Hogyan kell kiszámítani a határidős és határidős opciós ügyletek fedezeti követelményét?
A határidős opciós és fedezeti ügyleteket a tőzsde szabályozza egy SPAN fedezetszámítás nevű algoritmus útján. A SPAN-nel és annak működésével kapcsolatos további információkért kérjük, látogasson el a CME csoport tőzsdei weboldalára, www.cmegroup.com. Ha a weboldalon rákeres a SPAN kifejezésre, részletes információkat kaphat az algoritmusról és annak működéséről. A Sztenderd Kockázati Portfólióelemzés („Standard Portfolio Analysis of Risk”) rendszer egy rendkívül kifinomult módszertan, amely lényegében bármely piaci helyzet „mi történne ha” forgatókönyveinek elemzésével számítja ki a teljesítési biztosítékokra vonatkozó követelményeket.
Lényegében így működik a SPAN:
A SPAN egy származékos és fizikai instrumentumokból álló portfólión egységnyi idő (jellemzően egy kereskedési nap) alatt potenciálisan bekövetkező lehető legnagyobb veszteség kiszámításával értékeli a portfólió általános kockázatát. Ennek során a rendszer kiszámítja, hogy különböző piaci feltételek mellett mennyi lehetne a portfólión realizált nyereség/veszteség. A módszertan középpontjában a SPAN kockázati mátrix áll, azaz egy sor numerikus érték, amelyek megmutatják, hogy egy adott kontraktus különböző feltételek mellett milyen nyereséget/veszteséget termel. Minden feltétel egy kockázati forgatókönyvnek minősül. Az egyes kockázati forgatókönyvek numerikus értéke mutatja meg azt a nyereséget/veszteséget, amit az adott kontraktus generálna az árváltozás (mögöttes árváltozás), volatilitásváltozás és lejáratig hátralévő idő csökkenésének adott kombinációjában.
A SPAN fedezeti fájlokat a tőzsde a nap folyamán konkrét időközönként megküldi az IBKR-nek, ahol feltöltésre kerülnek a SPAN fedezeti kalkulátorba. A kalkuláció során minden határidős opciós ügylet kockázatosnak minősül mindaddig, amíg el nem éri a futamideje végét vagy lezárásra nem kerül. Ebből a szempontból nem számít, hogy az ügylet pénzen kívüli-e vagy sem. Minden forgatókönyvnek számolnia kell a szélsőséges piaci volatilitás esetével, és ennek megfelelően a fenti határidős opciós ügyletek fedezetre gyakorolt hatását az opciós pozíció megszűnéséig figyelembe kell venni. A SPAN fedezeti követelményeket összehasonlítjuk az IBKR előre meghatározott szélsőséges piaci forgatókönyveivel, és a kettő közül a magasabbat használjuk fedezeti követelményként.
Biztosít-e az IBKR brókeri támogatást a kereskedéshez?
Bár alapértelmezés szerint az ügyfeleink saját maguk nyújtják be a megbízásaikat közvetlenül a TraderWorkstation, az Ügyfélportál vagy az IBKR Mobile alkalmazásban, az IBKR brókeri támogatást nyújt egyes kötések vonatkozásában az alábbiakban részletezett esetekben.
1. Nagy vagy összetett megbízások - azon ügyfelek, akik nagy vagy összetett megbízásokat nyújtanak be, ahol a kötésméret legalább 100 opciós kontraktus vagy legalább 10 000 részvény, igénybe vehetik a Broker Assisted Block Desk nevű különleges szolgáltatásunkat. A Broker Assisted Block Desk szolgáltatás pozíciók nyitásakor és zárásakor is elérhető, és a munkatársak számának köszönhetően azonnali hozzáférést nyújt várakozási idő nélkül. Felhívjuk a figyelmet, hogy az ezen szolgáltatáson keresztül végrehajtott kötésekre a közvetlenül benyújtott megbízásokhoz képest magasabb jutalékkulcsok vonatkoznak. Mivel a jutalékkulcsok a terméktípus és a terméket jegyző tőzsde függvényében változnak, javasoljuk, hogy kérjen közvetlen árajánlatot az 1-203-618-4030 telefonszámon. További információkért kérjük, látogasson el a „Broker Assistance” weboldalra az alábbi linken.
2. Vészhelyzeti pozíciózárás - amennyiben az ügyfél átmenetileg nem fér hozzá a kereskedési platformhoz, és szeretne lezárni egy pozíciót, ehhez támogatást kaphat, ha felveszi a kapcsolatot valamelyik Ügyfélszolgálati Központunk Closing Order Desk szolgálatával. Felhívjuk a figyelmet, hogy ez a szolgáltatás kizárólag a pozíciók zárását szolgálja, és a telefonos megbízásbenyújtás esetén alkalmazott jutalékfelárat von maga után. Ezen jutalékfelár összege a számla Alapdevizájának függvényében változik. USD-alapú számlák esetén a felár 30 USD (a rendes jutalékokon felül).
Mi történik, ha olyan devizában denominált termékkel kereskedem, amit nem tartok a számlámon?
Egy adott termék megvásárlásához és elszámolásához szükséges deviza típusát nem az IBKR, hanem a terméket jegyző tőzsde határozza meg. Ha például Ön egy olyan devizában denominált értékpapír megvásárlására irányuló ügyletet köt, amely devizával nem rendelkezik, feltéve ugyanakkor, hogy Ön rendelkezik fedezeti számlával és elégséges fedezeti hozzáféréssel, akkor az IBKR hitelt fog nyújtani Önnek a kérdéses összegben. Ennek az az oka, hogy az IBKR-nek kizárólag a megjelölt devizában van lehetősége elszámolni a kérdéses ügyletet az elszámolóházzal. Amennyiben Ön nem kíván ilyen hitelt felvenni és megfizetni a kapcsolódó kamatokat, akkor először vagy (i) befizetést kell teljesítenie a számájára a szükséges devizában és összegben, vagy (ii) át kell váltania a számláján lévő megfelelő összeget, vagy az IdealPro (25 000 USD-t vagy annak megfelelő más devizát meghaladó összegek esetén), vagy kerekítetlen kötésegységek (25 000 USD-t vagy annak megfelelő más devizát el nem érő összegek esetén) használatával, amelyek közül mindkettő elérhető a TWS alkalmazáson keresztül.
Felhívjuk a figyelmet továbbá, hogy miután Ön lezár egy adott devizában denominált értékpapír-pozíciót, a hozam ugyan abban a devizában marad, függetlenül attól, hogy a kérdéses deviza az Ön által a számlájához választott Alapdeviza-e vagy sem. Ennek megfelelően az ilyen hozam árfolyamkockázatnak lesz kitéve az Alapdevizával szemben mindaddig, amíg Ön át nem váltja azt, vagy fel nem használja a hozamot egy másik, azonos devizában denominált termék megvételéhez
A stop megbízások alkalmazásával kapcsolatos további információk
Bár alapértelmezés szerint az ügyfeleink saját maguk nyújtják be a megbízásaikat közvetlenül a TraderWorkstation, az Ügyfélportál vagy az IBKR Mobile alkalmazásban, az IBKR brókeri támogatást nyújt egyes kötések vonatkozásában az alábbiakban részletezett esetekben.
1. Nagy vagy összetett megbízások - azon ügyfelek, akik nagy vagy összetett megbízásokat nyújtanak be, ahol a kötésméret legalább 100 opciós kontraktus vagy legalább 10 000 részvény, igénybe vehetik a Broker Assisted Block Desk nevű különleges szolgáltatásunkat. A Broker Assisted Block Desk szolgáltatás pozíciók nyitásakor és zárásakor is elérhető, és a munkatársak számának köszönhetően azonnali hozzáférést nyújt várakozási idő nélkül. Felhívjuk a figyelmet, hogy az ezen szolgáltatáson keresztül végrehajtott kötésekre a közvetlenül benyújtott megbízásokhoz képest magasabb jutalékkulcsok vonatkoznak. Mivel a jutalékkulcsok a terméktípus és a terméket jegyző tőzsde függvényében változnak, javasoljuk, hogy kérjen közvetlen árajánlatot az 1-203-618-4030 telefonszámon. További információkért kérjük, látogasson el a „Broker Assistance” weboldalra az alábbi linken.
2. Vészhelyzeti pozíciózárás - amennyiben az ügyfél átmenetileg nem fér hozzá a kereskedési platformhoz, és szeretne lezárni egy pozíciót, ehhez támogatást kaphat, ha felveszi a kapcsolatot valamelyik Ügyfélszolgálati Központunk Closing Order Desk szolgálatával. Felhívjuk a figyelmet, hogy ez a szolgáltatás kizárólag a pozíciók zárását szolgálja, és a telefonos megbízásbenyújtás esetén alkalmazott jutalékfelárat von maga után. Ezen jutalékfelár összege a számla Alapdevizájának függvényében változik. USD-alapú számlák esetén a felár 30 USD (a rendes jutalékokon felül).
Opciós szabályozói díj (ORF)
Az ORF az OCC által a klíringtagjaitól, köztük az IBKR-től beszedett tőzsdei díj. Kinyilvánított célja, hogy elősegítse az opciós piac felügyeletével és szabályozásával kapcsolatban felmerülő tőzsdei költségek (pl. rutinfelügyelet, vizsgálatok valamint szakpolitikai, szabályalkotási, értelmező és végrehajtási tevékenységek) ellentételezését. A díjat 2009 közepén vezette be a CBOE, 2010. januárjában a BOX, az ISE és a PHLX, 2011. májusában az AMEX és az ARCA, 2012. januárjában a Nasdaq, 2012. augusztusában a C2, 2013. januárjában Miami, 2013. augusztusában az ISE GEMINI, 2015. februárjában a BATS, 2016. februárjában a Nasdaq BX, 2017. februárjában a BATS EDGX, 2017. februárjában a PEARL és 2019. februárjában a MERCURY és az EMERALD. A díj jelenlegi mértéke ügyfélmegbízásonként 0,02135 USD minden amerikai tőzsdén jegyzett opciós kontraktus után. A tőzsdénkénti díjak az alábbiak szerint alakulnak:
Normal 0 false false false EN-US X-NONE X-NONE
|
TŐZSDE |
ORF |
|
AMEX |
0,0055 |
|
ARCA |
0,0055 |
|
BATS |
0,0001 |
|
BOX |
0,00295 |
|
CBOE |
0,0017 |
|
C2 |
0,0003 |
|
EDGX |
0,0001 |
|
EMERALD |
0,0006 |
|
ISE |
0,0000 |
|
GEMINI |
0,0000 |
|
MERCURY |
0,0004 |
|
MIAX |
0,0019 |
|
NOM |
0,0000 |
|
NASDAQBX |
0,0005 |
|
PEARL |
0,0018 |
|
PHLX |
0,0000 |
|
Összesen |
0,02135 |
Felhívjuk a figyelmet, hogy az ORF minden vételi és eladási tranzakció után felszámításra kerül, az IBKR jutalék illetve bármely más tőzsdei díj (pl. likviditáskivonási díj) mellett, és az Aktivitási Jelentésben szabályozói díjként jelenik meg.
FAQs: Securities subject to Special Requirements
We are seeing unprecedented volatility in GME, AMC, BB, EXPR, KOSS and a small number of other U.S. securities that has forced us reduce the leverage previously offered to these securities and, at times, limit trading to risk reducing transactions. Outlined below are a series of FAQs relating to these actions.
Q: Are there any current restrictions on my ability to trade GME and the other US securities that have been subject to the recent heightened volatility?
A: IBKR is currently not restricting customers from trading shares of AMC, GME, BB, EXPR, KOSS or the other stocks that have been the subject of extreme market volatility. That includes orders to open new positions or close existing ones.
Like many brokers, IBKR placed limits on opening new positions in certain of these securities for a period of time. Those restrictions have since been lifted.
IBKR has not restricted customers’ ability to close existing positions and does not plan to do so.
Q: Can I use margin in trading stocks, options or other derivatives on these products through IBKR?
A: IBKR has increased its margin requirements for securities in GME and the other US securities subject to the recent volatility, including up to 100% margin required for long positions and 300% margin on the short side. You can see these margin requirements in your trading platform prior to submitting an order.
Q: Why did IBKR place these restrictions on my ability to open new positions in certain securities?
A: IBKR took these actions for risk management purposes, to protect the firm and its customers from incurring outsized losses due to wild swings in prices in a volatile and unstable marketplace.
IBKR remains concerned about the effect of this unnatural volatility on the clearinghouses, brokers and market participants.
Q: Does IBKR or its affiliates have positions in these products that it was protecting by placing these restrictions?
A: No. IBKR itself has no proprietary positions in any of the securities.
Q: What allowed IBKR to place those restrictions?
A: Pursuant to its customer agreement, IBKR may decline to accept any customer’s order at IBKR’s discretion.
IBKR also has the right to modify margin requirements for any open or new positions at any time, in its sole discretion. After all, IBKR is the one whose money is being loaned in a margin trade.
Q: Did those restrictions apply to all or just some of IBKR’s customers?
A: All restrictions – all limits on opening new positions and margin increases – applied to all IBKR customers. They were placed based on the security, not based on the customer.
Q: Is my money at IBKR at risk? Has IBKR suffered material losses?
A: IBKR did not incur substantial losses. Through its prudent risk management, IBKR has navigated this market volatility well. In any event, on a consolidated basis, IBG LLC exceeds $9 billion in equity capital, over $6 billion in excess of regulatory requirements.
Q: What will IBKR do going forward? How will I know?
A: IBKR will continue to monitor developments in the market, and will make decisions based on market conditions. For current information, please continue to visit our website.
Bonus Certificates Tutorial
Introduction
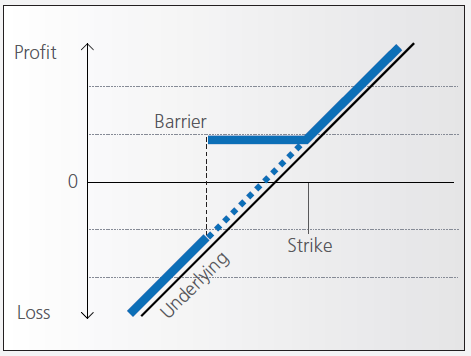
Bonus certificates are designed to provide a predictable return in sideways markets, and market returns in rising markets.
At the time they’re issued, bonus certificates normally have a term to maturity of two to four years. You will receive a specified cash pay-out (“bonus level” or “Strike”) if at maturity the price of the underlying is below or at the strike, as long as the underlying instrument has not touched or fallen below an established price level (“safety threshold” or “barrier”) during the term of the certificate.
Unless the certificate has a cap, you continue to participate in the price gains if the underlying instrument rises above the bonus level. In this case you either receive the corresponding number of shares or a cash settlement reflecting the value of the underlying instrument on the maturity date.
However, if the barrier is breached, you will no longer be entitled to the bonus payment. The value of the certificate then corresponds to the value of the underlying (times the ratio). In other words, once the barrier has been touched the certificate effectively converts to an index certificate. You will receive either the corresponding number of shares or a cash settlement reflecting the value of the underlying instrument on the maturity date.
Although there is no structured leverage, the presence of the barrier creates effective leverage. When the price of the underlying instrument approaches the barrier the probability of a breach increases, affecting the price of the certificate disproportionately.
Pay-out Profile
Example
Assume a bonus certificate on ABC share. The certificate has a strike of EUR 45.00 and a barrier set at EUR 36.00. The table below shows scenarios depending on the trading range of the underlying, the final price of the underlying and whether the barrier has been touched or not.
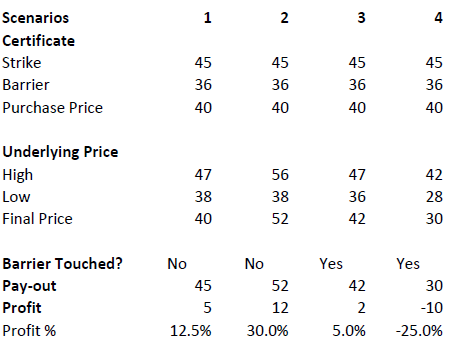
Warrant Tutorial
Introduction
A warrant confers the right to buy (call-warrant) or sell (put-warrant) a specific quantity of a specific underlying instrument at a specific price over a specific period of time.
Pay-out Profile
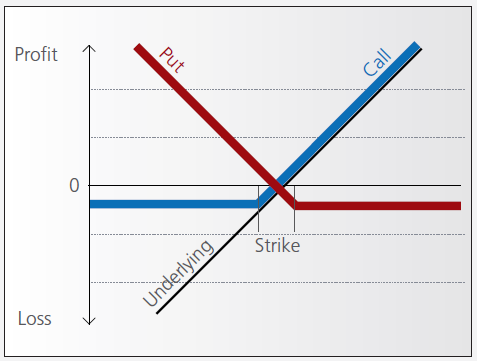
With some warrants, the option right can only be exercised on the expiration date. These are referred to as “European-style” warrants. With “American-style” warrants, the option right can be exercised at any time prior to expiration. The vast majority of listed warrants are cash-exercised, meaning that you cannot exercise the warrant to obtain the underlying physical share. The exception to this rule is Switzerland, where physically settled warrants are widely available.
Factors that influence pricing
Not only do changes in the price of the underlying instrument influence the value of a warrant, a number of other factors are also involved. Of particular importance to investors in this regard are changes in volatility, i.e. the degree to which the price of the underlying instrument fluctuates. In addition, changes in interest rates and the anticipated dividend payments on the underlying instrument also play a role.
However, changes in implied volatility - as well as interest rates and dividends - only affect the time value of a warrant. The primary driver - intrinsic value - is solely determined by the difference between the price of the underlying instrument and the specified exercise price.
Historical and implied volatility
In addressing this topic, a differentiation has to be made between historical and implied volatility. Implied volatility reflects the volatility market participants expect to see in the financial instrument in the days and months ahead. If implied volatility for the underlying instrument increases, so does the price of the warrant.
This is because the probability of profiting from a warrant during a particular time-frame increases if the price of the underlying instrument is highly volatile. The warrant is therefore more valuable.
Conversely, if implied volatility decreases, that leads to a decline in the value of warrants and hence occasionally to nasty surprises for warrant investors who aren’t familiar with the concept and influence of volatility.
Interest rates and dividends
Issuers hedge themselves against price changes in the warrant through purchases and sales of the underlying instrument. Due to the leverage afforded by warrants, the issuer needs considerably more capital to hedge its exposure than you require to buy the warrants. The issuer’s interest expense associated with that capital is included in the price of the warrant. The amount of embedded interest reduces over time and at expiration is zero.
In the case of puts, the situation is exactly the opposite. Here, the issuer sells the underlying instrument
short to establish the necessary hedge, and in so doing receives capital that can earn interest. Thus interest reduces the price of the warrant by an amount that decreases over time.
As the issuer owns shares as a part of its hedging operations, it is entitled to receive the related dividend
payments. That additional income reduces the price of call warrants and increases the price for puts. But if the dividend expectations change, that will have an influence on the price of the warrants. Unanticipated special dividends on the underlying instrument can lead to a price decline in the related warrants.
Key valuation factors
Let’s assume the following warrant:
Warrant Type: Call
Term to expiration: 2 years
Underlying : ABC Share
Share price: EUR 30.00
Strike: EUR 30.00
Exercise ratio: 0.1
Warrant’s price: EUR 0.30
Intrinsic value
Intrinsic value represents the amount you could receive if you exercised the warrant immediately and then bought (in the case of a call) or sold (put) the underlying instrument in the open market.
It’s very easy to calculate the intrinsic value of a warrant. In our example the intrinsic value is EUR 00.00
and is calculated as follows:
(price of underlying instrument – strike price) x exercise ratio
= (EUR 30.00 – EUR 30.00) x 0.1
= EUR 00.00
If the price of the ABC share increases by EUR 1, the intrinsic value becomes
= (EUR 31.00 – EUR 30.00) x 0.1
= EUR 00.10
The intrinsic value of a put warrant is calculated with this formula:
(strike price – price of underlying instrument) x exercise ratio
It’s important to note that the intrinsic value of a warrant can never be negative. By way of explanation:
if the price of the underlying instrument is at or below the exercise price, the intrinsic value of a call equals zero. In this instance, the price of the warrant consists only of “time value”. On the flipside, the intrinsic value of a put is equal to zero if the price of the underlying instrument is at or above the exercise price.
Time value
Once you’ve calculated the intrinsic value of a warrant, it’s also easy to figure out what the time value of that warrant is. You simply deduct the intrinsic value from the current market price of the warrant. In our example, the time value is equal to EUR 1.30 as you can see from the following calculation:
(warrant price – intrinsic value)
= (EUR 0.30 EUR – EUR 0.00)
= EUR 0.30
Time value gradually erodes during the term of a warrant and ultimately ends up at zero upon expiration. At that point, warrants with no intrinsic value expire worthless. Otherwise you can expect to receive payment of the intrinsic value. Take note, though: a warrant’s loss of time value accelerates during the final months of its term.
Premium
The premium indicates how much more expensive a purchase/sale of the underlying instrument would be via the purchase of a warrant and the immediate exercise of the option right as opposed to simply buying/selling the underlying instrument in the open market.
Hence the premium is a measure of how expensive a warrant actually is. It follows that, when given a choice between warrants with similar features, you should always buy the one with the lowest premium. By calculating the premium as an annualized percentage, warrants with different terms to expiry can be compared with each other.
The percentage premium for the call warrant in our example can be calculated as follows:
(strike price + warrant price / exercise ratio – share price) / share price * 100
= (EUR 30.00 + EUR 0.30 / 0.1 – EUR 30.00) / EUR 30.00 x 100
= 10 percent
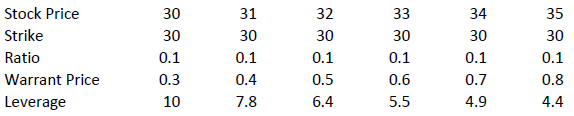
Leverage
The amount of leverage is the price of the share * ratio divided by the price of the warrant. In our example 30.00*0.1/0.3 = 10. So when the price of ABC increases by 1% the value of the warrant increases by 10%.
The amount of leverage is not constant however; it varies as intrinsic and time value changes, and is particularly sensitive to changes in intrinsic value. As a rule of thumb, the higher the intrinsic value of the warrant, the lower the leverage. For example (assuming constant time value):
Knock-out (Turbo) Tutorial
Introduction
Knock-out warrants (turbos), like vanilla warrants, derive their value from the difference between the price of the underlying and the strike. They differ significantly however from vanilla warrants in many important respects:
- They can expire (knock-out) prematurely if the price of the underlying instrument touches or falls below (in the case of knock-out calls) or exceeds (in the case of knockout puts) a predetermined barrier-level. It expires worthless if the barrier equals the strike, or it may have a residual stop-loss value if the barrier is set higher than the strike (in the case of a call).
- Changes in implied volatility have little or no impact on knock-out products, therefore their pricing is easier for investors to comprehend than that of warrants.
- They have little or no time value (because of the presence of the knock-out barrier), and therefore have a higher degree of leverage than a warrant with the same strike. This is because the absence of time value makes the instrument “cheaper”.
Pay-out Profile
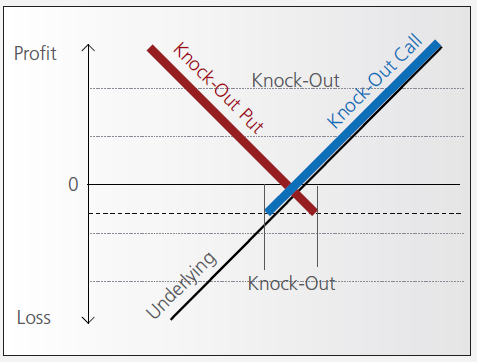
Leverage
As discussed above, knock-out warrants exhibit high degrees of leverage, particularly as the price of the underlying nears the strike/barrier. Consider the following example of a long turbo on the Dow Jones Index, compared to a vanilla warrant:
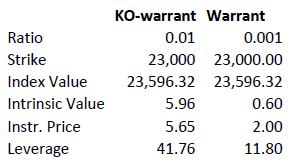
Intrinsic value = (index value – strike) x ratio
Leverage = Index Value x Ratio / Instrument Price
A vanilla warrant retains significant time value even as the underlying price approaches the strike, sharply reducing its leverage compared to a knock-out warrant.
Product types
As discussed above, the barrier may either equal the strike, or be set above (calls) or below (puts). In the latter cases a small residual value remains after knock-out, corresponding to the difference between the barrier (the stop-loss level) and the strike.
Moreover, knock-out products may either have an expiration date or may be open-ended. This makes a difference in the way interest is accounted for. If the contract has an expiration date interest is included in the premium, the amount of which reduces over time and is zero on expiration. This is analogous to a standard vanilla warrant.
in relation to an expiration date. The price of the contract therefore corresponds exactly to its intrinsic value. Interest however must be accounted for. This is done by a daily adjustment of the barrier and strike. The following example shows the daily adjustment for a long open-end turbo on the Dow Jones Index:
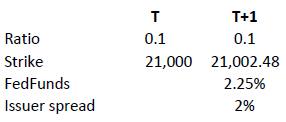
The adjustment = Strike T x (1+ FedFunds/360 + Issuer Spread/360).
The intrinsic value of the instrument is correspondingly reduced as follows, assuming no change in the value of the DJ Index):

Intrinsic value = (index value – strike) x ratio
