FX Traderを利用しての発注方法
トレーダー・ワークステーション(TWS)のFXTraderページから、Forex(FX)取引の作成ができます。
FXTraderの画面はオーダーマネージメントの画面と異なるように見えますが、取引機能は同じです。
FXTraderの画面では通貨ペアが「セル」のように見えるレイアウトに表示されます。こちらにはTWSのメイン画面の上部にあるFXTraderのアイコンからアクセスできます。
![]()
オーダーマネージメントの画面内にあるマーケットデータのラインの様に、ビッドが左、アスクが右に表示されます。 買い注文はアスクを、また売り注文はビッドをクリックして作成します。
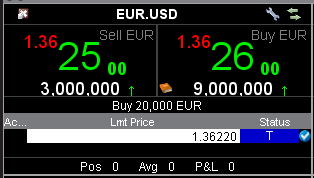
発注中の注文と取引はFXTraderウィンドウ内のふたつめの項目のそれぞれの欄に表示されます。

注意: FXTraderで作成された注文はTWSのオーダーマネジメントに表示されますが、オーダーマネジメントで作成された注文はFXTraderのウィンドウには表示されません。
FXTraderの使用に関する以前のウェビナーはこちらをクリックしてご覧ください。
外国為替取引(FX)に関して
IBでは、外国為替取引を中心としたトレーダーだけでなく、複数の通貨建ての株式やデリバティブ取引から外国為替取引を行うトレーダーも対象として取引場所や取引プラットフォームを提供しています。以下の記事では、TWSプラットフォームでのFX注文入力の基本と、クオートの慣習やポジション(取引後)の報告に関する注意点について説明します。
FX(外国為替)取引では、ある通貨の購入と別の通貨の売却を同時に行いますが、その組み合わせは一般的にクロスペアと呼ばれています。 以下の例では、EUR.USDのクロスペアをもとに説明します。クロスペアの第1通貨(EUR)を売却する取引通貨とし、第2通貨を決済通貨としています。
こちらのページの記事の特定のトピックに移動するには、下記リンクをクリックしてください。
外国為替気配値について
通貨ペアとは外国為替市場において、ある通貨単位の価値を別の通貨単位で表示するためのものです。別の通貨単位で価格を表示される元の通貨を基準通貨=取引通貨、一方で価格表示をする通貨をクオート通貨=決済通貨と呼びます。TWSでは、各通貨ペアに対して1つのティッカーシンボルとなります。FXTraderを使用すると、通貨ペアを逆にして、その価格を表示することもできます。トレーダーは基準通貨を売り、クオート通貨を買うことで通貨ペアの取引を行います。例えば、EUR/USDの通貨ペアのティッカーシンボルは次のようになります:
EUR.USD
となります。
- EURは基準通貨
- USDはクオート通貨
上記の通貨ペアの価格は、現在1ユーロ(基準通貨=取引通貨)が何米ドル(クオート通貨=決済通貨)になるのかを表しています。つまり、1ユーロの価格を米ドルで表示しているのです。
EUR.USDの買い注文は、表示されている取引価格に基づいてユーロを買い、そのユーロに相当する米ドルを売ることになります。
気配値の表示方法について
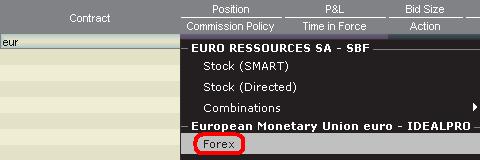
TWS上に通貨ペアの気配値を表示するための手順は以下のとおりです。
1. 取引通貨(例: EUR)を入力し、ENTERキーを押します。
2. 商品タイプのFX
を選択します。
3. 決済通貨(例: USD)を選択し、FXの取引所を選択します。
.jpg)
注意事項
IDEALFXにおける最低発注量(通常25,000米ドル)を超える注文は、IDEALFXにおいてインターバンクの外国為替市場に直接アクセスすることができます。IDEALFXに発注された注文のうち最低発注量を満たさないものは、主に外国為替取引用の少額注文取引所に自動的に振り分けられます。IDEALFXの最小・最大取引量に関する詳細は こちらをご覧ください。
外国為替取引において為替ディーラーが通貨ペアを表示する方法は決まっており、 例えば、通貨にCAD(カナダドル)を選択した場合、 決済通貨を選択する選択肢上にUSD(米ドル)が表示されないことがわかります。 これは、このペアが「USD.CAD」の順番で表示することが決まっており、基準通貨となる「USD」を入力してから「Forex」を選択しないとCADとUSDの通貨ペアにアクセスできないためです。
注文の作成方法について
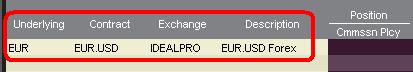
表示されているヘッダーに応じて、通貨ペアは次のように表示されます。
「コントラクト」と「詳細」のコラムには、取引通貨と決済通貨の形式で通貨ペアが表示されます(例: EUR.USD)。 「銘柄」のコラムには、取引通貨のみが表示されます。
表示されているヘッダーを変更する方法は、こちらをご覧ください。
1. 注文の発注にはBID=買気配(売り注文の作成のため)またはASK=売気配(買い注文の作成のため)を左クリックします。
2. 買い、または売りたい取引通貨(=基準通貨)の数量を指定します。注文の数量は、基準通貨=取引通貨で表されます。これはTWSで表示される通貨ペアの第1通貨です。
インタラクティブ・ブローカーズでは外国為替取引において、一定の決まった取引量を基準通貨(=取引通貨)で表す「コントラクト」という概念はなく、取引サイズは基準通貨(=取引通貨)における最小取引単位以上(例:ユーロの場合は1ユーロ)からとなります。
例えば、100,000 EUR.USDの買い注文は、表示されている為替レートに基づいて、100,000 EURを買い、同等の米ドルを売ることになります。
3. ご希望の注文タイプと為替レート(価格)を指定し、注文を発注します。
注意事項: 注文は全ての通貨の最小取引単位から行うことができ、上述のIDEALFX最低発注量の他に最小コントラクトや最小ロットサイズを考慮する必要はありません。
よくあるご質問: FXTraderではどのように注文を発注するのですか?
ピップ値について
ピップ値とは、通貨ペアの変化を表す尺度で、ほとんどの通貨ペアでは最小の変化を表します。通貨ペアの中には、少数ピップでの表示が可能なものもあります。
例えば、EUR.USDでは1ピップは0.0001、USD.JPYでは1ピップは0.01となります。
1ピップの値をクオート通貨単位で計算するには、以下の式を適用します。
(取引金額)x (1ピップ)
例:
- ティッカーシンボル = EUR.USD
- 取引金額 = 100,000ユーロ
- 1ピップ = 0.0001
1ピップの価値 = 100’000 x 0.0001= 10 USD
- ティッカーシンボル = USD.JPY
- 取引金額 = 100’000 USD
- 1ピップ = 0.01
1ピップの価値 = 100’000 x (0.01)= 1000円
基準通貨単位で1ピップの価値の計算するには、以下の式を適用します。
(取引金額)x (1ピップ/為替レート)
例:
- ティッカーシンボル = EUR.USD
- 取引金額 = 100’000ユーロ
- 1ピップ = 0.0001
- 為替レート = 1.3884
1ピップの価値 = 100’000 x (0.0001/1.3884)= 7.20ユーロ
- ティッカーシンボル = USD.JPY
- 取引金額 = 100’000 USD
- 1ピップ = 0.01
- 為替レート = 101.63
1ピップの価値 = 100’000 x (0.01/101.63)= 9.84 USD
取引後のポジション表示について
FXポジション情報はIBにおける取引の重要な側面であり、ライブ口座での取引を実行する前に理解しておく必要があります。 IBの取引ソフトウェアはFXポジションを2つの異なる場所に反映させ、その両方を口座ウィンドウから確認することができます。
1. 市場価格
口座ウィンドウの「市場価格」のセクションには、通貨ペアではなく個々の通貨単位で、リアルタイムの通貨ポジションが反映されます。
口座ウィンドウの「市場価格」のセクションは、トレーダーがリアルタイムに反映されたFXポジション情報を見ることができる唯一の場所です。 複数の通貨をFXの通貨ポジションとして保有する場合、ポジションを建てた時と同じ通貨ペアで決済する必要はありません。 例えばEUR.USDの買い(EURの買い、USDの売り)とUSD.JPYの買い(USDの買い、JPYの売い)を行ったトレーダーは、EUR.JPYの取引(EURの売り、JPYの買い)でポジションを決済することができます。
注意事項
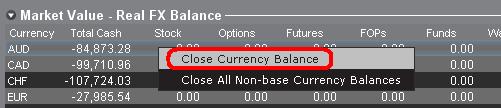
「市場価格」のセクションは拡張/縮小が可能です。 流動性資産価値のコラムのすぐ上に、緑色のマイナスの記号が表示されていることをご確認ください。 緑色のプラス記号が表示されている場合には、一部の保有ポジションが表示されていない可能性があります。
決済したい通貨を右クリックして「選択した通貨残高を口座通貨の残高へ両替」または「基準通貨以外の全ポジションのクローズ」を選択することで、「市場価格」のセクションから決済取引を行うことができます。
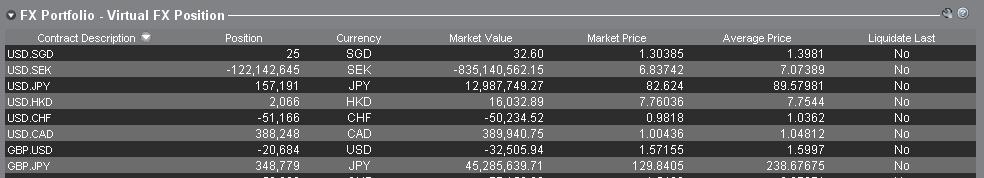
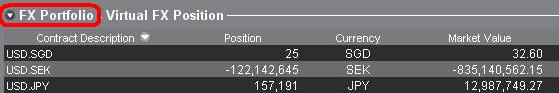
2. FXポートフォリオ
口座ウィンドウのFXポートフォリオのセクションでは、仮想ポジションを表示し、市場価格のセクションのよう個々の通貨ではなく、通貨ペアで表示されます。 この特別な表示方法は機関投資家のFXトレーダーに共通する習慣に合わせたもので、個人やFX取引を頻繁に行わないのトレーダーを対象とするものではありません。FXポートフォリオのポジション表示はすべてのFX取引を反映しているわけではありませんが、ここに表示されるポジション数と平均コストは変更することができます。 実際に取引を行うことなくポジション数と平均コストの情報を変更できるこの機能は、基準通貨に加えて非基軸通貨建ての商品の取引にも携わるトレーダーに向いています。 この機能を利用することにより、基準通貨建て以外の商品を取引する際に自動的に発生する通貨変換の係る取引を、明らかなFX取引と手動で分けて管理することができます。
FXポートフォリオのセクションには、他のすべての取引ウィンドウに表示されるFXポジションと損益情報が表示されます。 このため、実際のリアルタイムのポジション情報を判断するにあたって混乱が生じる傾向があります。 混乱を軽減また解消するため、下記の作業のいずれかを行っていただくことをお薦めします。
a. FXポートフォリオのセクションを非表示にする
「FXポートフォリオ」の左側にある矢印をクリックすると、FXポートフォリオのセクションを折りたたむことができます。 このセクションを折りたたむと、すべての取引ページにFXのバーチャルポジションの情報が表示されなくなります。(注意事項: FXポートフォリオの情報のみ表示されなくなり、市場価値の情報は表示されます。)
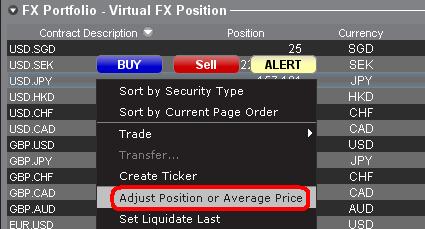
b. ポジションまたは平均価格の調整
口座ウィンドウのFXポートフォリオのセクションを右クリックすると、ポジションまたは平均価格を調整するオプションがあります。 非基準通貨によるポジションをすべて決済し、市場価格のセクションでも決済が確認できたら、ポジションおよび平均価格の欄を0にリセットすることができます。 この調整を行うことにより、FXポートフォリオのセクションに反映されるポジション数がリセットされ、画面上でより正確なポジションと損益情報を見ることができるようになります。注意事項: この作業は手動になるため、通貨ポジションが決済されるたびに行う必要があります。 ポジションに関する情報は常に市場価格のセクションからご確認の上、発注された注文のポジションがご希望通りに建ち、また決済されていることをご確認ください。
上記の内容をご参考にしていただき、ライブ口座でお取引を始める前にペーパー取引口座、またはデモ口座でFX取に慣れていただくことをお薦め致します。 上記の内容についてご不明な点などございましたら、お気軽にIBまでお問い合わせください。
その他のよくあるご質問:
Leveraged FX Currency Restrictions for Israeli Retail Clients
Due to a June 2018 ruling by the Israeli financial court, Interactive Brokers is no longer permitted to offer spot forex trading to Israeli retail clients. While IBKR's forex offering is a deliverable "spot" transaction, the ruling interpreted a 2014 amendment to Israeli Securities Law 5728-1968 to cover spot/cash transactions in addition to derivative/contract style transactions.
- Forex transactions that would create a negative balance or would increase a pre-existing negative balance in either component currency will not be allowed to Israeli retail clients.
- The negative cash balance test applies only to the component currencies and for the cash movements created directly by the forex trade. There is no restriction regarding the creation of negative balances by other means such as cashiering activity or trading activities in securities (stocks, bonds, options, etc).
| Currency | Cash | Cash |
| ILS | 10,000 | 10,000 |
| USD | 1,000 | -2,510 |
| EUR | 0 | 3,000 |
USD -2,000.
| Currency | Cash | Stock | Cash | Stock |
| USD | 1,000 | 0 | -2,000 | 3,000 |
Example: Having USD 1,000 and converting to ILD, value of ILS 3,600 (1 USD = 3.6 ILS)
|
Currency
|
Cash
|
Cash
|
|
ILS
|
0
|
3,600
|
|
USD
|
1,000
|
0
|
|
Currency
|
Cash
|
Cash
|
|
EUR
|
0
|
-600
|
|
USD
|
1,000
|
1,000
|
Procedure
In order to be consider a "Qualified Investor" IB requires client to meet the following criteria and procedural requirements.
Qualified Investor qualification need to be recertified every 3 years.
For Individuals
Individuals, which comply with at least one of the following alternatives:
- Total value of Liquid Assets greater than NIS 8 million; or
- Annual income in each preceding two years is greater than NIS 1.2 million or the income of the Household to which he belongs is greater than NIS 1.8 million.; or
- Total value of Liquid Assets greater than NIS 5 million and the annual income in each proceeding two years is greater than NIS 600,000 or such annual income of the Household to which he belongs is greater than NIS 900,000.
"Liquid Assets" means cash, deposits, securities, equities and funds.
"Household" means an individual and the persons living with him or who are dependent on him for their living.
The client must:
- compete the Qualified Investor Representation form and
- provide a written signed confirmation from a registered attorney or accountant certifying their qualification. This certification should be no older than 3 months.
For Corporates
The following entities can be exempted:
- Authorized mutual funds or fund managers
- Provident funds or fund managers
- Insurers
- Banking corporations
- Portfolio managers
- Investment advisors, who acquire for themselves
- Stock Exchange members
- Underwrites, who buy for themselves
- Venture capital funds
- Corporations (including funds, partnerships) other than corporations which were incorporated for the purpose of purchasing securities in a specific offer, with equity exceeding 50 million NIS
- Corporations, wholly owned by one of the aforementioned investors
Entities qualifying under exemptions 1-9 must provide confirmation of their status from a governmental register.
Entities that wish to be considered under exemptions 10 and 11 must:
- complete the Qualified Investor Representation form and
- provide a written signed confirmation from a registered attorney or accountant certifying their qualification. This certification should be no older than 3 months.
Forex Execution Statistics
IBKR clients can now analyze the quality of their forex executions in comparison to forex trades by other IBKR customers through the FX Browser tool in Client Portal. The tool provides transaction data for the 15 forex transactions that occur immediately before and after in the same currency pair of the client's transaction.
Note:
The number of transactions may be limited to fewer than the stated 15 as the NFA also has placed a 15 minute window on the query. Meaning, if within a 15 minute window before and after the customer's execution there are fewer than 15 executions the customer's query will return only those executions which occurred within the time window.
Accessing the FX Browser Tool
To Access the FX Browser tool, login to Client Portal using the Login button on our website. Click the Help menu (question mark icon in the top right corner) followed by Support Center. Please note, at this time only data for the live account will be provided.
.png)
From there, select "See Trades on IBKR's FX Platform" from the list of Information & Tools:

Submitting a Query
When the FX Browser is launched, you will be presented with the following screen:
Please note that only Trade Date is a mandatory field in the query. When clicking on the Trade Date field, a calendar widget will populate and allow you to select your trade date. Only transactions from the last 6 months will be available to search.
Active customers may wish to limit the results by further selecting the currency pair, side or time of the execution.
Once the desired query has been entered, click on the Submit button.
The next screen will display the list of executions for the given account on the specified day. From there, you may select the execution you wish to receive the execution statistics on.
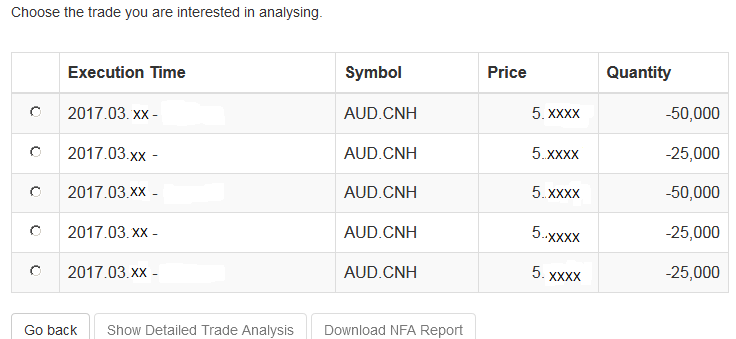
Once the execution you wish to view has been selected, click the "Download NFA Report" button.

Reading the Report
The results will be returned in a new tab and will contain the 15 executions before and 15 executions after the trade you selected on the previous screen. Per the note above, if fewer than 15 executions occurred in the 15 minute time frame only those executions will be displayed.
The query results will include the following information:
- Execution date and time, as expressed in Eastern time
- Side (buy or sell)
- Quantity (of Transaction Currency)
- Currency pair
- Execution price
- Commissions and other charges assessed by the FDM
- Currency denomination of commissions
Your trade will be marked as Trade Number "0" and the trades before and after your trade will be numbered from 1 to 15.
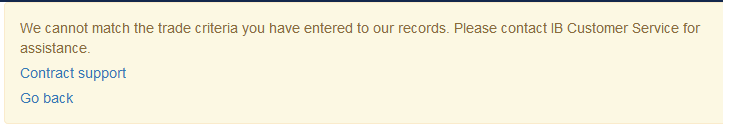
Error Messages
If the search criteria you enter does not bring up any trade information, you will be presented with the following error message:
インタラクティブ・ブローカーズ証券株式会社発行のFXCFDに関するリスク概要
このサマリーは店頭外国為替証拠金取引(“IB FXCFD"取引)に係わる重要なリスクを明確にするものです。規制を目的とするリスク開示書ではありません。
- IB FXCFD取引はすべての投資家のお客様に適したものではなく、お客様の知識や取引経験などをご考慮のうえ、ご自身が高いリスクを許容しうる投資経験や損失に耐えうる財産状況にない場合には、取引を取りやめるなど、ご自身の判断と責任において投資判断をされるようお願いいたします。
- 外国為替レートおよび金利レートのボラティリティーにより短時間で多額な損失が生じる可能性があります。FXCFDにはお客様の投資に係わるボラティリティーをさらに拡大させるレバレッジがかかっているため、投資額以上の損失が生じる可能性があります。IB FXCFDのロールオーバー金利はまた、金利レートの変動により受け取りから支払いに転じることがあります。
- 必要なIB維持証拠金を十分に補う資産が、いつでも口座に入っている必要があります。猶予期間はなく、当社はマージンコールの請求を行いません。資産はリアルタイムで計算され、これが不足した場合、当社では速やか、かつ自動的にポジションの強制決済を行って口座の証拠金不足を解消します。リアルタイムの強制決済は口座内の資産がマイナスになるリスクの最小化を目的としていますが、このリスクを取り除くことはできません。資産がマイナスになった場合には、不足分を補うために資金の追加が必要になります。
- 当社が提示するIB FXCFD取引の取引価格は現行の通貨市場に基づくものですが、この価格によって取引が約定されることを保証するものではありません。大きな数量の取引の場合、為替レートが素早く変動する市場において、また取引量が多い時間帯においてはスリッページが発生する可能性があります。
- またはお取引がタイミング良く行われるとの保障もありません。主要国の休日や取引が活発でない時間帯においては、取引レートの提示が困難になる場合があります。当社が表示する取引価格は、システムの不具合や故障など、あるいは当社が他の市場参加者などより受け取る価格情報の誤りなどの様々な理由により、市場価格から乖離する可能性があります(オフマーケット・プライス)。当社はオフマーケット・プライスにてお客様の取引が約定された場合、その内容を訂正する、あるいは取り消すことがあります。
- IB FXCFDは、お客様と当社との相対取引です。金融商品取引所で取引されるものではなく、また決済機関による決済もありません。従ってお客様は、当社の財務状況の変化などにより損失を被る可能性があります。
この概要の記載事項に関しご質問などございましたら、当社クライアント・サービスまでご連絡ください。またお取引にあたってはリスク開示書を良くお読みください。リスク開示書は当社のウェブサイト上、およびIB FXCFDの取引許可をリクエストしていただきますと、アカウント・マネジメントからもご確認いただけるようになります。
Automatic Forex Swap
OVERVIEW
In general, interest on account balances are credited/debited at benchmark rates plus/minus a spread as shown on our web pages. For qualified clients with substantial forex positions, however, IB has created a mechanism to carry large gross FX positions with higher efficiency with respect to carrying costs. We refer to it as the “auto swap program”. The design allows clients to benefit from IB’s participation in the interbank forex swaps market where implied interest rate spreads are usually much narrower than the spreads available in the retail deposit market.
a. Concept
Interest is charged on settled balances, so the intent of a Forex swap as used here is to defer the settlement of a currency position from one day to the next business day. This is done by a simultaneous sell and buy of the same amount of base (first) currency but for two different value dates e.g. on T you go long 10 mio. EUR.USD for value date T+2. By example, on T+1 the position is swapped T+2 to T+3, here a sell of 10 mio EUR.USD for T+2 and a purchase of 10 mio. EUR.USD for T+3. As a result you have deferred settlement from T+2 to T+3, with the difference in prices of the two trades representing the financing cost from T+2 to T+3.
b. Cost
This service is provided as a free service and no commission or markup is charged by Interactive Brokers. The interbank market bid/ask spread inherent in the swap prices may be regarded as a cost but is not determined by Interactive Brokers. Interactive Brokers provides the service on a best efforts basis to our large Forex clients.
c. Position Criteria
Swap activity is only applied to accounts with gross FX positions larger than 10 mio. USD or approximate equivalent of other currencies. Positions are swapped (rolled) in increments or multiples of USD 1 mio. (or equivalent). The residual settled balances are traded under IB‘s standard interest model1. Positions that are swapped (rolled) are real positions, i.e. the projected T+1 settled cash balances.
The so-called “Virtual Positions” are not considered; the virtual position is only a representation of the original trades expressed as currency pairs, for example EUR.CHF.
Settled cash balances are a single currency concept, e.g. EUR or CNH. IB executes all swaps against USD as it is the most efficient funding currency. Should you have a position in a cross, e.g. EUR against CHF, two swaps, one in EUR.USD and one in USD.CHF will be done. The threshold(s) and increment(s) may change at any time without notice.
d. Client Eligibility
As we offer this service for free, only clients with substantial currency positions are eligible for inclusion in the service. US legal residents need to be an Eligible Contract Participant (ECP) and be in the possession of an LEI number (legal entity identifier). Interactive Brokers cannot guarantee a client’s inclusion in the program and all inquiries require compliance approval prior to become active.2
e. Swap Price Recognition
Interactive Brokers may conduct a series of swaps in a currency during a day. Interactive Brokers will use average bid and ask prices at which it executed, respectively average bid and asks as quoted in the interbank market. Swap prices are not published but can be seen (or calculated) in the statement after execution. The swaps are applied in the account at the end of the day.
f. Recognition in the Statement
You will find the swap transaction(s) in the Trades section of the statement. The swap are represented as simultaneous purchase/sale or vice versa, do not have a time stamp and shows an M (manual entry) in the code column. The actual swap prices are the difference in between the two prices.
Here an example for cob 20150203 that shows a swap from 20150203 to 20150204.
![]()
.jpg)
g. Examples of Swap Prices
Here a couple of examples that use swap prices from a major interbank provider. Often bid/ask spreads are even tighter.
|
Currency Pair |
Spot Bid |
Spot Ask |
Tenor |
Days in Period (TN) |
Swap Points Bid |
Swap Points Ask |
Implied Currency |
Implied Rate Bid |
Implied Rate Ask |
|
EUR.USD |
1.04481 |
1.04483 |
TomNext(TN) |
1 |
0.00004220 |
0.00004280 |
EUR |
-0.77% |
-0.75% |
|
USD.HKD |
7.76810 |
7.76810 |
TomNext(TN) |
1 |
-0.00011500 |
-0.00011000 |
HKD |
0.17% |
0.19% |
|
USD.JPY |
117.050 |
117.052 |
TomNext(TN) |
1 |
-0.0038 |
-0.0032 |
JPY |
-0.47% |
-0.47% |
|
USD.CNH |
6.93101 |
6.93105 |
TomNext(TN) |
1 |
0.0021 |
0.0028 |
CNH |
11.77% |
15.46% |
In more detail, let’s assume you want to calculate the implied CNH rate resulting from a USD.CNH swap. We are looking for the implied rate of the quote currency CNH (Currency 2). Therefore the following formula is used:
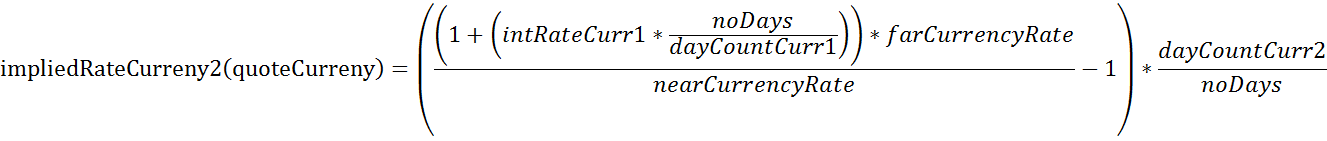
| Description | Variable | Value |
| Currency Pair (Currency1.Currency2) | USD.CNH | |
| day count convention Currency 1 (base Currency), i.e. USD | dayCountCurr1 | 360 |
| day count convention Currency 2 (quote Currency), i.e. CNH | dayCountCurr2 | 365 |
| Tenor | TomNext | |
| number of days in the Tenor | noDays | 1 |
| interest rate of Currency 1 (in decimals, i.e. 1% = 0.01) | inRateCurr1 | 0.0070 |
| Currency rate (Spot) | currencyRate | 6.939500 |
| swap Points expressed in decimals | swapPoints | 0.0012 |
| near Currency Rate (Spot - swap points) | nearCurrencyRate | 6.938300 |
| far Currency Rate (in a Tomnext swap this is the spot rate) | farCurrencyRate | 6.939500 |
| implied interes rate of Currency2, i.e. CNH | impliedRateCurrncy2(quoteCurrency) | 0.0702 |
So using above figures, this results in a 7.02% implied interest rate for CNH.
Now if you wanted to calculate the implied rate for the base currency (Currency 1) the formula would change slightly. Here an example using EUR.USD:
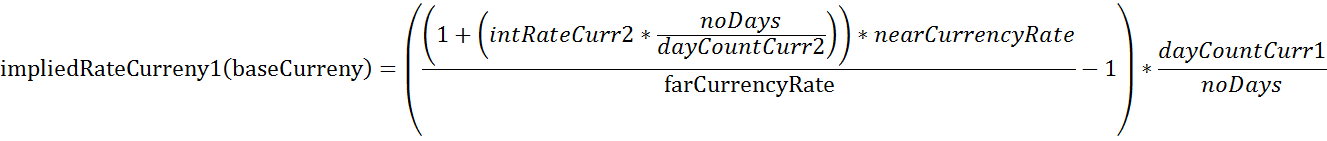
| Description | Variable | Value |
| Currency Pair (Currency1.Currency2) | EUR.USD | |
| day count convention Currency 1 (base Currency), i.e. EUR | dayCountCurr1 | 360 |
| day count convention Currency 2 (quote Currency), i.e. USD | dayCountCurr2 | 360 |
| Tenor | TomNext | |
| number of days in the Tenor | noDays | 1 |
| interest rate of Currency 2 (in decimals, i.e. 1% = 0.01) | inRateCurr2 | 0.0070 |
| Currency rate (Spot) | currencyRate | 1.039900 |
| swap Points expressed in decimals | swapPoints | 0.000042 |
| near Currency Rate (Spot - swap points) | nearCurrencyRate | 1.039858 |
| far Currency Rate (in a Tomnext swap this is the spot rate) | farCurrencyRate | 1.039900 |
| implied interes rate of Currency1, i.e. EUR | impliedRateCurrncy1(baseCurrency) | -0.0075 |
Using above example, this results in a -0.75 % implied interest rate for EUR.
1. For example, in the case of a USD 20.3 mio. position only 20 mio. will be swapped. USD 0.3 remains in the account and interest using benchmark and spreads will be applied. A USD 300k position will not be considered for swapping at all. The position by currency is taken as the reference, regardless of the overall position.
2 US, Australian and Israeli domiciled residents are currently not eligible for inclusion in the Automated Forex Swap Program.
Summary of Risks relating to Forex CFDs issued by Interactive Brokers Securities Japan, Inc.
This summary highlights the principal risks associated with trading Forex CFDs issued by IBSJ (“IB FXCFDs"). It is not a risk disclosure for regulatory purposes.
- Trading of IB FXCFDs is not suitable for all investors, and you should not trade them unless you are an experienced investor with a high risk tolerance and the capability to sustain losses if they occur
- The volatility of foreign exchange rates and interest rates may quickly cause significant losses. Forex CFDs employ leverage that further amplifies the volatility relative to your investment and you may lose more than you have invested. In addition, IB FXCFD roll over interest may turn from a credit to a debit due to changes in interest rates
- You are required to maintain sufficient equity in your account at all times to cover IBSJs maintenance margin requirement. There are no grace-periods and IBSJ does not issue margin calls. Your equity is calculated in real time and should it become insufficient, IBSJ will immediately and automatically liquidate positions to bring your account into margin compliance. Real time liquidations aim to minimize the risk that your account equity becomes negative, but they cannot eliminate that risk. Should your equity become negative you are required to deposit additional funds to cover the deficit
- The price IBSJ displays to you for IB FXCFDs is based on the prevailing foreign exchange market. However there is no guarantee for executions at that price. Slippage may occur for large trades or in fast moving markets and during heavily traded hours
- Moreover, your ability to establish or close positions on a timely basis is not guaranteed. It may become difficult to display quotes during major holidays or during hours when foreign exchange trading is not active. IBSJ may display prices that deviate from a fair market due to system-malfunctions or failures, or erroneous quotes that IBSJ may receive from market participants or for other reasons (off-market prices). IBSJ will adjust or cancel trades executed with off-market prices
- IB FXCFDs are over-the-counter trades between you and IBSJ. They are not traded on any exchange or cleared by any central counterparty. You are therefore exposed to counterparty risk and should IBSJ become insolvent you may not be able to fully recoup your investment, or at all
Please contact IBSJs Client Service Department should you have questions about the content of this summary and read the full risk disclosure carefully before commencing trading. The risk disclosure is available in Account Management when you request IB FXCFD trading permissions, and on IBSJs web site.
IB Forex CFD - 詳細およびQ&A
リスク警告
CFDはレバレッジによる損失のリスクが高い複雑な商品です。
62%の個人投資家口座に、IBKR(UK)とのCFD取引による損失が発生しています。
お取引を開始される前に、CFDの機能の仕方および損失の際のリスクをご理解ください。
CFDに関わるESMAルール(リテールクライアントのみ)
欧州証券市場監督局(ESMA)は2018年8月1日より有効となるCFDルールを実施しました。
ルールには以下が含まれます: 1) CFDのポジションを建てるにあたってレバレッジの上限; 2) 口座ごとの証拠金解約; および 3) マイナス残高に対する口座ごとの保護。ESMAによる決定はリテールクライアントのみに適用されます。
特定投資家のお客様への影響はありません。
詳細はIBKRにおけるESMA CFDルールの実施をご参照ください。
IBKR Forex CFDの特徴
透明性の高いDMSクオート:弊社ではグローバルインターバンク市場のマーケットシェア70%を占める14の世界最大級の為替ディーラーによるレート表示により、最小の変動スプレッドと高い流動性を確保しています。*これが0.1PIPまで表示した価格クオートを可能にしています。IBではクオートのマークアップはせず、 低額の約定手数料とその他の諸費用を直接お客様にパススルーしております。
*出典: Euromoney FX survey FX Poll 2016。
例:2016年4月21日の英ポンドのベンチマーク・レートは0.483%、米ドルのベンチマーク・レートは0.37%でした。適用されるベンチマーク・レートは:
英ポンド・米ドルBM +0.48% - 0.37% = +0.113%
適用される顧客レートは、ロング・ポジションに対しペアBM – IBスプレッド、 ショート・ポジションに対しBM + スプレッドとなり:
GBP.USD ロング・レート +0.113% - 1.00% = -0.887%
GBP.USD ショート・レート +0.113% + 1.00% = +1.113%
ロング・レートは受取り、ショート・レートは支払いとして適用されます。この結果、ロング・ポジションに対するプラスのレートは受取り、マイナスのレートは支払いとなりますが、ショート・ポジションに対するプラスのレートは支払い、マイナスのレートは受取りとなります。
金利はクオート通貨で表示された取引価値に対して計算され、この通貨で受取りまたは支払いがされます。 具体例
具体例
| 日次の金利 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ポジション | GBP.USD クローズ | 米ドル価値 | レート | USD | |
| GBP.USD | -20,000 | 1.43232 | -28,646.40 | 1.113% | -0.89 |
Forex CFDのバランスに対する金利は各取引ごと別々に計算され、Spot FXを含めるその他の通貨エクスポージャーと組み合わせる、または 足し引きされるものではありません。IBでは直接スワップ・レートを参照することはありませんが、事業年度末などスワップ・レートが大きく変動する時期などの例外的なマーケット状況においては、スプレッドを上げる権利を 有します。
取引例(プロフェッショナル・クライアント)
ポジションのオープン
EUR.CHF CFDを10ロット(200000)$1.16195で総額CHF 232,390分購入し、5日間保有します。
| EUR.CHF Forex CFD – 新規ポジション | |
|---|---|
| 参照原資産価格 | 1.16188 - 1.16195 |
| CFD参照価格 | 1.16188 - 1.16195 |
| アクション | 買い |
| 数量 | 200,000 |
| 取引価値 | CHF 232,390.00 |
| 証拠金(3% x 232,390) | AUD 9,100 |
| 金利額(CHF 232,390に対して5日間) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ティア I(ペアBM 0.42% - IBスプレッド1%) | CHF 232,390.00 | -0.58% | (CHF 18.72) |
ポジションのクローズ
| CFDポジションをクローズ | ||
|---|---|---|
| 収益シナリオ | 損失シナリオ | |
| 参照原資産価格 | 1.16840 - 1.16848 | 1.15539 - 1.15546 |
| CFD参照価格 | 1.16840 - 1.16848 | 1.15539 - 1.15546 |
| アクション | 売り | 売り |
| 数量 | 200,000 | 200,000 |
| 取引価値 | CHF 233,680.00 | CHF 231,078.00 |
| 取引損益 | CHF 1,290.00 | (CHF 1,312.00) |
| 金利 | (CHF 18.72) | (CHF 18.72) |
| エントリー手数料0.002% | (CHF 4.65) | (CHF 4.65) |
| エントリー手数料0.002% | (CHF 4.67) | (CHF 4.62) |
| 損益合計 | CHF 1,261.96 | (CHF 1,339.99) |
CFDのリソース
以下はIB提供のCFDに関する詳細を記載したリンクです:
よくあるご質問
誰でもIB Forex CFDの取引はできますか?
米国、カナダおよび香港以外の国の居住者はIB CFD取引が可能です。居住地に基づいて設定される例外で、特定の投資家タイプに適用されるものはありません。
IB Forex CFDとIB Cash Forexの違いは何ですか?
IB Cash Forexは、ペアを構成する2通貨の受渡を取るレバレッジのかかったキャッシュ取引です。Forex取引に関連するバランスはお客様のその他のアクティビティから発生するバランスと組み合わされ、お客様には統合されたバランスに対し、各通貨のベンチマーク・レートに基づいて計算された金利をお支払またはお受け取りいただきます。
これに対し、IB Forex CFDにはエクスポージャーはありますが原資産通貨の引渡しはないため、お客様には取引の想定元本に対しての金利をお支払またはお受け取りいただきます。取引に対するベンチマークは2つの原資産通貨に対するベンチマーク・レートの差異です。これは基本的には他のブローカーの利用するTOM Next rollsに似ていますが、 ベンチマーク・レートはスワップ・レートに比べて変動が少ないため、安定性がより高くなります。
詳細は上記の持ち越し金利に関する項目をご覧ください。
必要なマーケットデータはありますか?
IB Forex CFD用のマーケットデータはレバレッジFXのものと同じです。 グローバル許可のひとつであり無料でご利用いただけます。
CFD取引およびポジションはステートメントにどのように表示されますか?
IB LLCの口座をお持ちの場合、 CFDポジションは主要口座番号の末尾に「F」を追加した形で別の口座セグメントに維持されます。アクティビティー・ステートメント上のFセグメントは、別途またはメイン口座と合わせて表示することができます。選択は アカウント・マネジメントのステートメント画面より可能です。
Forex CFDにはSpot FXと同じ注文タイプとアルゴリズムが使えますか?また取引はFX Traderからできますか?
はい。取引方法は同じです。
Allocation of Partial Fills
How are executions allocated when an order receives a partial fill because an insufficient quantity is available to complete the allocation of shares/contracts to sub-accounts?
Overview:
From time-to-time, one may experience an allocation order which is partially executed and is canceled prior to being completed (i.e. market closes, contract expires, halts due to news, prices move in an unfavorable direction, etc.). In such cases, IB determines which customers (who were originally included in the order group and/or profile) will receive the executed shares/contracts. The methodology used by IB to impartially determine who receives the shares/contacts in the event of a partial fill is described in this article.
Background:
Before placing an order CTAs and FAs are given the ability to predetermine the method by which an execution is to be allocated amongst client accounts. They can do so by first creating a group (i.e. ratio/percentage) or profile (i.e. specific amount) wherein a distinct number of shares/contracts are specified per client account (i.e. pre-trade allocation). These amounts can be prearranged based on certain account values including the clients’ Net Liquidation Total, Available Equity, etc., or indicated prior to the order execution using Ratios, Percentages, etc. Each group and/or profile is generally created with the assumption that the order will be executed in full. However, as we will see, this is not always the case. Therefore, we are providing examples that describe and demonstrate the process used to allocate partial executions with pre-defined groups and/or profiles and how the allocations are determined.
Here is the list of allocation methods with brief descriptions about how they work.
· AvailableEquity
Use sub account’ available equality value as ratio.
· NetLiq
Use subaccount’ net liquidation value as ratio
· EqualQuantity
Same ratio for each account
· PctChange1:Portion of the allocation logic is in Trader Workstation (the initial calculation of the desired quantities per account).
· Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user
· Inline Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user.
· Model1:
Roughly speaking, we use each account NLV in the model as the desired ratio. It is possible to dynamically add (invest) or remove (divest) accounts to/from a model, which can change allocation of the existing orders.
Basic Examples:
Details:
CTA/FA has 3-clients with a predefined profile titled “XYZ commodities” for orders of 50 contracts which (upon execution) are allocated as follows:
Account (A) = 25 contracts
Account (B) = 15 contracts
Account (C) = 10 contracts
Example #1:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 10 am (ET) the order begins to execute2but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 2 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 7 of the 50 contracts are filled or 14%). For each account the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 14% of 25 = 3.5 rounded down to 3
Account (B) = 14% of 15 = 2.1 rounded down to 2
Account (C) = 14% of 10 = 1.4 rounded down to 1
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.10).
A: final allocation of 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 2 contract, which is 2/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.20)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #2:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be filled3 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 1 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is executed (i.e., 5 of the 50 contracts are filled or 10%).For each account, the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 10% of 25 = 2.5 rounded down to 2
Account (B) = 10% of 15 = 1.5 rounded down to 1
Account (C) = 10% of 10 = 1 (no rounding necessary)
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. to Account B which currently has a ratio of 0.067).
A: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #3:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be executed2 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 12 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 3 of the 50 contracts are filled or 6%). Normally the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers, however for a fill size of less than 4 shares/contracts, IB first allocates based on the following random allocation methodology.
In this case, since the fill size is 3, we skip the rounding fractional amounts down.
For the first share/contract, all A, B and C have the same initial fill ratio and fill quantity, so we randomly pick an account and allocate this share/contract. The system randomly chose account A for allocation of the first share/contract.
To Summarize3:
A: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
C: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
Next, the system will perform a random allocation amongst the remaining accounts (in this case accounts B & C, each with an equal probability) to determine who will receive the next share/contract.
The system randomly chose account B for allocation of the second share/contract.
A: 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
The system then allocates the final [3] share/contract to an account(s) with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.00).
A: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Available allocation Flags
Besides the allocation methods above, user can choose the following flags, which also influence the allocation:
· Strict per-account allocation.
For the initially submitted order if one or more subaccounts are rejected by the credit checking, we reject the whole order.
· “Close positions first”1.This is the default handling mode for all orders which close a position (whether or not they are also opening position on the other side or not). The calculation are slightly different and ensure that we do not start opening position for one account if another account still has a position to close, except in few more complex cases.
Other factor affects allocations:
1) Mutual Fund: the allocation has two steps. The first execution report is received before market open. We allocate based onMonetaryValue for buy order and MonetaryValueShares for sell order. Later, when second execution report which has the NetAssetValue comes, we do the final allocation based on first allocation report.
2) Allocate in Lot Size: if a user chooses (thru account config) to prefer whole-lot allocations for stocks, the calculations are more complex and will be described in the next version of this document.
3) Combo allocation1: we allocate combo trades as a unit, resulting in slightly different calculations.
4) Long/short split1: applied to orders for stocks, warrants or structured products. When allocating long sell orders, we only allocate to accounts which have long position: resulting in calculations being more complex.
5) For non-guaranteed smart combo: we do allocation by each leg instead of combo.
6) In case of trade bust or correction1: the allocations are adjusted using more complex logic.
7) Account exclusion1: Some subaccounts could be excluded from allocation for the following reasons, no trading permission, employee restriction, broker restriction, RejectIfOpening, prop account restrictions, dynamic size violation, MoneyMarketRules restriction for mutual fund. We do not allocate to excluded accountsand we cancel the order after other accounts are filled. In case of partial restriction (e.g. account is permitted to close but not to open, or account has enough excess liquidity only for a portion of the desired position).
Footnotes:
Additional Information Regarding the Use of Stop Orders
U.S. equity markets occasionally experience periods of extraordinary volatility and price dislocation. Sometimes these occurrences are prolonged and at other times they are of very short duration. Stop orders may play a role in contributing to downward price pressure and market volatility and may result in executions at prices very far from the trigger price.