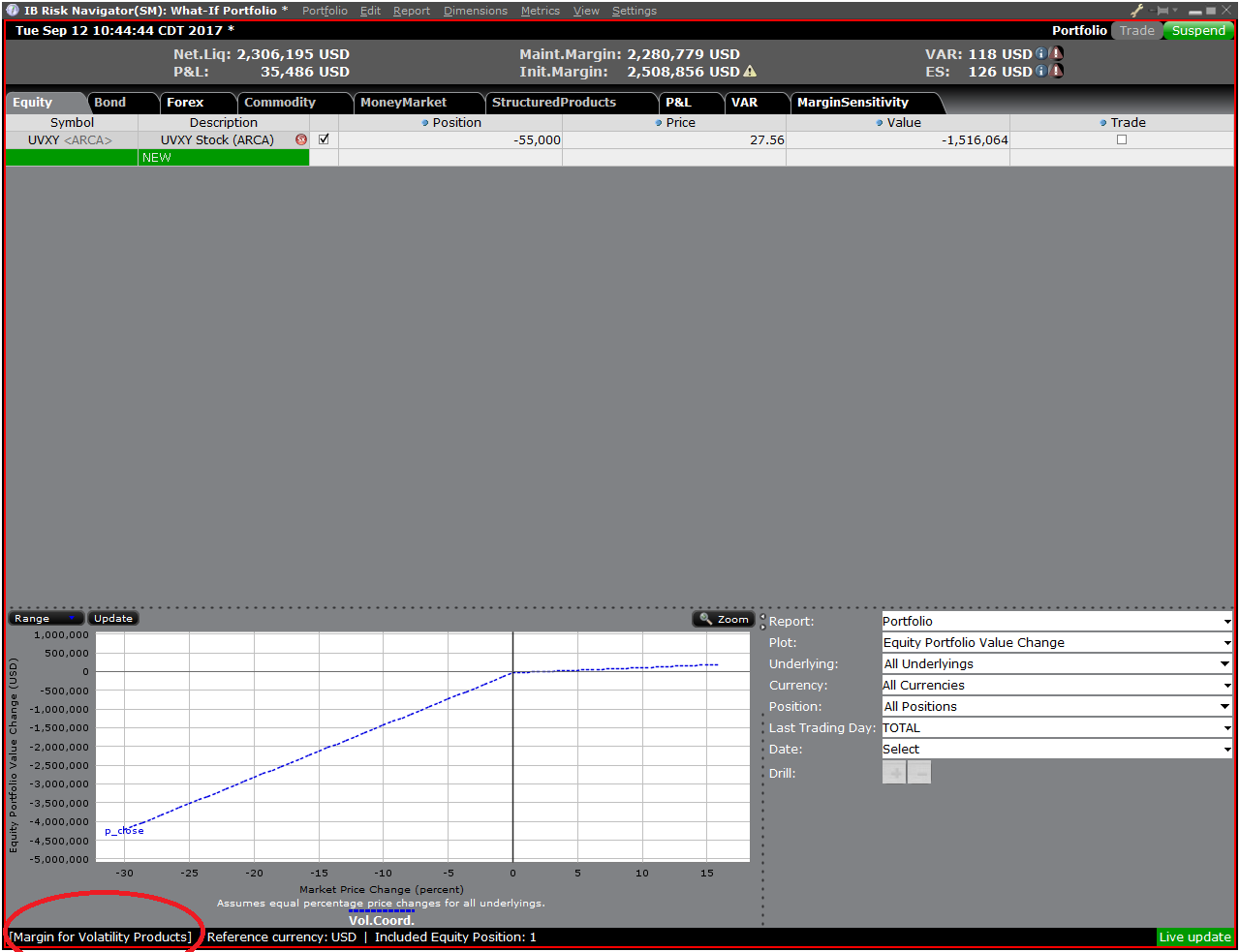
Step 4: Add Positions
To add a position to the "What - If" portfolio, click on the green row titled "New" and then enter the underlying symbol (Exhibit 6), define the product type (Exhibit 7) and enter position quantity (Exhibit 8)
Exhibit 6
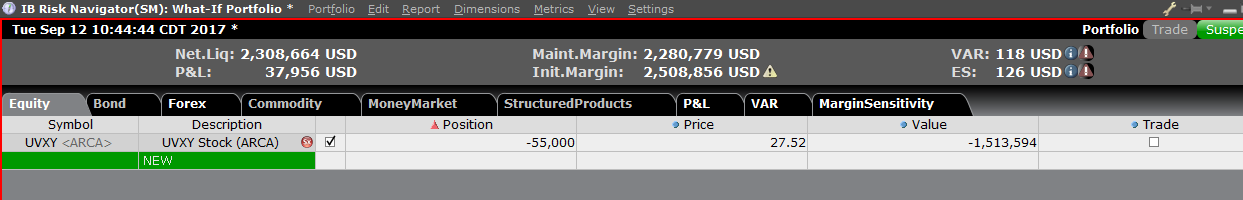
Exhibit 7
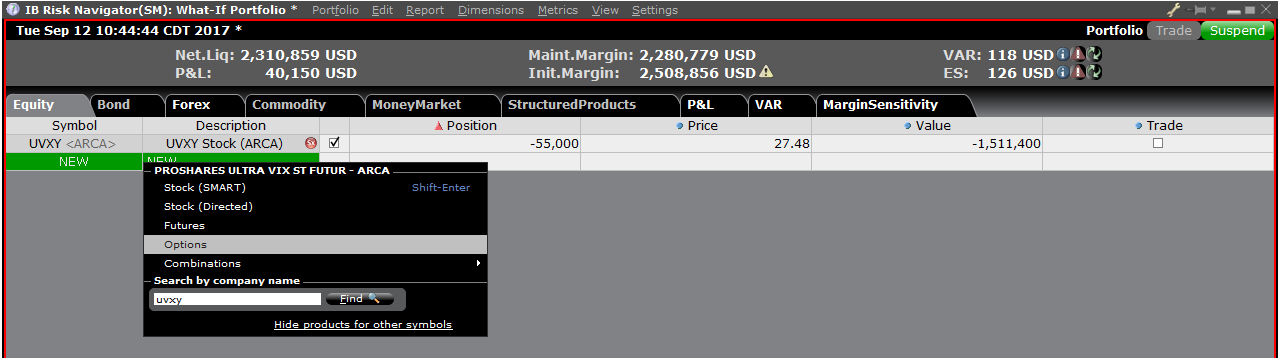
Exhibit 8
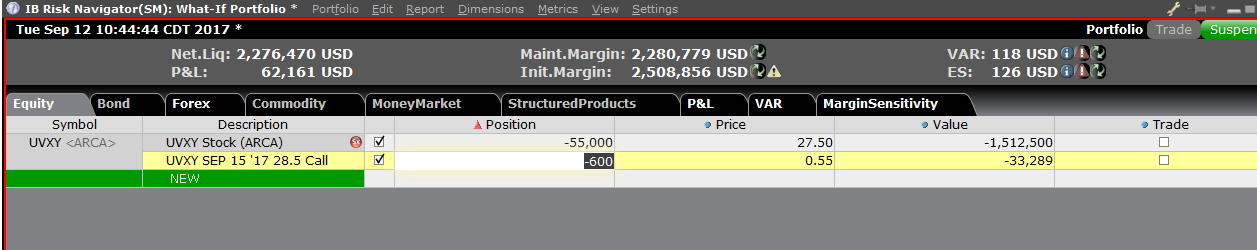
You can modify the positions to see how that changes the margin. After you altered your positions you will need to click on the recalculate icon (![]() ) to the right of the margin numbers in order to have them update. Whenever that icon is present the margin numbers are not up-to-date with the content of the What-If Portfolio.
) to the right of the margin numbers in order to have them update. Whenever that icon is present the margin numbers are not up-to-date with the content of the What-If Portfolio.