Forex Execution Statistics
IBKR clients can now analyze the quality of their forex executions in comparison to forex trades by other IBKR customers through the FX Browser tool in Client Portal. The tool provides transaction data for the 15 forex transactions that occur immediately before and after in the same currency pair of the client's transaction.
Note:
The number of transactions may be limited to fewer than the stated 15 as the NFA also has placed a 15 minute window on the query. Meaning, if within a 15 minute window before and after the customer's execution there are fewer than 15 executions the customer's query will return only those executions which occurred within the time window.
Accessing the FX Browser Tool
To Access the FX Browser tool, login to Client Portal using the Login button on our website. Click the Help menu (question mark icon in the top right corner) followed by Support Center. Please note, at this time only data for the live account will be provided.
.png)
From there, select "See Trades on IBKR's FX Platform" from the list of Information & Tools:

Submitting a Query
When the FX Browser is launched, you will be presented with the following screen:
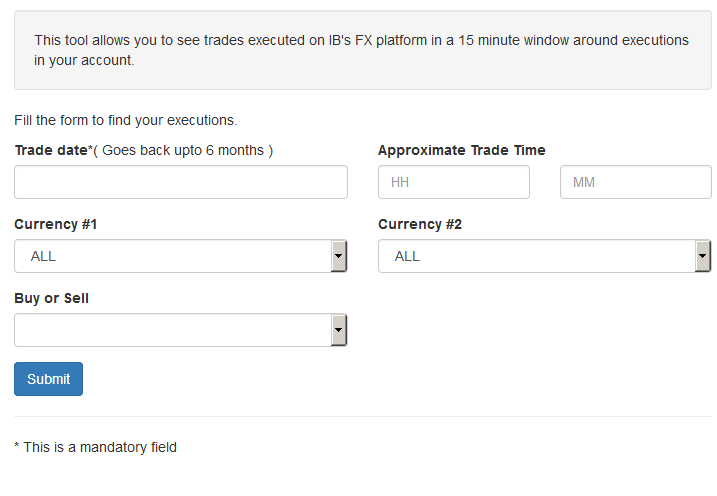
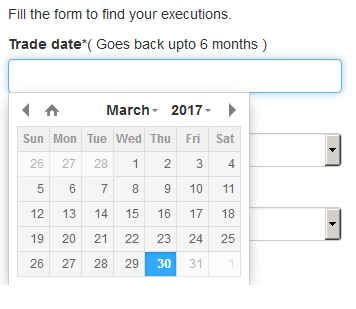
Please note that only Trade Date is a mandatory field in the query. When clicking on the Trade Date field, a calendar widget will populate and allow you to select your trade date. Only transactions from the last 6 months will be available to search.
Active customers may wish to limit the results by further selecting the currency pair, side or time of the execution.
Once the desired query has been entered, click on the Submit button.
The next screen will display the list of executions for the given account on the specified day. From there, you may select the execution you wish to receive the execution statistics on.
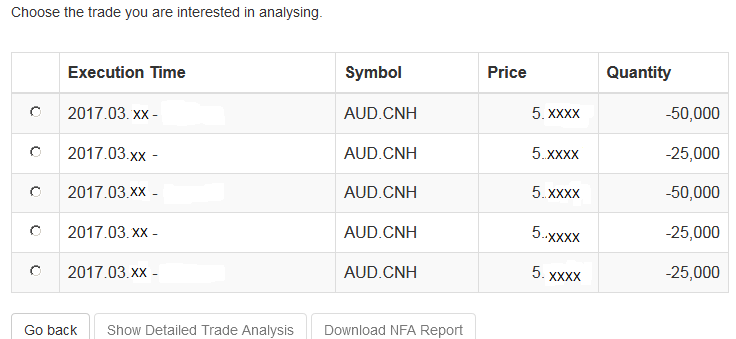
Once the execution you wish to view has been selected, click the "Download NFA Report" button.

Reading the Report
The results will be returned in a new tab and will contain the 15 executions before and 15 executions after the trade you selected on the previous screen. Per the note above, if fewer than 15 executions occurred in the 15 minute time frame only those executions will be displayed.
The query results will include the following information:
- Execution date and time, as expressed in Eastern time
- Side (buy or sell)
- Quantity (of Transaction Currency)
- Currency pair
- Execution price
- Commissions and other charges assessed by the FDM
- Currency denomination of commissions
Your trade will be marked as Trade Number "0" and the trades before and after your trade will be numbered from 1 to 15.
Error Messages
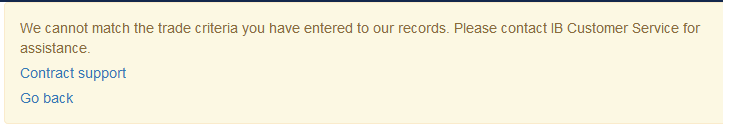
If the search criteria you enter does not bring up any trade information, you will be presented with the following error message:
Automatic Forex Swap
OVERVIEW
In general, interest on account balances are credited/debited at benchmark rates plus/minus a spread as shown on our web pages. For qualified clients with substantial forex positions, however, IB has created a mechanism to carry large gross FX positions with higher efficiency with respect to carrying costs. We refer to it as the “auto swap program”. The design allows clients to benefit from IB’s participation in the interbank forex swaps market where implied interest rate spreads are usually much narrower than the spreads available in the retail deposit market.
a. Concept
Interest is charged on settled balances, so the intent of a Forex swap as used here is to defer the settlement of a currency position from one day to the next business day. This is done by a simultaneous sell and buy of the same amount of base (first) currency but for two different value dates e.g. on T you go long 10 mio. EUR.USD for value date T+2. By example, on T+1 the position is swapped T+2 to T+3, here a sell of 10 mio EUR.USD for T+2 and a purchase of 10 mio. EUR.USD for T+3. As a result you have deferred settlement from T+2 to T+3, with the difference in prices of the two trades representing the financing cost from T+2 to T+3.
b. Cost
This service is provided as a free service and no commission or markup is charged by Interactive Brokers. The interbank market bid/ask spread inherent in the swap prices may be regarded as a cost but is not determined by Interactive Brokers. Interactive Brokers provides the service on a best efforts basis to our large Forex clients.
c. Position Criteria
Swap activity is only applied to accounts with gross FX positions larger than 10 mio. USD or approximate equivalent of other currencies. Positions are swapped (rolled) in increments or multiples of USD 1 mio. (or equivalent). The residual settled balances are traded under IB‘s standard interest model1. Positions that are swapped (rolled) are real positions, i.e. the projected T+1 settled cash balances.
The so-called “Virtual Positions” are not considered; the virtual position is only a representation of the original trades expressed as currency pairs, for example EUR.CHF.
Settled cash balances are a single currency concept, e.g. EUR or CNH. IB executes all swaps against USD as it is the most efficient funding currency. Should you have a position in a cross, e.g. EUR against CHF, two swaps, one in EUR.USD and one in USD.CHF will be done. The threshold(s) and increment(s) may change at any time without notice.
d. Client Eligibility
As we offer this service for free, only clients with substantial currency positions are eligible for inclusion in the service. US legal residents need to be an Eligible Contract Participant (ECP) and be in the possession of an LEI number (legal entity identifier). Interactive Brokers cannot guarantee a client’s inclusion in the program and all inquiries require compliance approval prior to become active.2
e. Swap Price Recognition
Interactive Brokers may conduct a series of swaps in a currency during a day. Interactive Brokers will use average bid and ask prices at which it executed, respectively average bid and asks as quoted in the interbank market. Swap prices are not published but can be seen (or calculated) in the statement after execution. The swaps are applied in the account at the end of the day.
f. Recognition in the Statement
You will find the swap transaction(s) in the Trades section of the statement. The swap are represented as simultaneous purchase/sale or vice versa, do not have a time stamp and shows an M (manual entry) in the code column. The actual swap prices are the difference in between the two prices.
Here an example for cob 20150203 that shows a swap from 20150203 to 20150204.
![]()
.jpg)
g. Examples of Swap Prices
Here a couple of examples that use swap prices from a major interbank provider. Often bid/ask spreads are even tighter.
|
Currency Pair |
Spot Bid |
Spot Ask |
Tenor |
Days in Period (TN) |
Swap Points Bid |
Swap Points Ask |
Implied Currency |
Implied Rate Bid |
Implied Rate Ask |
|
EUR.USD |
1.04481 |
1.04483 |
TomNext(TN) |
1 |
0.00004220 |
0.00004280 |
EUR |
-0.77% |
-0.75% |
|
USD.HKD |
7.76810 |
7.76810 |
TomNext(TN) |
1 |
-0.00011500 |
-0.00011000 |
HKD |
0.17% |
0.19% |
|
USD.JPY |
117.050 |
117.052 |
TomNext(TN) |
1 |
-0.0038 |
-0.0032 |
JPY |
-0.47% |
-0.47% |
|
USD.CNH |
6.93101 |
6.93105 |
TomNext(TN) |
1 |
0.0021 |
0.0028 |
CNH |
11.77% |
15.46% |
In more detail, let’s assume you want to calculate the implied CNH rate resulting from a USD.CNH swap. We are looking for the implied rate of the quote currency CNH (Currency 2). Therefore the following formula is used:
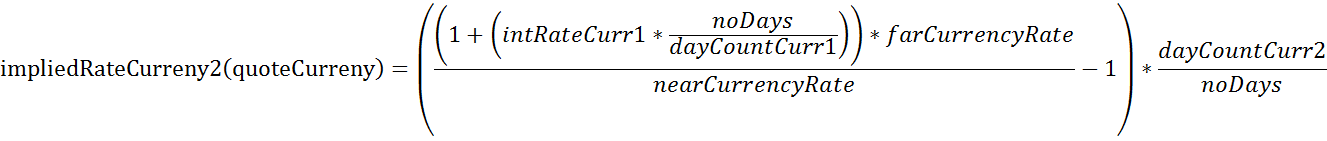
| Description | Variable | Value |
| Currency Pair (Currency1.Currency2) | USD.CNH | |
| day count convention Currency 1 (base Currency), i.e. USD | dayCountCurr1 | 360 |
| day count convention Currency 2 (quote Currency), i.e. CNH | dayCountCurr2 | 365 |
| Tenor | TomNext | |
| number of days in the Tenor | noDays | 1 |
| interest rate of Currency 1 (in decimals, i.e. 1% = 0.01) | inRateCurr1 | 0.0070 |
| Currency rate (Spot) | currencyRate | 6.939500 |
| swap Points expressed in decimals | swapPoints | 0.0012 |
| near Currency Rate (Spot - swap points) | nearCurrencyRate | 6.938300 |
| far Currency Rate (in a Tomnext swap this is the spot rate) | farCurrencyRate | 6.939500 |
| implied interes rate of Currency2, i.e. CNH | impliedRateCurrncy2(quoteCurrency) | 0.0702 |
So using above figures, this results in a 7.02% implied interest rate for CNH.
Now if you wanted to calculate the implied rate for the base currency (Currency 1) the formula would change slightly. Here an example using EUR.USD:
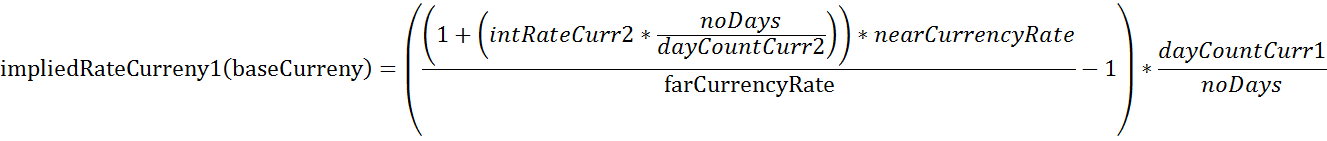
| Description | Variable | Value |
| Currency Pair (Currency1.Currency2) | EUR.USD | |
| day count convention Currency 1 (base Currency), i.e. EUR | dayCountCurr1 | 360 |
| day count convention Currency 2 (quote Currency), i.e. USD | dayCountCurr2 | 360 |
| Tenor | TomNext | |
| number of days in the Tenor | noDays | 1 |
| interest rate of Currency 2 (in decimals, i.e. 1% = 0.01) | inRateCurr2 | 0.0070 |
| Currency rate (Spot) | currencyRate | 1.039900 |
| swap Points expressed in decimals | swapPoints | 0.000042 |
| near Currency Rate (Spot - swap points) | nearCurrencyRate | 1.039858 |
| far Currency Rate (in a Tomnext swap this is the spot rate) | farCurrencyRate | 1.039900 |
| implied interes rate of Currency1, i.e. EUR | impliedRateCurrncy1(baseCurrency) | -0.0075 |
Using above example, this results in a -0.75 % implied interest rate for EUR.
1. For example, in the case of a USD 20.3 mio. position only 20 mio. will be swapped. USD 0.3 remains in the account and interest using benchmark and spreads will be applied. A USD 300k position will not be considered for swapping at all. The position by currency is taken as the reference, regardless of the overall position.
2 US, Australian and Israeli domiciled residents are currently not eligible for inclusion in the Automated Forex Swap Program.
Summary of Risks relating to Forex CFDs issued by Interactive Brokers Securities Japan, Inc.
This summary highlights the principal risks associated with trading Forex CFDs issued by IBSJ (“IB FXCFDs"). It is not a risk disclosure for regulatory purposes.
- Trading of IB FXCFDs is not suitable for all investors, and you should not trade them unless you are an experienced investor with a high risk tolerance and the capability to sustain losses if they occur
- The volatility of foreign exchange rates and interest rates may quickly cause significant losses. Forex CFDs employ leverage that further amplifies the volatility relative to your investment and you may lose more than you have invested. In addition, IB FXCFD roll over interest may turn from a credit to a debit due to changes in interest rates
- You are required to maintain sufficient equity in your account at all times to cover IBSJs maintenance margin requirement. There are no grace-periods and IBSJ does not issue margin calls. Your equity is calculated in real time and should it become insufficient, IBSJ will immediately and automatically liquidate positions to bring your account into margin compliance. Real time liquidations aim to minimize the risk that your account equity becomes negative, but they cannot eliminate that risk. Should your equity become negative you are required to deposit additional funds to cover the deficit
- The price IBSJ displays to you for IB FXCFDs is based on the prevailing foreign exchange market. However there is no guarantee for executions at that price. Slippage may occur for large trades or in fast moving markets and during heavily traded hours
- Moreover, your ability to establish or close positions on a timely basis is not guaranteed. It may become difficult to display quotes during major holidays or during hours when foreign exchange trading is not active. IBSJ may display prices that deviate from a fair market due to system-malfunctions or failures, or erroneous quotes that IBSJ may receive from market participants or for other reasons (off-market prices). IBSJ will adjust or cancel trades executed with off-market prices
- IB FXCFDs are over-the-counter trades between you and IBSJ. They are not traded on any exchange or cleared by any central counterparty. You are therefore exposed to counterparty risk and should IBSJ become insolvent you may not be able to fully recoup your investment, or at all
Please contact IBSJs Client Service Department should you have questions about the content of this summary and read the full risk disclosure carefully before commencing trading. The risk disclosure is available in Account Management when you request IB FXCFD trading permissions, and on IBSJs web site.
Allocation of Partial Fills
How are executions allocated when an order receives a partial fill because an insufficient quantity is available to complete the allocation of shares/contracts to sub-accounts?
Overview:
From time-to-time, one may experience an allocation order which is partially executed and is canceled prior to being completed (i.e. market closes, contract expires, halts due to news, prices move in an unfavorable direction, etc.). In such cases, IB determines which customers (who were originally included in the order group and/or profile) will receive the executed shares/contracts. The methodology used by IB to impartially determine who receives the shares/contacts in the event of a partial fill is described in this article.
Background:
Before placing an order CTAs and FAs are given the ability to predetermine the method by which an execution is to be allocated amongst client accounts. They can do so by first creating a group (i.e. ratio/percentage) or profile (i.e. specific amount) wherein a distinct number of shares/contracts are specified per client account (i.e. pre-trade allocation). These amounts can be prearranged based on certain account values including the clients’ Net Liquidation Total, Available Equity, etc., or indicated prior to the order execution using Ratios, Percentages, etc. Each group and/or profile is generally created with the assumption that the order will be executed in full. However, as we will see, this is not always the case. Therefore, we are providing examples that describe and demonstrate the process used to allocate partial executions with pre-defined groups and/or profiles and how the allocations are determined.
Here is the list of allocation methods with brief descriptions about how they work.
· AvailableEquity
Use sub account’ available equality value as ratio.
· NetLiq
Use subaccount’ net liquidation value as ratio
· EqualQuantity
Same ratio for each account
· PctChange1:Portion of the allocation logic is in Trader Workstation (the initial calculation of the desired quantities per account).
· Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user
· Inline Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user.
· Model1:
Roughly speaking, we use each account NLV in the model as the desired ratio. It is possible to dynamically add (invest) or remove (divest) accounts to/from a model, which can change allocation of the existing orders.
Basic Examples:
Details:
CTA/FA has 3-clients with a predefined profile titled “XYZ commodities” for orders of 50 contracts which (upon execution) are allocated as follows:
Account (A) = 25 contracts
Account (B) = 15 contracts
Account (C) = 10 contracts
Example #1:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 10 am (ET) the order begins to execute2but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 2 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 7 of the 50 contracts are filled or 14%). For each account the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 14% of 25 = 3.5 rounded down to 3
Account (B) = 14% of 15 = 2.1 rounded down to 2
Account (C) = 14% of 10 = 1.4 rounded down to 1
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.10).
A: final allocation of 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 2 contract, which is 2/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.20)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #2:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be filled3 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 1 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is executed (i.e., 5 of the 50 contracts are filled or 10%).For each account, the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 10% of 25 = 2.5 rounded down to 2
Account (B) = 10% of 15 = 1.5 rounded down to 1
Account (C) = 10% of 10 = 1 (no rounding necessary)
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. to Account B which currently has a ratio of 0.067).
A: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #3:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be executed2 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 12 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 3 of the 50 contracts are filled or 6%). Normally the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers, however for a fill size of less than 4 shares/contracts, IB first allocates based on the following random allocation methodology.
In this case, since the fill size is 3, we skip the rounding fractional amounts down.
For the first share/contract, all A, B and C have the same initial fill ratio and fill quantity, so we randomly pick an account and allocate this share/contract. The system randomly chose account A for allocation of the first share/contract.
To Summarize3:
A: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
C: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
Next, the system will perform a random allocation amongst the remaining accounts (in this case accounts B & C, each with an equal probability) to determine who will receive the next share/contract.
The system randomly chose account B for allocation of the second share/contract.
A: 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
The system then allocates the final [3] share/contract to an account(s) with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.00).
A: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Available allocation Flags
Besides the allocation methods above, user can choose the following flags, which also influence the allocation:
· Strict per-account allocation.
For the initially submitted order if one or more subaccounts are rejected by the credit checking, we reject the whole order.
· “Close positions first”1.This is the default handling mode for all orders which close a position (whether or not they are also opening position on the other side or not). The calculation are slightly different and ensure that we do not start opening position for one account if another account still has a position to close, except in few more complex cases.
Other factor affects allocations:
1) Mutual Fund: the allocation has two steps. The first execution report is received before market open. We allocate based onMonetaryValue for buy order and MonetaryValueShares for sell order. Later, when second execution report which has the NetAssetValue comes, we do the final allocation based on first allocation report.
2) Allocate in Lot Size: if a user chooses (thru account config) to prefer whole-lot allocations for stocks, the calculations are more complex and will be described in the next version of this document.
3) Combo allocation1: we allocate combo trades as a unit, resulting in slightly different calculations.
4) Long/short split1: applied to orders for stocks, warrants or structured products. When allocating long sell orders, we only allocate to accounts which have long position: resulting in calculations being more complex.
5) For non-guaranteed smart combo: we do allocation by each leg instead of combo.
6) In case of trade bust or correction1: the allocations are adjusted using more complex logic.
7) Account exclusion1: Some subaccounts could be excluded from allocation for the following reasons, no trading permission, employee restriction, broker restriction, RejectIfOpening, prop account restrictions, dynamic size violation, MoneyMarketRules restriction for mutual fund. We do not allocate to excluded accountsand we cancel the order after other accounts are filled. In case of partial restriction (e.g. account is permitted to close but not to open, or account has enough excess liquidity only for a portion of the desired position).
Footnotes:
Additional Information Regarding the Use of Stop Orders
U.S. equity markets occasionally experience periods of extraordinary volatility and price dislocation. Sometimes these occurrences are prolonged and at other times they are of very short duration. Stop orders may play a role in contributing to downward price pressure and market volatility and may result in executions at prices very far from the trigger price.
IB Forex CFDs - Facts and Q&A
Risk Warning
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage.
61% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with IBKR.
You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
ESMA Rules for CFDs (Retail Clients only)
The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) has enacted new CFD rules effective 1st August 2018.
The rules include: 1) leverage limits on the opening of a CFD position; 2) a margin close out rule on a per account basis; and 3) negative balance protection on a per account basis. The ESMA Decision is only applicable to retail clients.
Professional clients are unaffected.
Please refer to the following articles for more detail:
ESMA CFD Rules Implementation at IBKR (UK) and IBKR LLC
ESMA CFD Rules Implementation at IBIE and IBCE
IBKR Forex CFD Features
Transparent DMA Quotes: IBKR ensures tight spreads and substantial liquidity as a result of combining quotation streams from 14 of the world's largest foreign exchange dealers which constitute more than 70% of market share in the global interbank market*. This results in displayed quotes as small as 0.1 PIP. IBKR does not mark up the quotes, rather passes through the prices that it receives and charges a separate low commission.
*Source: Euromoney FX survey FX Poll 2016.
For example, April 21, 2016 the GBP benchmark rate was 0.483%, the USD rate was 0.37%. The applicable benchmark rate is:
GBP.USD BM +0.48% - 0.37% = +0.113%
The applicable customer rate is Pair BM – IBKR spread for long positions, BM + spread for short positions:
GBP.USD Long Rate +0.113% - 1.00% = -0.887%
GBP.USD Short Rate +0.113% + 1.00% = +1.113%
It is important to note that the long rate is applied as a credit, the short rate as a debit. Consequently for a long position a positive rate means a credit, a negative rate a charge. However for short positions a positive rate means a charge, a negative rate a credit.
Interest is calculated on the contract value expressed in the quote currency, and credited or debited in that currency. For example:
For example:
| Daily Interest | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | GBP.USD Close | USD Value | Rate | USD | |
| GBP.USD | -20,000 | 1.43232 | -28,646.40 | 1.113% | -0.89 |
Interest on Forex CFD balances is calculated on a stand-alone contract basis, and not combined or netted with other currency exposures, including Spot FX. Although IBKR does not directly reference swap rates, IBKR reserves the right to apply higher spreads in exceptional market conditions, such as during spikes in swap rates that can occur around fiscal year-ends.
If your account is with IBKR (UK) or with IBKR LLC, IBKR will then set up a new account segment (identified with your existing account number plus the suffix “F”). Once the set-up is confirmed you can begin to trade. You do not need to fund the F-account separately, funds will be automatically transferred to meet CFD margin requirements from your main account.
If your account is with another IBKR entity, only the permission is required; an additional account segment is not necessary.
Trading Example (Professional Clients)
Opening the position
You purchase 10 lots (200000) EUR.CHF CFDs at $1.16195 for CHF 232,390, which you then hold for 5 days.
| EUR.CHF Forex CFDs – New Position | |
|---|---|
| Reference Underlying Price | 1.16188 - 1.16195 |
| CFDs Reference Price | 1.16188 - 1.16195 |
| Action | Buy |
| Quantity | 200,000 |
| Trade Value | CHF 232,390.00 |
| Margin (3% x 232,390) | AUD 9,100 |
| Interest Charged (on CHF 232,390 over 5 days) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier I (Pair BM 0.42% - IB Spread 1%) | CHF 232,390.00 | -0.58% | (CHF 18.72) |
Closing the position
| Exit CFD Position | ||
|---|---|---|
| Profit Scenario | Loss Scenario | |
| Reference Underlying Price | 1.16840 - 1.16848 | 1.15539 - 1.15546 |
| CFDs Reference Price | 1.16840 - 1.16848 | 1.15539 - 1.15546 |
| Action | Sell | Sell |
| Quantity | 200,000 | 200,000 |
| Trade Value | CHF 233,680.00 | CHF 231,078.00 |
| Trade P&L | CHF 1,290.00 | (CHF 1,312.00) |
| Financing | (CHF 18.72) | (CHF 18.72) |
| Entry Commission 0.002% | (CHF 4.65) | (CHF 4.65) |
| Entry Commission 0.002% | (CHF 4.67) | (CHF 4.62) |
| Total P&L | CHF 1,261.96 | (CHF 1,339.99) |
CFD Resources
Below are some useful links with more detailed information on IBKR’s CFD offering:
Frequently Asked Questions
Can anyone trade IBKR Forex CFDs?
All clients can trade IBKR CFDs, except residents of the USA, Canada, and Hong Kong. There are no exemptions based on investor type to the residency-based exclusions.
What is the difference between IBKR Forex CFDs and IBKR Cash Forex?
IBKR Cash Forex is a leveraged cash trade where you take delivery of the two currencies making up the pair. Your Forex-trading related balances are combined with your other balances arising out of your other trading activity, and you pay or receive interest on these consolidated balances based on the benchmark rate for each currency.
By contrast IBKR Forex CFDs are a contract which provides exposure but does not deliver the underlying currencies, and you pay or receive interest on the notional value of the contract. The benchmark rate for the contract is the difference between the benchmark rates for the two underlying currencies. This is in principle similar to the TOM Next rolls used by other brokers, but offers greater stability as benchmark rates generally are less volatile than swap rates.
Please see the Carry Interest section above for a detailed example.
Are there any market data requirements?
The market data for IBKR Forex CFDs is the same as for Leverage FX. It is a global permission and free of charge.
How are my CFD trades and positions reflected in my statements?
If you are a client of IBKR (U.K.) or IBKR LLC, your CFD positions are held in a separate account segment identified by your primary account number with the suffix “F”. You can choose to view Activity Statements for the F-segment either separately or consolidated with your main account. You can make the choice in the statement window in Client Portal.
If you are a client of other IBKR entities, there is no separate segment. You can view your positions normally alongside your non-CFD positions.
Can I trade Forex CFDs with the same order types and algos as Spot FX, and can I trade them in the FX Trader?
Yes, the trading experience is identical.
Welcome to Interactive Brokers
Now that your account is funded and approved you can start trading. The information below will help you getting
started as a new customer of Interactive Brokers.
- Your Money
- Configure your account to trade
- How to trade
- Trade all over the World
- Five points to enrich your IB experience
1. Your Money
Deposits & Withdrawals General Info. All transactions are administered through your secure Account Management
Deposits
First, you create a deposit notification through your Account Management > Funding > Fund Transfers > Transaction Type: “Deposit” How to create a deposit notification. The second step is to instruct your Bank to do the wire transfer with the bank details provided in your Deposit Notification.
Withdrawals
Create a withdrawal instruction via your secure Account Management > Funding > Fund Transfers > Transaction Type: "Withdrawals" How to create a withdrawal instruction
If you instruct a withdrawal over the Withdrawal limits, it will be considered an exceptional withdrawal and we will therefore need to match bank account holder and IB account. If destination bank account has been used for a deposit, withdrawal will be processed; otherwise, you must contact customer service and provide the documents needed.
Troubleshooting
Deposits: My bank sent the money but I do not see it credited into my IB account. Possible reasons:
a) A fund transfer takes 1-4 business days
b) A Deposit Notification is missing. You have to create it via your Account Management and send a ticket to Customer Service
c) Amending details are missing. Your name or IB account number is missing in the transfer details. You have to contact your bank and ask for the full amending details.
d) ACH initiated by IB is limited to 100k USD in a 7 business period. If you opened a Portfolio Margin account where the initial requirement is 110k, a wire deposit might be the better deposit option to reduce wait time for your first trade. If selecting ACH a wait time of almost 2 weeks or a temporary downgrade to RegT can be possible solutions.
Withdrawals: I have requested a withdrawal but I do not see the money credited to my bank account. Possible reasons:
a) A fund transfer takes 1-4 business days
b) Rejected. Over the max it can be withdrawn. Please check your account cash balance. Note that for regulatory requirements, when the funds are deposited, there is a 3 day holding period before they can be withdrawn.
c) Your bank returned the funds. Probably because receiving bank account and remitting bank account names do not match.
2. Configure your account to trade
Difference between Cash and Margin accounts: If you have chosen the FastTrack application, by default your account type is a cash account with US stock permission. If you would like to get leverage and trade on margin, here how to upgrade to a RegT Margin account
Trading Permissions
In order to be able to trade a particular asset class in a particular country, you need to get the trading permission for it via your Account Management. Please note that trading permissions are free. You might however be asked to sign risk
disclosures required by local regulatory authorities. How to Request Trading Permissions
Market Data
If you want to have market data in real-time for a particular product/exchange, you need to subscribe to a market data package charged by the exchange. How to subscribe to Market data
The Market data assistant will help you choose the right package. Please watch this Video explaining how it works.
Customers have the option to receive delayed market data for free by clicking the Free Delayed Data button from a non-subscribed ticker row.
Advisor Accounts
Have a look at the user guide getting started as advisors. Here you see how to create additional users to your advisor account and grant them access and much more.
3. How to trade
The Trader's University is the place to go when you want to learn how to use our Platforms. Here you will find our webinars, live and recorded in 10 languages and tours and documentation about our various Trading Platforms.
Trader Workstation (TWS)
Traders who require more sophisticated trading tools can use our market maker-designed Trader Workstation (TWS), which optimizes your trading speed and efficiency with an easy-to-use spreadsheet interface, support for more than 60 order types, task-specific trading tools for all trading styles, and real-time account balance and activity monitoring. Try the two models
TWS Mosaic: for intuitive usability, easy trading access, order management, watchlist, charts all in one window or
TWS Classic: the Advanced Order Management for traders who need more advanced tools and algos.
General Description and Information / Quick start guide / Usersguide
Interactive Tours: TWS Basics / TWS configuration / TWS Mosaic
How to place a trade: Video Classic TWS / Video Mosaic
Trading tools: General Description and Information / Users guide
Requirements: How to install Java for Windows / How to install Java for MAC / Port 4000 and 4001 needs to be open
Login TWS / Download TWS
WebTrader
Traders who prefer a clean and simple interface can use our HTML-based WebTrader, which makes it easy to view market data, submit orders, and monitor your account and executions. Use the latest WebTrader from every browser
Quick Start Guide / WebTrader User's Guide
Introduction: Video WebTrader
How to place a Trade: Video WebTrader
Login WebTrader
MobileTrader
Our mobile solutions allow you to trade your IB account on the go. The mobileTWS for iOS and the mobileTWS for BlackBerry are custom-designed for these popular models, while the generic MobileTrader supports most other Smart phones.
General Description and Information
Order Types Order Types available and Description / Videos / Tour / Users guide
Paper Trading General Description and Information / How to get a Paper Trading Account
Once your paper account is created, you can share the market data of your real account with your paper trading account: Account Management > Manage Account > Settings > Paper trading
4. Trade all over the World
IB accounts are multi-currency accounts. Your account can hold different currencies at the same time, this allows you to trade multiple products around the world from a single account.
Base Currency
Your base currency determines the currency of translation for your statements and the currency used for determining margin requirements. Base currency is determined when you open an account. Customers may change their base currency at any time through Account Management.
We do not automatically convert currencies into your Base currency
Currency conversions must be done manually by the customer. In this video you can learn how to do a currency conversion.
In order to open a position denominated in a currency that you do not have in your account, you have two possibilities:
A) Currency conversion.
B) IB Margin Loan. (Not available for Cash Accounts)
Please see this course explaining the mechanics of a foreign transaction.
5. Five points to enrich your IB experience
1. Contract Search
Here you will find all our products, symbols and specifications.
2. IB Knowledge Base
The Knowledge Base is a repository of glossary terms, how-to articles, troubleshooting tips and guidelines designed to assist IB customers with the management of their IB accounts. Just enter in the search button what you are looking for and you will get the answer.
3. Account Management
As our trading platforms give you access to the markets, the Account Management grants you access to your IB account. Use Account Management to manage account-related tasks such as depositing or withdrawing funds, viewing your statements, modifying market data and news subscriptions, changing your trading permissions, and verifying or changing your personal information.
Log In Account Management / AM Quick Start Guide / AM Users Guide
4. Secure Login System
To provide you with the highest level of online security, Interactive Brokers has implemented a Secure Login System (SLS) through which access to your account is subject to two-factor authentication. Two-factor authentication serves to confirm your identity at the point of login using two security factors: 1) Something you know (your username and password combination); and 2) Something you have (an IB issued security device which generates a random, single-use security code). As both knowledge of your username/password and physical possession of the security device are required to login to your account, participation in the Secure Login System virtually eliminates the possibility of anyone other than you accessing your account.
How to Activate your Security Device / How to Obtain a Security Code Card / How to return Security device
In case you forgot your password or lost your security code card, please call us for immediate assistance.
5. Statements and Reports
Easy to view and customize, our statements and reports cover all aspects of your Interactive Brokers account. How to view an Activity Statement
Information regarding high precision forex quotes
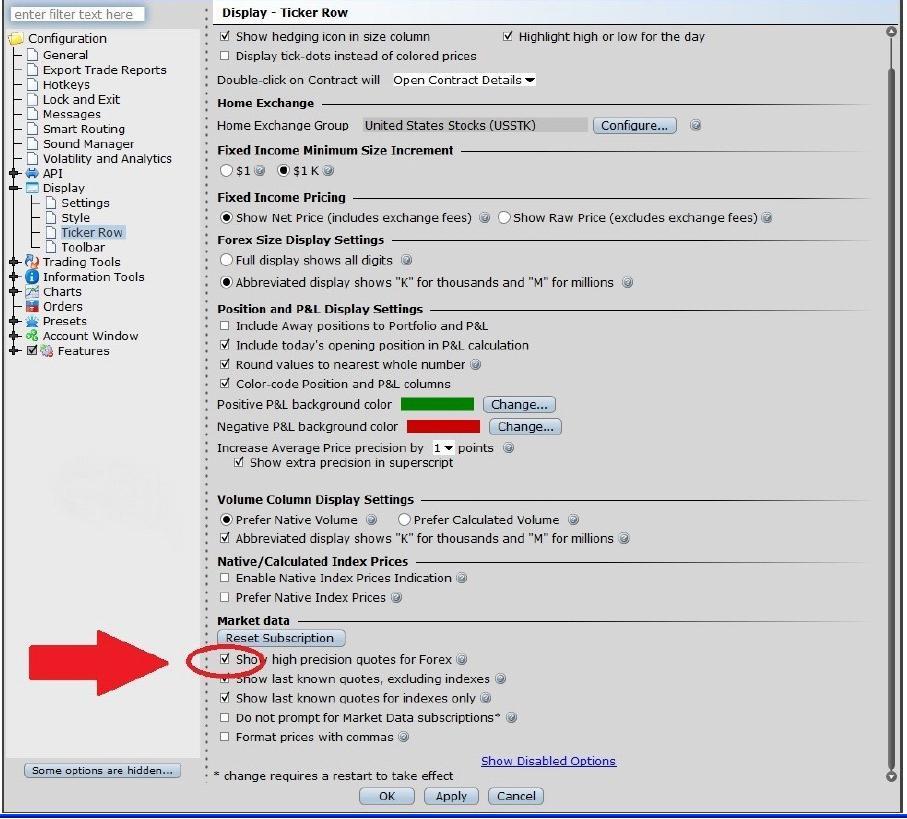
Clients wishing to see forex (IDEALPRO) market data in a more detailed way can now control the order book display mode via the Global Configuration. In order to access this feature you must use TWS release 944.2b or higher. The display mode selection allows the order book to be viewed either as:
- Rounded prices (default): market data is rounded out to the next 0.5 pip. This is identical to the current display functionality for the IB trading platforms. This setting provides a more stable visible quote and a larger ‘top-of-book’ size since it includes the available size at multiple price levels up to the rounded price.
- Unrounded prices: market data is visible in 0.1 pip increments. This allows you to see prices in a more granular fashion, but the displayed values will change more rapidly and the sizes for the top-of-book may appear to be smaller.
It is important to understand that either display mode accesses the same IDEALPRO order book. Order submission will still be in 0.5 pip increments and orders submitted in either display mode will execute in exactly the same way. As in the past (and currently), in cases where the order book has prices at better than your order’s limit price, you will receive the full price improvement.
Instructions on how to display high precision forex quotes
In Global Configuration go to Display, choose Ticker Row and then at the bottom of the window in the Market Data section tick Show high precision quotes for Forex. Then press apply or ok to enable the new setting.
"EMIR": Reporting to Trade Repository Obligations and Interactive Brokers Delegated Service to help meet your obligations
Determining Tick Value
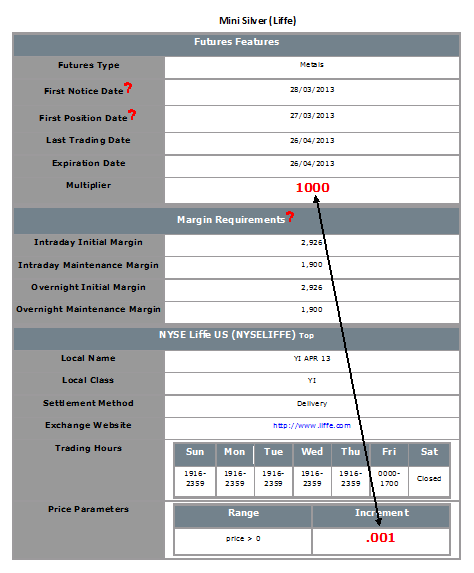
Financial instruments are subject to minimum price changes or increments which are commonly referred to as ticks. Tick values vary by instrument and are determined by the listing exchange. IB provides this information directly from the Contract Search tool on the website or via the Trader Workstation (TWS). To access from TWS, enter a symbol on the quote line, right click and from the drop-down window select the Contract Info and then Details menu options. The contract specifications window for the instrument will then be displayed (Exhibit 1).
To determine the notional value of a tick, multiple the tick increment by the contract trade unit or multiplier. As illustrated in the example below, the LIFFE Mini Silver futures contact has a tick value or minimum increment of .001 which, when multiplied by the contract multiplier of 1,000 ounces, results in a minimum tick value of $1.00 per contract. Accordingly, every tick change up or down results in a profit or loss of $1.00 per LIFFE Mini Silver futures contract.
Exhibit 1