FAQs: Securities subject to Special Requirements
We are seeing unprecedented volatility in GME, AMC, BB, EXPR, KOSS and a small number of other U.S. securities that has forced us reduce the leverage previously offered to these securities and, at times, limit trading to risk reducing transactions. Outlined below are a series of FAQs relating to these actions.
Q: Are there any current restrictions on my ability to trade GME and the other US securities that have been subject to the recent heightened volatility?
A: IBKR is currently not restricting customers from trading shares of AMC, GME, BB, EXPR, KOSS or the other stocks that have been the subject of extreme market volatility. That includes orders to open new positions or close existing ones.
Like many brokers, IBKR placed limits on opening new positions in certain of these securities for a period of time. Those restrictions have since been lifted.
IBKR has not restricted customers’ ability to close existing positions and does not plan to do so.
Q: Can I use margin in trading stocks, options or other derivatives on these products through IBKR?
A: IBKR has increased its margin requirements for securities in GME and the other US securities subject to the recent volatility, including up to 100% margin required for long positions and 300% margin on the short side. You can see these margin requirements in your trading platform prior to submitting an order.
Q: Why did IBKR place these restrictions on my ability to open new positions in certain securities?
A: IBKR took these actions for risk management purposes, to protect the firm and its customers from incurring outsized losses due to wild swings in prices in a volatile and unstable marketplace.
IBKR remains concerned about the effect of this unnatural volatility on the clearinghouses, brokers and market participants.
Q: Does IBKR or its affiliates have positions in these products that it was protecting by placing these restrictions?
A: No. IBKR itself has no proprietary positions in any of the securities.
Q: What allowed IBKR to place those restrictions?
A: Pursuant to its customer agreement, IBKR may decline to accept any customer’s order at IBKR’s discretion.
IBKR also has the right to modify margin requirements for any open or new positions at any time, in its sole discretion. After all, IBKR is the one whose money is being loaned in a margin trade.
Q: Did those restrictions apply to all or just some of IBKR’s customers?
A: All restrictions – all limits on opening new positions and margin increases – applied to all IBKR customers. They were placed based on the security, not based on the customer.
Q: Is my money at IBKR at risk? Has IBKR suffered material losses?
A: IBKR did not incur substantial losses. Through its prudent risk management, IBKR has navigated this market volatility well. In any event, on a consolidated basis, IBG LLC exceeds $9 billion in equity capital, over $6 billion in excess of regulatory requirements.
Q: What will IBKR do going forward? How will I know?
A: IBKR will continue to monitor developments in the market, and will make decisions based on market conditions. For current information, please continue to visit our website.
期权到期前被行权
美式期权卖方(沽出方)在期权到期前随时可能会被行权。也就是说,期权卖方在卖出期权后到期权到期或通过买回期权将头寸平仓这段时间随时可能会被行权。看涨或看跌期权所有者在期权到期前调用其权利即为提早行权。作为期权卖方,您无法控制期权被行权,也无法知晓其会何时发生。通常,越临近到期,被行权的风险越大,但即使这样,美式期权交易仍然随时会发生被行权。
空头看跌期权
卖出看跌期权时,卖方有义务在指定时间窗口内(到期日)以约定价格(行使价)买入底层股票或资产。如果期权的行使价低于股票的当前市价,则期权持有者把股票卖给期权卖方并不会获利,因为市场价格比行使价要高。反过来,如果期权的行使价高于股票的当前市价,则期权卖方就会有被行权的风险。
空头看涨期权
卖出看涨期权后,看涨期权的所有者有权在给定时间范围内以约定价格从期权卖方买入股票。如果股票的市价低于期权的行使价,则对看涨期权持有者来说,以高于市价的价格买入股票没有任何好处。但如果股票的市价高于期权的行使价,则期权持有者可以低于市价的价格买入股票。如果期权处于价内或如果即将派息且空头看涨期权的内在价值低于股息,则空头看涨期权会有被行权风险。
期权会发生什么?
如果空头看涨期权被行权,则空头看涨期权持有者将被分配空头股票。例如,如果ABC公司的股价为$55,行使价为$50的空头看涨期权被行权,则空头看涨期权将会转换成价格为$50的空头股票。然后账户持有人可以决定以$55的价格买回股票平仓空头头寸。100股的净损失会是$500,再减去最开始卖出看涨期权时收到的权利金。
如果空头看跌期权被行权,则空头看跌期权持有者相当于是以看跌期权行使价多头持有股票。例如,XYZ的股价为$90,空头看跌期权卖方按行使价$96被分配了股票,则看跌期权卖方有责任以$96(高于市价)的价格买入股票。假设账户持有人以$90的价格平仓了多头股票头寸,那么100股的净损失会是$600,再减去最开始卖出看跌期权时收到的权利金。
期权被行权导致保证金不足
如果被行权发生在期权到期之前并且产生的股票头寸导致保证金不足,则根据我们的保证金政策,账户将面临自动平仓清算以重新满足保证金要求。平仓清算并不只限于期权被行权产生的股票头寸。
此外,对于期权价差的空头边被行权的账户,IBKR不会将其持有的多头期权行权。IBKR无法推测多头期权持有者的意图,并且在到期前行使多头期权将导致放弃期权的时间价值(时间价值通过卖出期权实现)。
到期后风险敞口、公司行动和除息
盈透证券会根据到期时间或公司行动相关事件采取积极措施降低风险。有关我们到期政策的更多信息,请阅读知识库文章“到期&公司行动相关清算”。
账户持有人应参阅“标准期权的特征与风险”披露文件,IBKR在账户申请时便向所有有期权交易资格的客户提供了此文件,其中明确说明了被行权风险。此文件还可在期权清算公司(OCC)网站上查看。
Risk Based Margin Considerations
| LLC Risk Based (i.e. Portfolio Margin) | Non-LLC Risk Based Margin | |
| $110,000 initial value requirement | Yes | N/A |
| Minimum equity to operate on margin | USD 100,000 | IB-HK: USD 2,000 IB-AU: AUD 2,000 IB-LUX, IB-IE and IB-CE: EUR 2,000 IB-SG: SGD 2,000 |
| Full options trading approval | Yes | N/A |
| PDT | Yes | N/A |
| Stress testing | Yes | Yes |
| Dynamic House Scanning Charges (TOMS) ¹ | Yes | Yes |
| Shifts in option Implied Volatility (IV) | Yes | Yes |
| A $0.375 multiplied by the index per contract minimum is computed (Only applied to Portfolio Margin eligble products) | Yes | Yes |
| Initial margin will be 110% of Maintenance Margin (US securities only) | Yes | Yes |
| Initial margin will be 125% of Maintenance Margin (Non-US securities) | Yes | Yes |
| Extreme Price Scans | Yes | Yes |
| Large Position Charge (A position which is 1% or more of shares outstanding) | Yes | Yes |
| Days to Liquidate (A large position in relation to the average daily trading volume, which may result in higher initial margin requirements) | Yes | Yes |
| Global Concentration Charge (2 riskiest position stressed +/-30% remaining assets +/-5%) | Yes | Yes |
| Singleton Margin Method for Small Cap Stocks (Stress Test which simulates a price change reflective of a $500 million USD in market capitalization)² | Yes | Yes |
| Singleton Margin Method for stocks domiciled in China (Stress Test which simulates a price change reflective of a $1.5 billion USD in market capitalization)² | Yes | Yes |
| Default Singleton Margin Method (Stress Test which simulates a price change +30% and down -25%)² | Yes | Yes |
| Singleton Margin Method for HK Real Estate Stocks (Stress test +/-50%)² | Yes | Yes |
1 Dynamic House Scanning Charges are available only on select exchanges (Asian Exchanges and MEXDER)
2 IBKR will calculate the potential loss for each stock and its derivates by subjecting them to a stress test. The requirement for the stock (and its derivatives) which projects the greatest loss in the above scenario will be compared to what would otherwise be the aggregate portfolio margin requirement, and the greater of the two will be the margin requirement for the portfolio
风险漫游:替代保证金计算器
概述:
随着市场条件的变化,IB会经常评估保证金水平并根据需要在法定最低保证金要求的基础上
提高保证金要求。为帮助客户了解此类保证金变动对其投资组合的影响,我们在“风险漫游”
应用中提供了一个被称为“替代保证金计算器”的功能。下文列出了创建“假设情境”投资
组合的步骤,用以评估保证金调整带来的影响。
第一步:打开全新的“假设情境”投资组合
在标准模式TWS 交易平台内,依次选择“分析工具(Analytical Tools)”、“风险漫游(Risk
Navigator)”和“打开新的假设情境(Open New What-If)”菜单选项(见图1)。
图1
.png)
在魔方模式TWS交易平台下,依次选择“新窗口(New Window)”、“风险漫游(Risk Navigator)”
和“打开新的假设情境(Open New What-If)”菜单选项。
第二步:定义起始投资组合
跳出的弹出窗口(图2)会询问您是想用您当前的投资组合来创建假设投资组合还是重新创
建一个投资组合。点击“是”将把已有的头寸下载至新的“假设情境”投资组合。.
图2
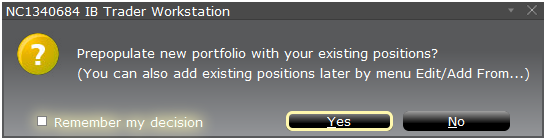
点击“否”将打开一个没有头寸的“假设情境”投资组合。
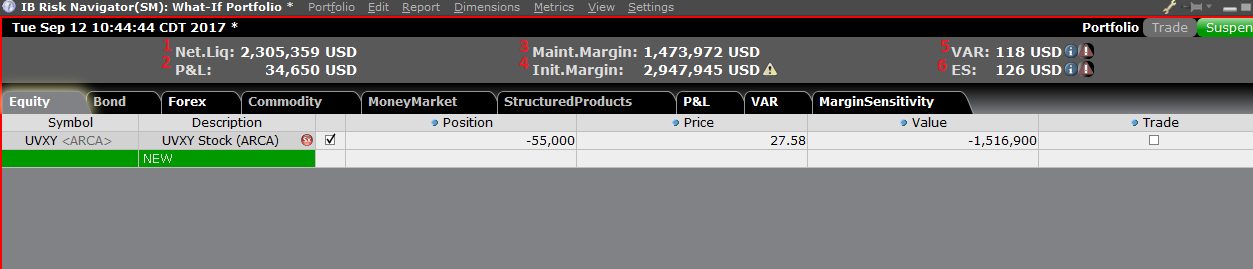
风险控制面板
“风险控制面板”位于产品标签组的顶部,“假设情境”投资组合和真实的活跃投资组合均
可使用。“假设情境”投资组合可按需计算各类数值。用户可通过该控制面板一目了然地查
看以下账户信息:
1) 净清算价值:账户的总净清算价值
2) 盈亏:整个投资组合的每日总盈亏
3) 维持保证金:当前总的维持保证金
4) 初始保证金:总的初始保证金要求
5) 风险价值(VAR):整个投资组合的风险价值
6) 预期亏损(ES):预期亏损(平均风险价值)是投资组合在最差的情境下的预期回报
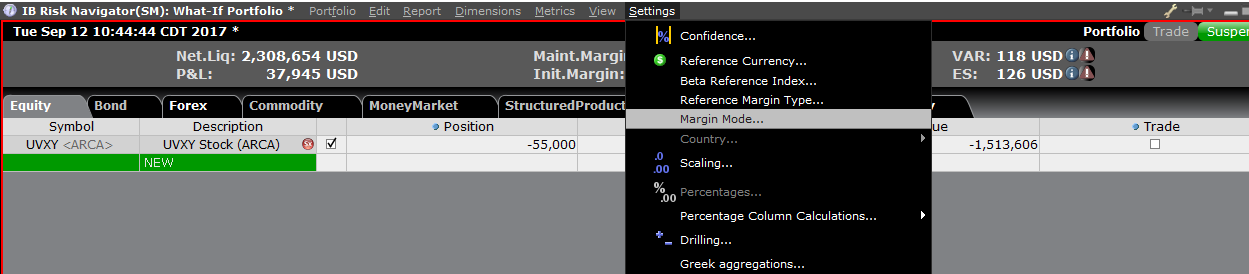
替代保证金计算器
在“设置(Setting)”菜单下点击“保证金模式(Margin Mode)”(图3)可打开替代保证金
计算器。该工具会显示当保证金调整被完全实施后投资组合的保证金要求会发生什么变化。
图3
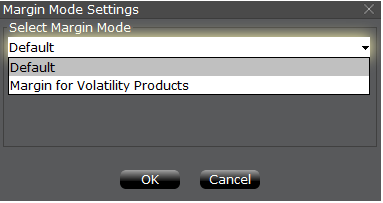
第三步:选择保证金模式设置
出现一个名为“保证金模式设置”的弹出窗口(图4)。您可使用该窗口中的下拉菜单将保
证金计算方式从“默认”(即当前政策)变更为新标题的保证金设置(即新的保证金政策)。
选择完毕后点击窗口中的“确定”按钮。
图4
设置好新的保证金模式后,风险漫游控制面板会自动更新以反映您的选择。您可在新旧保证
金模式设置中切换。注意,当前的保证金模式会在“风险漫游”窗口的左下角显示(图5)。
图5
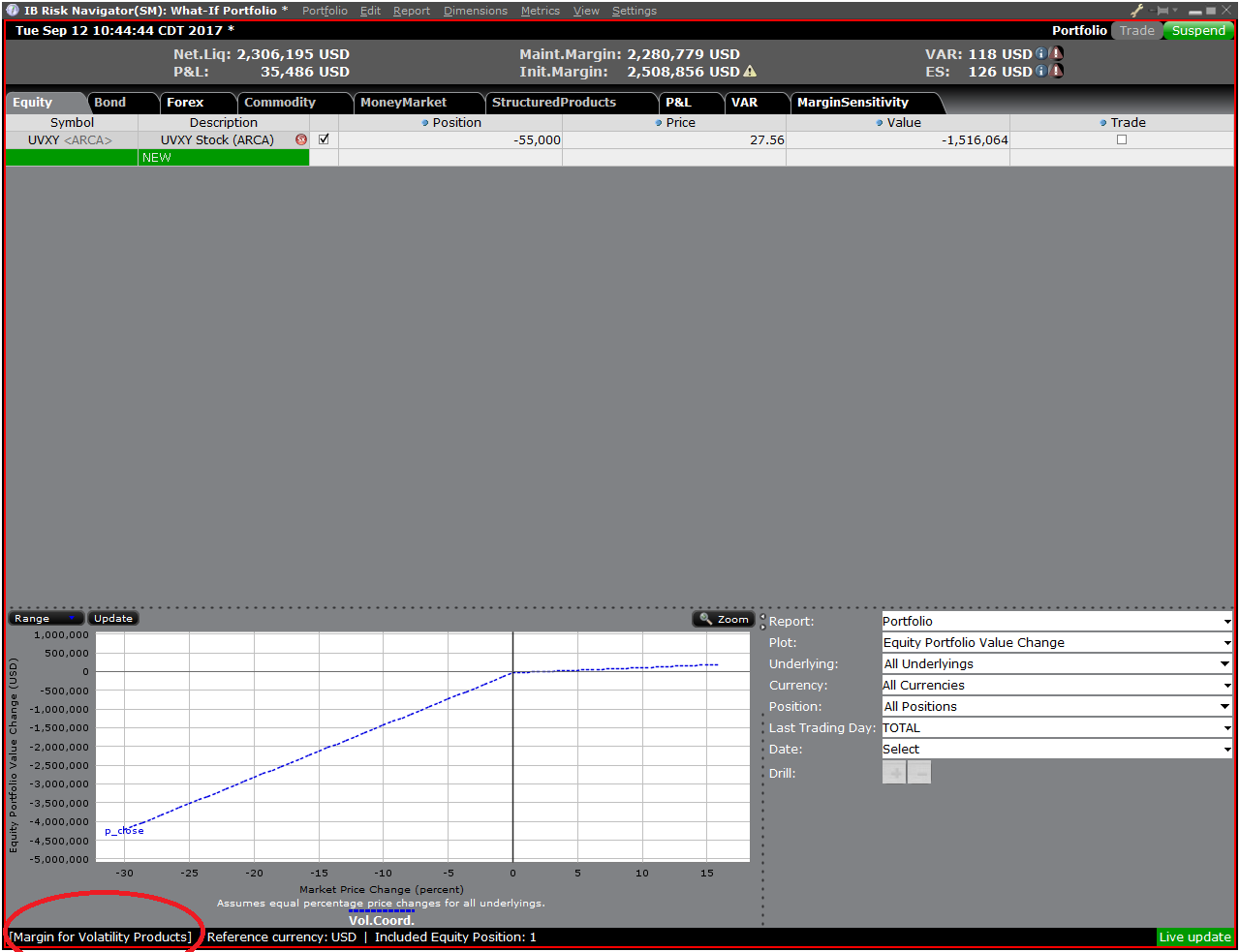
第四步:添加头寸
要在“假设情境”投资组合中添加头寸,点击标题叫“新”的绿色行,然后依次输入底层产
品的代码(图6)、选择产品类型(图7)及输入头寸数量(图8)
图6
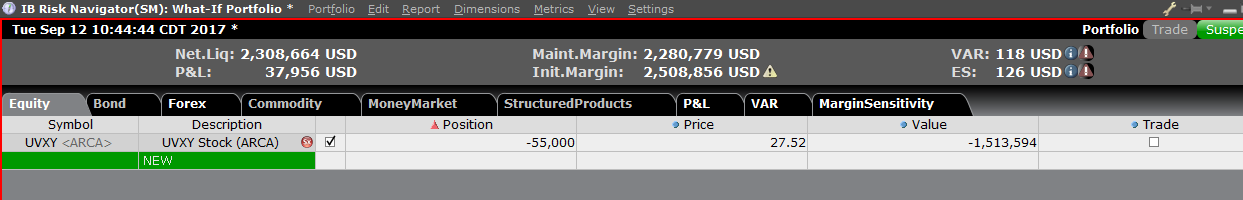
图7
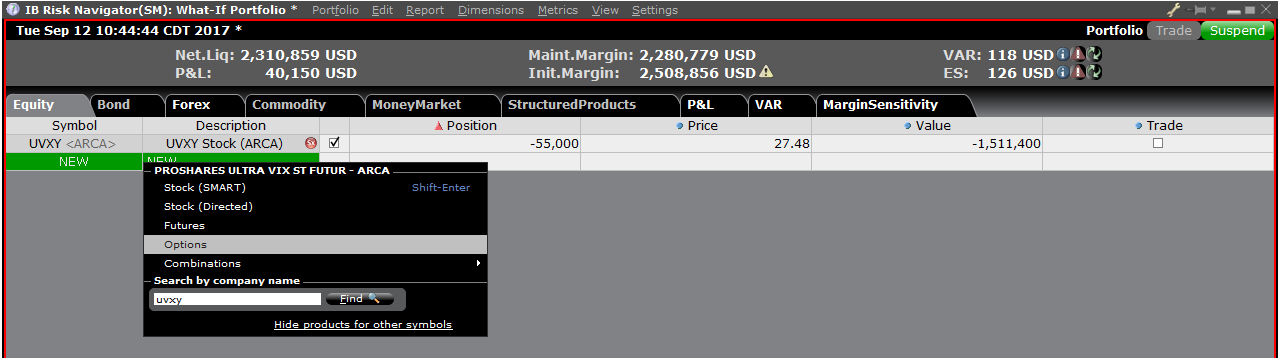
图8
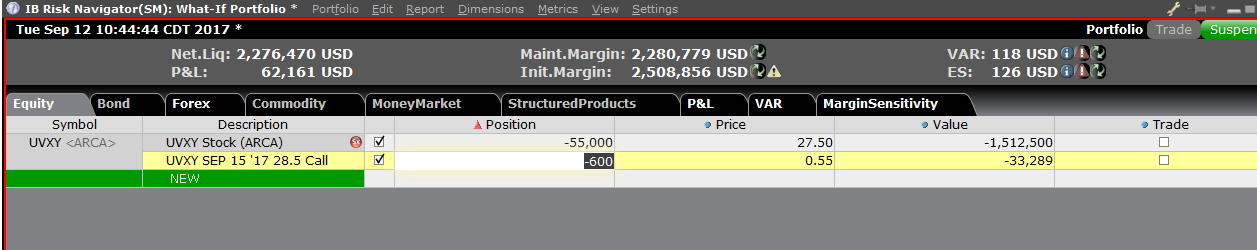
您可修改头寸以查看保证金会发生什么变化。在您修改了头寸后,您需要点击保证金数字右
边重新计算的图标 (![]() ) 以更新数值。只要出现了该图标就表明保证金数据没有根据“假
) 以更新数值。只要出现了该图标就表明保证金数据没有根据“假
设情境”投资组合的内容更新至最新。
2020年美国大选保证金增加
考虑到即将发生的美国总统选举带来的潜在市场波动,盈透证券将针对所有在美国交易的股
指期货、衍生品及在大阪证券交易所(OSE.JPN)上市的道琼斯期货提高保证金要求。
客户如持有美国股指期货及其衍生品及/或在大阪证券交易所上市的道琼斯期货头寸,请知
悉,保证金要求预计将在正常水平上提高35%左右。保证金要求将在20 个自然日内逐步提
高,其中维持保证金将从2020年10月5日起提高,直至2020年10月30日。
下表列举了一些常见产品预计发生的保证金变动
| 期货代码 | 描述 | 上市交易所 | 交易类型 | 当前比例(价 格扫描范围) * |
预计比例(价 格扫描范围) |
| ES | E-mini S&P 500 | GLOBEX | ES | 7.13 | 9.63 |
| YM | Mini DJIA | ECBOT | YM | 6.14 | 8.29 |
| RTY | Russell 2000 | GLOBEX | RTY | 6.79 | 9.27 |
| NQ | NASDAQ E-mini | GLOBEX | NQ | 6.57 | 8.87 |
| DJIA | OSE 道琼斯 工业平均 |
OSE.JPN | DJIA | 5.14 | 6.94 |
*截至2020年10月2日开市。
注:IBKR 的风险漫游工具能帮助您评估最新的维持保证金要求对您现有的投资组合或您想
构建或测试的其它投资组合有何影响。有关“替代保证金计算器”的更多信息,请见知识库
文章2957:风险漫游:替代保证金计算器,并在风险漫游的保证金模式设置下选择“美国
大选保证金”。
Normal 0 21 false false false DE-CH X-NONE X-NONE
U.S. 2020 Election Margin Increase
In light of the potential market volatility associated with the upcoming United States presidential election, Interactive Brokers will implement an increase in the margin requirement for all U.S. traded equity index futures and derivatives and Dow Jones Futures listed on the OSE.JPN exchange.
Clients holding a position in a U.S. equity index future and their derivatives and/or Down Jones Futures listed on the OSE.JPN exchange should expect the margin requirement to increase by approximately 35% above the normal margin requirement. The increase is scheduled to be implemented gradually over a 20-calendar day period with the maintenance margin increase starting on October 5, 2020 through October 30, 2020.
The table below provides examples of the margin increases projected for some of the more widely held products
| Future Symbol |
Description | Listing Exchange | Trading Class | Current Rate (Price scan range)* | Projected Rate (Price scan range) |
| ES | E-mini S&P 500 | CME | ES | 7.13 | 9.63 |
| YM | MINI DJIA | CBOT | YM | 6.14 | 8.29 |
| RTY | Russell 2000 | CME | RTY | 6.79 | 9.17 |
| NQ | NASDAQ E-MINI | CME | NQ | 6.57 | 8.87 |
| DJIA | OSE Dow Jones Industrial Average | OSE.JPN | DJIA | 5.14 | 6.94 |
*As of 10/2/20 open.
NOTE: IBKR's Risk Navigator can help you determine the impact the new maintenance margin requirements will have on your current portfolio or any other portfolio you would like to construct or test. For more information about the Alternative Margin Calculator feature, please see KB Article 2957: Risk Navigator: Alternative Margin Calculator and from the margin mode setting in Risk Navigator, select " US Election Margin".
Overview of Central Bank of Ireland CFD Rules Implementation for Retail Clients at IBIE
|
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 61% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with IBKR. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money. |
The Central Bank of Ireland (CBI) enacted new rules applicable to retail clients trading CFDs, effective 1st August 2019. Professional clients are unaffected.
The rules consist of: 1) leverage limits; 2) a margin close out rule on a per account basis; 3) negative balance protection on a per account basis; 4) a restriction on the incentives offered to trade CFDs; and 5) a standardized risk warning.
Most clients (excepting regulated entities) are initially categorised as Retail Clients. IBKR may in certain circumstances agree to reclassify a Retail Client as a Professional Client, or a Professional Client as a Retail Client. Please see MiFID Categorisation for further detail.
The following sections detail how IBKR has implemented the CBI Decision.
1 Leverage Limits
1.1 Margins
Leverage limits were set by CBI at different levels depending on the underlying:
- 3.33% for major currency pairs; Major currency pairs are any combination of USD; CAD; EUR; GBP; CHF; JPY
- 5% for:
- Non-major currency pairs are any combination that includes a currency not listed above, e.g., USD.CNH
- Major indices are IBUS500; IBUS30; IBUST100; IBGB100; IBDE40; IBEU50; IBFR40; IBJP225; IBAU200
- Gold
- 10% for non-major equity indices; IBES35; IBCH20; IBNL25; IBHK50
- 20% for individual equities
1.2 Applied Margins - Standard Requirement
In addition to the CBI Margins, IBKR establishes its own margin requirements (IB Margins) based on the historical volatility of the underlying, and other factors. We will apply the IB Margins if they are higher than those prescribed by CBI .
Details of applicable IB and CBI margins can be found here.
1.2.1 Applied Margins - Concentration Minimum
A concentration charge is applied if your portfolio consists of a small number of CFD and/or Stock positions, or if the three largest positions have a dominant weight. We stress the portfolio by applying a 30% adverse move on the three largest positions and a 5% adverse move on the remaining positions. The total loss is applied as the maintenance margin requirement if it is greater than the standard requirement for the combined Stock and CFD positions. Note that the concentration charge is the only instance where CFD and Stock positions are margined together.
1.3 Funding of Initial Margin Requirements
You can only use cash to post initial margin to open a CFD position.
Initially all cash used to fund the account is available for CFD trading. Any initial margin requirements for other instruments and cash used to purchase cash stock reduce the available cash. If your cash stock purchases have created a margin loan, no funds are available for CFD trades even if your account has significant equity. We cannot increase a margin loan to fund CFD margin under the CBI rules.
Realized CFD profits are included in cash and are available immediately; the cash does not have to settle first. Unrealized profits however cannot be used to meet initial margin requirements.
2 Margin Close Out Rule
2.1 Maintenance Margin Calculations & Liquidations
The CBI requires IBKR to liquidate CFD positions latest when qualifying equity falls below 50% of the initial margin posted to open the positions. IBKR may close out positions sooner if our risk view is more conservative. Qualifying equity for this purpose includes CFD cash and unrealized CFD P&L (positive and negative). Note that CFD cash excludes cash supporting margin requirements for other instruments.
The basis for the calculation is the initial margin posted at the time of opening a CFD position. In other words, and unlike margin calculations applicable to non-CFD positions, the initial margin amount does not change when the value of the open position changes.
2.1.1 Example
You have EUR 2000 cash in your account and no open positions. You want to buy 100 CFDs of XYZ at a limit price of EUR 100. You are first filled 50 CFDs and then the remaining 50. Your available cash reduces as your trades are filled:
|
|
Cash |
Equity* |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Pre Trade |
2000 |
2000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2000 |
|
|
Post Trade 1 |
2000 |
2000 |
50 |
100 |
5000 |
0 |
1000 |
500 |
1000 |
No |
|
Post Trade 2 |
2000 |
2000 |
100 |
100 |
10000 |
0 |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
No |
*Equity equals Cash plus Unrealized P&L
The price increases to 110. Your equity is now 3000, but you cannot open additional positions because your available cash is still 0, and under the CBI rules IM and MM remain unchanged:
|
|
Cash |
Equity |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Change |
2000 |
3000 |
100 |
110 |
11000 |
1000 |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
No |
The price then drops to 95. Your equity declines to 1500 but there is no margin violation since it is still greater than the 1000 requirement:
|
|
Cash |
Equity |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Change |
2000 |
1500 |
100 |
95 |
9500 |
(500) |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
No |
The price falls further to 85, causing a margin violation and triggering a liquidation:
|
|
Cash |
Equity |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Change |
2000 |
500 |
100 |
85 |
8500 |
(1500) |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
Yes |
3 Negative Equity Protection
The CBI Decision limits your CFD-related liability to the funds dedicated to CFD-trading. Other financial instruments (e.g., shares or futures) cannot be liquidated to satisfy a CFD margin-deficit.*
Therefore, non-CFD assets are not part of your capital at risk for CFD trading.
Should you lose more than the cash dedicated to CFD trading, IB must write off the loss.
As Negative Equity Protection represents additional risk to IBKR, we will charge retail investors an additional financing spread of 1% for CFD positions held overnight. You can find detailed CFD financing rates here.
*Although we cannot liquidate non-CFD positions to cover a CFD deficit, we can liquidate CFD positions to cover a non-CFD deficit.
IB LLC大宗商品账户保证金要求
引言
作为一家在19个国家或地区提供期货交易的全球性经纪商,IB受多种监管要求的约束,某些监管要求仍保留了在日末计算一次保证金的概念,而IB的保证金是连续、实时计算的。为满足大宗商品监管要求并以务实的方式控制经济风险,我们会在收盘时应用两种保证金计算方式,两种方式计算得出的保证金要求须同时满足。两种方式的概述如下。
概述
所有定单在执行前均须满足初始保证金要求,执行后则须始终满足维持保证金要求。由于某些产品的日中保证金可能会低于交易所要求的最低保证金比例,为确保日末能满足保证金要求,IB通常会在休市前清算头寸,而不是要求客户追加保证金。然而,如果账户在休市时仍不满足保证金要求,我们会通知客户追加保证金,同时仅允许客户做减少占用保证金的交易,如在之后的第三个工作日休时仍不能满足最初的要求,则头寸将被清算。
在确定是否需追加保证金时,IB会应用实时计算和监管计算这两种方式,而某些情况下,这两种方法得出的结果可能不同:
实时:在本方法下,初始保证金是用同一个时间点收集的头寸和价格计算的,不考虑产品所在的交易所及正式的休市时间;鉴于大部分交易所的交易时间均接近连续,我们认为本方法有其适用性。
监管:在本方法下,初始保证金是用各家交易所常规交易时间终止时收集的头寸和价格计算的。比如,对于交易香港交易所、EUREX和CME期货产品的客户,保证金要求将根据各家交易所休市时的信息计算。
影响
交易单一时段、单一国家或地区的期货的客户不受影响。在某个交易所的常规交易时段及盘后交易时段交易、或在不同国家或地区的交易所(这些交易所的休市时间不同)交易的客户更可能受影响。比如,一个客户在香港常规交易时段开仓期货合约并在美国交易时段平仓,则保证金要求只取决于开仓时的头寸。在新的计算方式下,这种交易将适用不同的保证金要求,甚至产生在当前方法下不存在的追加保证金。下表举例说明了该情况。
举例
本例试图说明,如果一个同时在亚洲和美国两个时区交易期货的客户在延长的交易时段(即在常规交易时段以外、该日已正式休市时)交易时会如何受影响。本例中,客户在香港常规交易时段开仓,并在延长的交易时段内平仓,进而腾出资金在美国常规交易时段开仓。为说明起见,假设交易损失了1,000美元。本例说明,监管的日末保证金计算方法可能不能识别在正式休市后进行的会占用保证金的交易,因此产生了追加初始保证金的要求。
| 天数 | 时间(美东) | 事件 |
初始头寸 |
结束头寸 | IB保证金 | 监管保证金 | |||
| 含贷款的净资产 | 维持 | 初始 | 隔夜 | 追加保证金 | |||||
| 1 | 22:00 | 买1份 HHI.HK | 无 | 1份HHI.HK多头 | $10,000 | $3,594 | $4,493 | 不适用 | 不适用 |
| 2 | 04:30 | 香港交易所正式休市 | 1份HHI.HK多头 | 1份HHI.HK多头 | $10,000 | $7,942 | $9,927 | $4,493 | 不适用 |
| 2 | 08:00 | 卖1份HHI.HK | 1份HHI.HK多头 | 无 | $9,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | 不适用 |
| 2 | 10:00 | 买1份ES | 无 | 1份ES多头 | $9,000 | $2,942 | $3,677 | 不适用 | 不适用 |
| 2 | 17:00 | 美国交易所正式休市 | 1份ES多头 | 1份ES多头 | $9,000 | $5,884 | $7,355 | $9,993 | 是 |
| 3 | 17:00 | 美国交易所正式休市 | 1份ES多头 | 1份ES多头 | $9,000 | $5,884 | $7,355 | $5,500 | 否 |
Margin Considerations for Intramarket Futures Spreads
Background
Clients who simultaneously hold both long and short positions of a given futures contract having different delivery months are often provided a spread margin rate that is less than the margin requirement for each position if considered separately. However, as the settlement prices of each contract may deviate significantly as the front month contract approaches its close out date, IBKR will reduce the benefit of the spread margin rate to reflect the risk of this price deviation.
Spread Margin Adjustment
This reduction is accomplished by effectively decoupling or breaking the spread in phases on each of the 3 business days preceding the close out date of the front contract month, as follows:
- On the 3rd business day prior to close out, the initial and maintenance margin requirements will be equal to 10% of their respective requirements on each contract month as if there was no spread, plus 90% of the spread requirement;
- On the 2nd business day prior to close out, the initial and maintenance margin requirements will be equal to 20% of their respective requirements on each contract month as if there was no spread, plus 80% of the spread requirement;
- On the business day prior to close out, the initial and maintenance margin requirements will be equal to 30% of their respective requirements on each contract month as if there was no spread, plus 70% of the spread requirement.
Working Example
Assume a hypothetical futures contract XYZ with the margin requirements as outlined in the table below:
| XYZ | Front Month - 1 Short Contract (Uncovered) | Back Month - 1 Long Contract (Uncovered) | Spread - 1 Short Front Month vs. 1 Long Back Month |
| Initial Margin | $1,250 | $1,500 | $500 |
| Maintenance Margin | $1,000 | $1,200 | $400 |
Further assume a position consisting of 1 short front month contract and 1 long back month contract with the front month contract close out date = T. using this hypothetical example, the initial margin requirement over the 3 business day period preceding close out date is outlined in the table below:
| Day | Initial Margin Requirement | Calculation Details |
| T-4 | $500 | Unadjusted |
| T-3 | $725 | .1($1,250 + $1,500) + .9($500) |
| T-2 | $950 | .2($1,250 + $1,500) + .8($500) |
| T-1 | $1,175 | .3($1,250 + $1,500) + .7($500) |
| T | $1,175 | Positions not in compliance with close out requirements are subject to liquidation. |
