空売り株式からの収益に対する利息
株式借入ポジションに関連する利息または費用の割り出し方
口座保有者が株式を空売りする場合、IBKRでは購入者に株式を引き渡す義務を履行するため、口座保有者に変わって同額の株式の借入を行います。 株式の借入を行うための株式借入に関する同意書は、IBKRが株式の貸し手に対し、借入のための現金担保を提供することを義務としています。 現金担保の金額は、担保マークと呼ばれる、株価の業界標準計算に基づいています。
株式の貸し手は、現金担保の利息をIBKRに提供し、また現金担保預金の実勢市場金利(通常、米ドル建て現金預金に対するフェデラル・ファンド実行金利に固定されています)よりも低い金額に支払われる利息を調整することによって、このサービスを提供することに対する手数料を請求します。 借入困難な銘柄の場合、株式提供に対する貸し手の手数料により、IBKRにマイナス金利が請求される可能性があります。
多くの証券会社ではこのリベートの一部を機関投資家にのみパススルーしますが、IBKRではすべてのお客様に対し、 USD 100,000または他通貨での同等額を超える空売り株式の売却収益に対して利息をお支払いしています。借入可能な証券の供給が借入需要に対して多い場合、口座保有者は、ベンチマーク・レート(例:米ドル建て残高に対するフェデラル・ファンドによるオーバーナイト実行金利)からスプレッド(現在、USD 100,000の残高に対して1.25%、USD 3,000,000以上の残高に対して0.25%の範囲)を差し引いた額と同額の空売り株式残高に対する利息の受け取りを期待できます。レートは予告なく変更される可能性があります。
特定の銘柄の需要と供給の属性によって銘柄が借入困難になる場合、貸し手が提供するリベートが減少し、口座に対する請求が発生する可能性があります。リベートまたは請求は、より高い借入手数料として口座保有者にパススルーされ、これが空売り収益の利息を上回り、口座に対する請求となる可能性があります。レートは銘柄と日付の両方に左右されるため、IBKRでは、クライアントポータル/アカウント・マネジメントからアクセス可能な空売り可能株式ツールを使用して、空売りに対する指標レートをご確認いただくことをお勧めします。ツールに表示される指標レートは、IBKRがTier IIIの残高に対して支払う空売り収益利息、つまり300万米ドル以上の空売り収益にも適用されることにご留意ください。残高が少ない場合、レートは取引通貨に関連するティアおよびベンチマークレートに基づいて調整されます。正確なレートは、「空売り(ショートセル)の売却代金の現金に対する受取金利計算機能」からご確認いただけます。
その他の例や計算機能は、有価証券ファイナンシングのページをご参照ください。
ご留意事項
空売り可能株式ツール及びTWSで提供される、借入可能な株式及び指標レートに関する情報は、正確性または有効性に関する保証なしに、ベストエフォートベースで提供されます。空売り可能株式には、リアルタイムで更新されない、サードパーティからの情報が含まれます。レートに関する情報はあくまでも目安です。現在の取引セッションで約定される取引は通常、2営業日で決済され、実際の借入可能株式と借入にかかるコストは決済日に決定されます。取引が特に少ない株式、小型株、および今後のコーポレートアクション(配当を含め)がある株式クラスの場合、取引日から決済日までの間にレートと利用可能株が大幅に変化する可能性があることにご注意ください。詳細は、空売りにかかる運用リスクをご参照ください。
IBKR株式利回り向上プログラム
プログラム概要
株式利回り向上プログラムでは、お客様の口座にある全額支払い済みの株式を、弊社が担保(米国国債または現金)と引き換えにお客様から借受け、金利を支払ってこれを借受けて空売りを希望するトレーダーに貸出しすることによって、追加収入を得ることができます。株式利回り向上プログラムに関する詳細はこちらより、またはよくあるご質問のページをご参照ください。
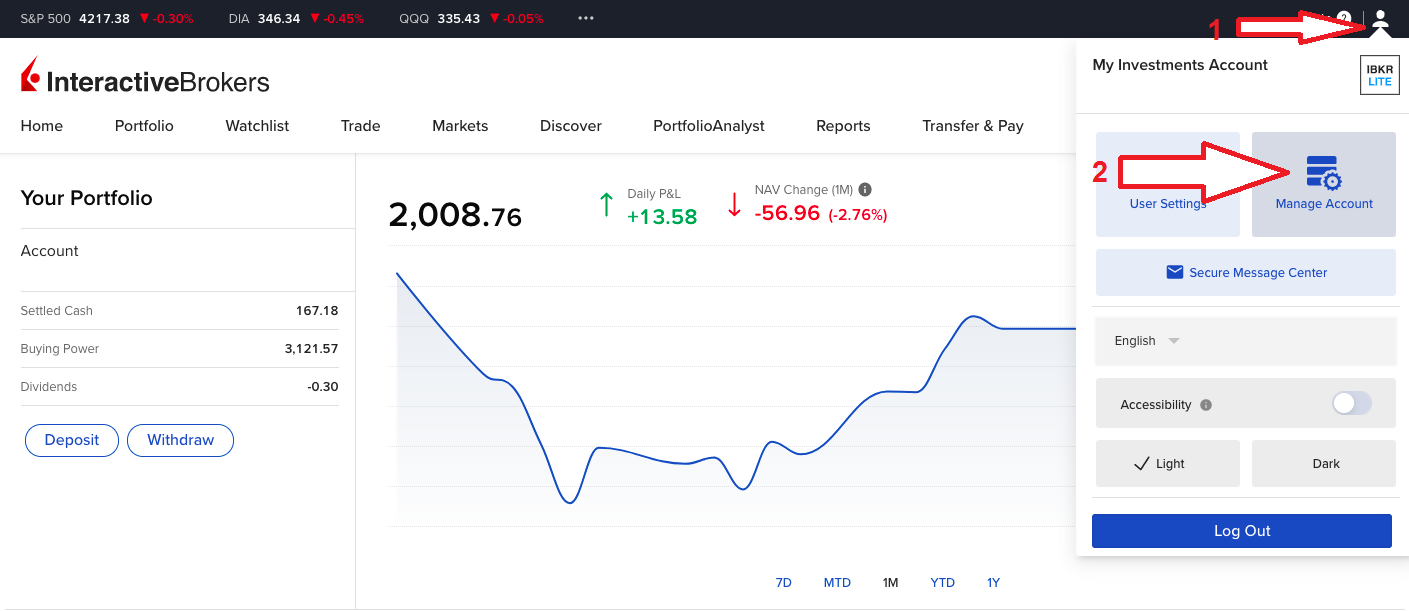
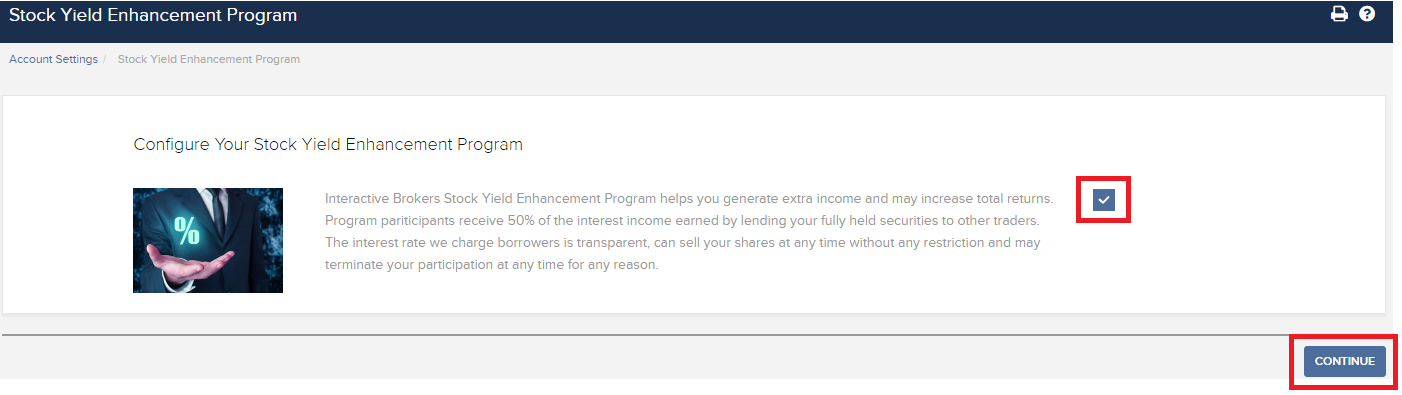
お申込みには、クライアント・ポータルにログインしてください。ログインしたらユーザーメニュー(右上にある人型のアイコンです)をクリックしてから、口座管理を選択してください。設定の項目から、株式利回り向上プログラムの横にある「設定」(ギア)のアイコンをクリックしてください。次の画面のチェックボックスを選択して、次に進むをクリックしてください。プログラムへのお申込みにあたって必要となる書類とディスクロージャーが表示されます。フォームをご確認の上でご署名ください。リクエストがお手続きされます。お申込みの完了には24-48時間かかります。
.png)
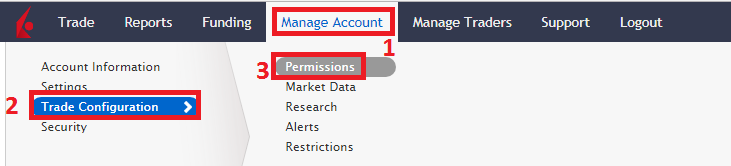
クラシックのアカウント・マネジメントよりお申込みいただく場合には、下記のボタンを指定されている順番にクリックしてください。
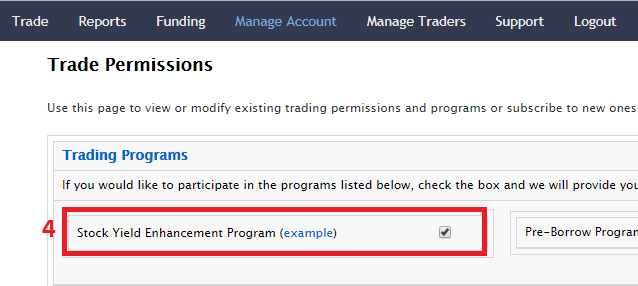
株式利回り向上プログラムに関連してよくあるご質問
株式利回り向上プログラムの目的
株式利回り向上プログラムは、分離管理されている証券ポジション(全額支払い済みや超過証拠金となる株式)をIBKRがサードパーティに貸付することを許可することによって副収入につなげるプログラムです。ご参加されるお客様は、貸付されている株式が終了時に確実に返却されるための担保(米国国債または現金)をお受取りされます。
全額支払済みおよび超過証拠金となる株式とは
全額支払済みの株式とは、口座に保有されている有価証券で完全に支払いの済んでいるものを指します。超過証拠金となる株式とは、支払いの済んでいない株式で、市場価格が証拠金バランスの140%を超えているものを指します。
株式利回り向上プログラムの貸付による取引から発生する収入はどのように計算されますか?
株式の貸付によってお客様に発生する収入は、店頭株式貸付市場の金利によって変わります。金利は貸付される株式の種類だけでなく、貸付日にも大きく左右されます。弊社では通常、参加者のお客様に対し、株式の貸付によって弊社に発生した金額の約50%の利息を担保にお支払い致します。
貸付の担保額はどのように計算されるのですか?
株式の貸付に必要となる金利を決定する担保(米国国債または現金)は、株式の終値に一定の割合(通常102-105%)掛けた上で一番近いドル/セント/ペンス等に切り上げられる、業界協定による方法で設定されます。通貨によって業界協定が異なります。例えば終値がUSD 59.24の株式100株貸付は$6,100に値します($59.24 * 1.02 = $60.4248。これが$61に切り上げられた上で100を掛けたもの)。下記は通貨ごとの業界協定のチャートになります:
| USD | 102%: 一番近いドルに切り上げ |
| CAD | 102%: 一番近いドルに切り上げ |
| EUR | 105%: 一番近いセントに切り上げ |
| CHF | 105%: 一番近いラッペンに切り上げ |
| GBP | 105%: 一番近いペンスに切り上げ |
| HKD | 105%: 一番近いセントに切り上げ |
詳細はKB1146をご確認ください。
株式利回り向上プログラム用の担保はどこにどうやって保有されるのですか?
IBLLCのお客様の担保は米国国債または現金として、IBLLCの関連会社であるIBKR Securities Services LLC(「IBKRSS」)に移管の上で保有されます。本プログラムによる担保はIBKRSSがお客様用の口座に保有し、担保に対する権利は完全にお客様が優先となります。万が一、IBLLCが債務不履行を起こした場合でも、IBLLCを経由せずにIBKRSSを通して直接、担保にアクセスすることができます。詳細はこちらより、証券口座の管理に関する同意書をご参照ください。IBLLCのお客様ではない方の担保は、口座を管理する事業体による保有および保管となります。例えば、IBIE口座の場合、担保はIBIEによる保有および保管となります。
IBKRの株式利回り向上プログラムによって貸付されている株式が売却や移管された場合や、プログラムへの参加をやめた場合にはどのような影響がありますか?
金利は取引が行われた日の翌日(T+1)より発生しなくなります。また、移管やプログラム参加の解約があった場合には、翌営業日より金利が発生しなくなります。
株式利回り向上プログラムへの参加資格はどのようになっていますか?
| 参加資格のある事業体* |
| IB LLC |
| IB UK(SIPP口座は対象外) |
| IB IE |
| IB CE |
| IB HK |
| IB Canada(RRSP/TFSA口座は対象外) |
| IB Singapore |
| 参加対象となる口座 |
| キャッシュ(登録日の時点で資産が最低$50,000であること) |
| マージン |
| ファイナンシャルアドバイザー管理のクライアント口座* |
| 証券会社管理のクライアント口座: Fully DisclosedおよびNon-Disclosed* |
| 証券会社管理のオムニバス口座 |
| セパレート・トレーディング・リミット口座(STL) |
*お申込みされる口座は、マージン口座やキャッシュ口座の必要最低額を達成している必要があります。
こちらのプログラムは、IBジャパン、IBヨーロッパSARL、IBKRオーストラリア、ならびにIBインドのお客様にはご利用いただけません。IB LLCにおける口座をお持ちの日本およびインドのお客様はプログラムにご参加いただくことができます。
また、ファイナンシャルアドバイザー管理のクライアント口座、fully disclosedタイプの証券会社管理のクライアント口座、ならびにオムニバス・ブローカー口座をお持ちのお客様で上記の条件を達成されている方にはご利用いただくことができます。ファイナンシャルアドバイザーおよびfully disclosedタイプの証券会社管理のクライアント口座の場合には、クライアントによる同意書へのサインが必要となります。オムニバス・ブローカー口座の場合には、ブローカーによる同意書へのサインが必要となります。
IRA口座は株式利回り向上プログラムに参加できますか?
できます。
Interactive Brokers Asset Managementの管理によるIRA口座のパーティションは、株式利回り向上プログラムに参加できますか?
いいえ。
UK SIPP口座は株式利回り向上プログラムに参加できますか?
いいえ。
プログラムに参加しているキャッシュ口座の資産が必要額である$50,000を下回った場合にはどうなりますか?
キャッシュ口座に必要となる最低資金額は、プログラムへの参加時点のみに必要となります。それ以降に資金額が下がったとしても、既存の貸付および新規の貸付に対する影響はありません。
株式利回り向上プログラムへはどうやって申込みできますか?
お申込みはクライアント・ポータルからできます。ログインしたら、ユーザーメニュー(右上にある人型のアイコン)をクリックし、設定を選択します。この後、口座設定にある取引の項目の株式利回り向上プログラムをクリックしてお申込みください。プログラムへのお申込みにあたって必要となる書類とディスクロージャーが表示されます。フォームをご確認のうえ、ご署名ください。リクエストがお手続きのために送信されます。お申込みの完了には24-48時間かかります。
株式利回り向上プログラムはどのように解約できますか?
ご解約はクライアント・ポータルからできます。ログインしたら、ユーザーメニュー(右上にある人型のアイコン)をクリックし、設定を選択します。この後、口座設定にある取引の項目の株式利回り向上プログラムをクリックして必要手続きを行ってください。リクエストがお手続きのために送信されます。 解約リクエストは通常、同日の終了時に処理されます。
プログラム参加後に解約した場合、いつからまたプログラムへの参加ができるようになりますか?
プログラム解約後、暦日で90日間はお申込みいただくことができません。
貸付対象となる有価証券ポジションのタイプ
| 米国マーケット | ヨーロッパマーケット | 香港マーケット | カナダマーケット |
| 普通株(上場株式、PINKおよびOTCBB) | 普通株(上場株式) | 普通株(上場株式) | 普通株(上場株式) |
| ETF | ETF | ETF | ETF |
| 優先株 | 優先株 | 優先株 | 優先株 |
| 社債* |
*地方債は対象外です。
IPOに続いて流通市場で取引されている株式を貸付するにあたって何か規制はありますか?
口座に保有される対象証券に規制がない限りありません。
貸付対象となる株数はどうやって割り出されますか?
株式がある場合には先ずこの価値を割り出します。IBKRではこれに対する担保権を保有し、お客様が株式利回り向上プログラムにご参加されていない場合でも貸し出すことができます。お客様が株式を購入する際に証拠金貸付によって融資を行うブローカーは、お客様の株式を現金負債額の140%まで担保として貸出できるよう、規制によって許可されています。$50,000の現金残高を保有するお客様が、市場価格が$100,000の株式を購入するケースを例として見てみます。この場合の貸付高は$50,000となり、ブローカーはこの残高の140%に値する金額または$70,000の株式を担保権として保有します。この金額を超えてお客様が保有する株式は超過証拠金証株式(この例では$30,000となります)とみなされ、株式利回り向上プログラムの一環として弊社がこれの貸付を行うことを許可されない場合には分別管理が必要になります。
負債額はまずUSD建てでない残高をすべてUSDに変換し、この後ショート株式からの収益がある場合にはこれを差し引いて(必要な場合にはUSDに変換し)割り出されます。結果としてマイナスの数値が出る場合には、これの140%までを弊社が確保します。またコモディティのセグメントやスポットメタル、およびCFD用に保有される残高は計算に入りません。 詳細は、こちらをご参照ください。
例 1: USDを基準通貨とする口座において、EUR.USDが1.40の換算レートでEUR 100,000保有しています。USD建てで株価が$112,000(EUR 80,000同等額)の株式を購入します。USDに変換された現金額がプラス残高であるため、株式は全額支払い済みとみなされます。
| 要素 | EUR | USD | 基準(USD) |
| 現金 | 100,000 | (112,000) | $28,000 |
| ロング株式 | $112,000 | $112,000 | |
| 流動性資産価値(NLV) | $140,000 |
例 2: USDで$80,000、USD建てで$100,000のロング株式、そしてUSD建てで$100,000のショート株式を保有しています。合計$28,000のロング株式は証拠金証券、また残りの$72,000は超過証拠金証券とみなされます。これはショート株式の収益を現金残高から差し引き($80,000 - $100,000)この結果となるマイナス残高に140%をかけて算出されます($20,000 * 1.4 = $28,000)。
| 要素 | 基準(USD) |
| 現金 | $80,000 |
| ロング株式 | $100,000 |
| ショート株式 | ($100,000) |
| 流動性資産価値(NLV) | $80,000 |
IBKRでは利用可能な株式すべてを貸付するのですか?
貸付対象となる株式に対する有利なレートを提供するマーケットがない、借手のいるマーケットに弊社がアクセスできない、または弊社が貸付を希望しないなどの理由により、口座内の貸付可能な株式すべてが株式利回り向上プログラムを通して貸付される保証はありません。
株式利回り向上プログラムの貸付は100株単位で行われますか?
いいえ。弊社から外部への貸付は100株単位のみで行っていますが、お客様からの貸付には決まった単位はなく、外部へ100株の貸付が必要となる場合には、1人のお客様からの75株、また別のお客様からの25株をあわせて100株しにて貸付を行う可能性があります。
貸付することのできる株数が必要な株数を上回る場合、貸付は顧客に対してどのように振り分けられるのですか?
プログラムによって貸付可能な株数が借手が必要とする株数を超える場合、貸付は比例計算で割当られます。例えば、プログラムによるXYZ株の合計数が20,000株で、10,000株が必要とされている場合、それぞれのお客様より対象となる株式の50%が貸付されます。
株式の貸付はIBKRの顧客のみにされますか?それともサードパーティにもされるのでしょうか?
株式は、IBKRおよびサードパーティの顧客に貸付されることがあります。
株式利回り向上プログラムの参加者は、IBKRが貸付する株式を指定することができますか?
いいえ。こちらのプログラムは弊社が完全に管理を行うものであり、証拠金ローンの抵当権により弊社が貸付許可を有する貸付可能な証券がある場合、全額支払い済みまたは超過証拠金の株式の貸付が可能かどうか、またこれの開始は弊社の裁量により決定されます。
株式利回り向上プログラムで貸付に出されている株式の売却には何か規制がありますか?
貸付されている株式に規制はなく、いつでも売却することができます。株式は売却にあたって返還の必要はなく、売却からの収益は通常の決済日にお客様の口座に入金されます。貸付は売却日の翌営業日開始時に終了します。
株式利回り向上プログラムで貸付されている株式に対してカバード・コールを売却し、証拠金信用力を受けることはできますか?
できます。貸付されているポジションに関連する損益は株式所有者のものとなるため、株式の貸付によってアンカバードやヘッジベースの必要証拠金に影響はありません。
貸付対象の株式で実際に引渡しが行われたものに対してコールの割当やプットの権利行使が発生した場合にはどうなりますか?
ポジションのクローズまたは減少となるアクションからT+1(取引、割当、権利行使)の時点で貸付停止となります。
貸付の対象となった後で取引が中止された株式はどうなりますか?
取引中止によって株式の貸付機能への直接的な影響はなく、対象株式の貸付が可能である限り、中止に関わらず株式の状態は変わりません。
証拠金や変動をカバーするために貸付による担保をコモディティ口座にスイープすることはできますか?
いいえ。貸付保証のための担保が証拠金などに関わることはありません。
プログラム参加者が証拠金ローンを始める、または既存のローン残高を増やすとどうなりますか?
全額支払い済みの株式をお持ちのお客様がプログラムを利用してこれを貸付された後で証拠金ローンを行う場合、超過証拠金証券の対象とならなくなるため貸付は停止されます。同様に、超過証拠金証券をお持ちのお客様がプログラムを利用してこれを貸付された後で証拠金ローンを上げる場合には、これも超過証拠金証券の対象とならなくなるため貸付は停止されます。
貸付されている株式はどのような状況で解約されますか?
以下のいずれかの状況(これに限らず)が発生した場合、株式の貸付は解約となります:
- プログラムの解約
- 株式の移管
- 株式を元にした借入
- 株式の売却
- コール割当/プット権利行使
- 口座の解約
株式利回り向上プログラムの参加者は、貸付されている株式の配当を受け取ることができますか?
貸出された株式利回り向上プログラムの株式は、 配当金を獲得し、配当金相当額(PIL)による受け取りを回避するため、通常、配当の権利落日前日までにリコールを試みます。ただし、PILとしての受け取りとなる場合もあります。
株式利回り向上プログラムの参加者には、貸付されている株式への議決権がありますか?
いいえ。承諾やアクションを行う選択日や基準日が貸付期間内の場合、選択や承諾を行う権利は証券の借手のものとなります。
株式利回り向上プログラムの参加者は、貸付されている株式のライツやワラント、またをスピンオフによる株式を受け取ることができますか?
できます。貸付されている株式のライツ、ワラント、スピンオフ株式や分配はすべて株式所有者が受け取ります。
貸付されている株式はアクティビティ・ステートメント上にどのように表示されますか?
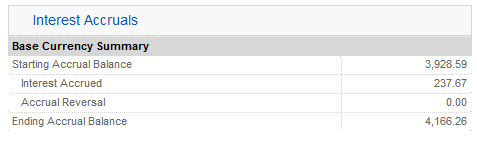
貸付担保、発行済み株式、アクティビティおよび収入は、以下の6項目に表示されます:
1. 現金詳細 – 開始時の担保(米国国債または現金)残高、貸付アクティビティによる純変化(新しい貸付の場合にはプラス、純利益の場合にはマイナス)および終了時の現金担保残高が記載されます。
2. 純株式ポジションのサマリー – 株式ごとにIBKRにおける合計株数、借入られている株数、貸付られている株数および純株数(IBKRでの株数+借入株数+貸付株数)が記載されます。
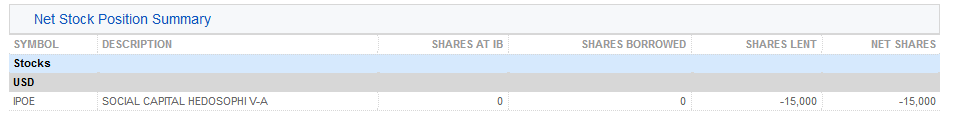
3. IBKR管理の貸付証券(株式利回り向上プログラム) – 株式利回り向上プログラムで貸付された株式ごとに、貸付株数および金利(%)が記載されます。
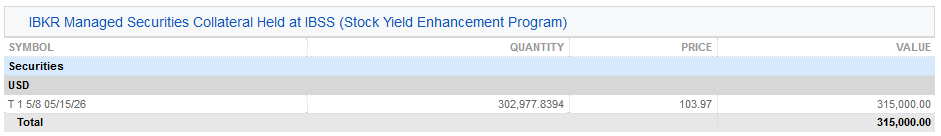
3a. IBSSに保管されるIBKR管理の証券担保(株式利回り向上プログラム) – 証券の貸付用担保として保有される米国国債とその数量、価格、合計価値がIBLLCのお客様のステートメントに表示されます。
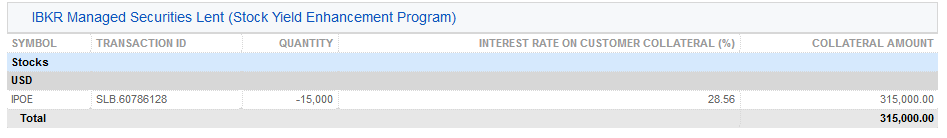
4. IBKR管理の証券貸付状況 (株式利回り向上プログラム)– 証券ごとに、貸付返却の割当(解約された貸付)、新しい貸付の割当(開始された貸付)、株数、純利率(%)、お客様の担保への利率(%)、ならびに担保額の詳細が記載されます。
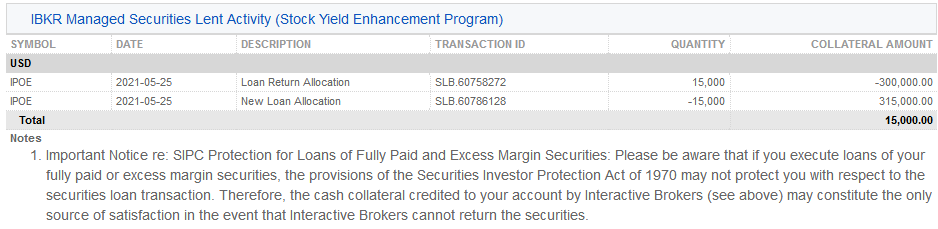
5. IBKR管理の貸付証券アクティビティ金利詳細 (株式利回り向上プログラム)– 貸付ごとに、IBKRのものとなる利子(%)、IBKRの収入({担保額*金利}/360に相当する、貸付によってIBKRのものとなる収入の合計)、お客様の担保への利子(貸付によってIBKRのものとなる収入の約半分)、ならびにお客様のものとなる利子(お客様の担保への利子)の詳細が記載されます。
注意: この項目は発生した利子がステートメント期間にUSD $1を超える場合のみ表示されます。
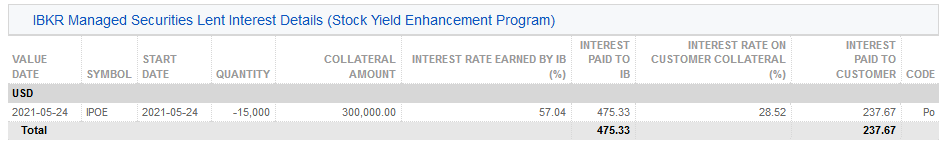
6. 未払い利息 – ここでの利子収入は未払い利息であり、その他の未払い利息と同じように扱われます(集約してUSD $1以上になる場合のみ未払い利息として、マンスリーの現金に表示されます)。年末報告のため、この利息は米国納税者に発行されるForm 1099にレポートされます。
T+2決済に関する概要
イントロダクション
- 財政システムへのリスクの軽減 – 有価証券の価格が変動する可能性は時間と共に増加するため、決済にかかる日数を減らすことにより、不払いや有価証券の不渡しによる信用リスク発生の軽減につながります。 決済進行中における有価証券の想定元本を減らすことにより、市場に深刻な混乱が起きた際に考えられるシステム的な問題から、金融セクターを防御することができます。
- 現金使用の効率 – 「キャッシュ」タイプの口座をお持ちのお客様は、決済済みでない資金による取引(「フリーライド」および支払をせずに有価証券の購入や売却をすること)に対する規制の対象となります。 T+2への変更後は、有価証券の売却による資金が1営業日早く利用可能になります。資金へのアクセスがすばやくできるようになる分、早く次の購入に資金を利用することができるようになります。
- グローバル決済の強化 - T+2決済サイクルへの変更により、すでにこれを導入しているヨーロッパおよびアジアの主要な国際市場と、米国およびカナダの市場の調和が強化されます。
オプションや先物、または先物オプションコントラクトの購入および売却の決済に変更はありますか?
いいえ。これらの商品は現在T+1で決済されており、 これに対する変更はありません。
IB発行株式CFDに関する概要
以下の記事はIB発行の株式ベースの差金決済取引(CFD)に関する概略をご提供することを目的としています。
IB株価指数CFDに関する情報はこちらをクリックしてください。Forex CFDに関する情報はこちらをクリックしてください。
ここでは以下のトピックを取り上げます:
I. CFDの定義
II. CFDと原資産株式の比較
III. 費用および証拠金に関する留意点
IV. 例
V. CFDのリソース
VI. よくあるご質問
リスク警告
CFDはレバレッジによる損失のリスクが高い複雑な商品です。
62%の個人投資家口座に、IBKR(UK)とのCFD取引による損失が発生しています。
お取引を開始される前に、CFDの機能の仕方および損失の際のリスクをご理解ください。
CFDに関わるESMAルール(リテールクライアントのみ)
欧州証券市場監督局(ESMA)は2018年8月1日より有効となるCFDルールを実施しました。
ルールには以下が含まれます: 1) CFDのポジションを建てるにあたってレバレッジの上限; 2) 口座ごとの証拠金解約; および 3) マイナス残高に対する口座ごとの保護。
ESMAによる決定はリテールクライアントのみに適用されます。特定投資家のお客様への影響はありません。
詳細はIBKRにおけるESMA CFDルールの実施をご参照ください。
I. 株式CFDの定義
IB CFDは配当およびコーポレートアクション(CFDコーポレートアクションに関する詳細)を含む、原資産株式のリターンを生むOTC取引です。
これは言い方を変えれば、株式の現在と将来の価値の差額を交換するという、購入者(お客様)と弊社間における合意になります。お客様がロングポジションを保有し差額がプラスの場合には、弊社がお客様にお支払します。差額がマイナスの場合にはお客様にお支払いただくことになります。
IB株式CFD取引は証拠金口座を通して行われるため、ロングおよびショートのレバレッジ・ポジションを建てることができます。CFD価格は原資産株式の取引所クオート価格になります。実際にIB CFDクオートは、トレーダー・ワークステーションで見ることのできる株式用のスマートルーティング・クオートと同じであり、IBではダイレクト・マーケット・アクセス(DMA)をご提供しております。株式同様に、成行とならない(指値の)注文の原資産ヘッジは、取引されている取引所の 板画面に直接表示されています。 これはまたCFDを原資産のビッド価格で購入しオファー価格で売る注文の発注ができるということになります。
弊社の透明性のあるCFDモデルをマーケット上にある他社のものと比較される場合にはCFDマーケットモデルの概要をご覧ください。
IBでは現在、米国、ヨーロッパおよびアジアの主なマーケットをカバーする約6500の株式CFDご提供しております。 下記にリストされている主要指数の構成銘柄は、現在IB株式CFDとしてご利用可能です。IBではまた多くの国で流動小型株の取引もご提供しております。これは最低5億米ドルの時価総額の浮動株を持ち、また平均最低60万米ドルに値する日次の取引を行う株式です。 詳細はCFD商品リストをご覧ください。ご利用可能国は近い将来、さらに追加される予定です。
| 米国 | S&P 500, DJA, Nasdaq 100, S&P 400(中型株), 流動小型株 |
| イギリス | FTSE 350 + 流動小型株 (IOBを含む) |
| ドイツ | Dax, MDax, TecDax + 流動小型株 |
| スイス | Swiss portion of STOXX Europe 600 (48 shares) + 流動小型株 |
| フランス | CAC Large Cap, CAC 中型株 + 流動小型株 |
| オランダ | AEX, AMS 中型株 + 流動小型株 |
| ベルギー | BEL 20, BEL 中型株 + 流動小型株 |
| スペイン | IBEX 35 + 流動小型株 |
| ポルトガル | PSI 20 |
| スウェーデン | OMX Stockholm 30 + 流動小型株 |
| フィンランド | OMX Helsinki 25 + 流動小型株 |
| デンマーク | OMX Copenhagen 30 + 流動小型株 |
| ノルウェー | OBX |
| チェコ | PX |
| 日本 | Nikkei 225 + 流動小型株 |
| 香港 | HSI + 流動小型株 |
| オーストラリア | ASX 200 + 流動小型株 |
| シンガポール* | STI + 流動小型株 |
| 南アフリカ | トップ40 + 流動小型株 |
*シンガポール居住者にはご利用いただけません
II. CFDと原資産株式の比較
| IB CFDのメリット | IB CFDのデメリット |
|---|---|
| 印紙税や金融取引税はありません(英国、フランス、ベルギー) | 所有権がありません |
| 株式に比べ手数料や証拠金が一般的に低めです | 複雑なコーポレトアクションがいつでも反映されるわけではありません |
| 配当金は租税条約レートの対象となり、請求の必要がありません | 収益に対する税金は株式への税金と異なる場合があります(専門の税理士にご相談ください) |
| デイ・トレーディング規制の対象外です |
III. 費用および証拠金に関する留意点
IB CFDは、IB提供のすでに競争性のある株式と比較しても効率的なヨーロッパ株式の取引方法です。
先ず、IB CFDにかかる手数料は株式と比べて低額ですがスプレッドは同じです:
| ヨーロッパ | CFD | 株式 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 手数料 | GBP | 0.05% | GBP 6.00 + 0.05%* |
| EUR | 0.05% | 0.10% | |
| 金利** | ベンチマーク +/- | 1.50% | 1.50% |
*注文につき+ 50,000英ポンドを超える場合は0.05%の超過金
**ポジションの合計価値に対するCFD金利、借入額に対する株式金利
CFDの手数料は取引が増えるほど低額になり、0.02%まで下がります。借入金利はポジションが大きいほど減少し、0.5%まで下がります。 詳細はCFD手数料およびCFD借入金利をご覧ください。
次に、CFDの必要証拠金は株式と比べて低額です。リテールクライアントは欧州証券市場監督局ESMAによる追加の必要証拠金の対象となります。詳細はIBKRにおけるESMA CFDルールの実施をご参照ください。
| CFD | 株式 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| すべて | 標準 | ポートフォリオ・マージン | |
| 維持証拠金率* |
10% |
25% - 50% | 15% |
*ブルーチップ用に一般的な証拠金です。リテールクライアントは最低20%の委託証拠金の対象となります。株式には標準的な25%の日中維持証拠金、オーバーナイトは50%。 表示されているポートフォリオ・マージンは維持証拠金です(オーバーナイトを含み)。ボラティリティの高い場合には必要証拠金額も上がります
詳細はCFD必要証拠金をご参照ください。
IV. 例(プロフェッショナル・クライアント)
例を見てみましょう。Unilever’s Amsterdamリストからの過去一ヶ月(2012年5月14日から20取引日)のリターンは3.2%となり、今後のパフォーマンスも良好に見えます。200,000ユーロのエクスポージャーを建て、5日保有したいとします。取引を10回行って蓄積した後、さらに10回行って相殺します。かかる直接の費用は以下のようになります:
株式
| CFD | 株式 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 200,000ユーロのポジション | 標準 | ポートフォリオ・マージン | |
| 必要証拠金 | 20,000 | 100,000 | 30,000 |
| 手数料(往復) | 200.00 | 400.00 | 400.00 |
| 金利(簡略化されたもの) | 1.50% | 1.50% | 1.50% |
| 提供される資金額 | 200,000 | 100,000 | 170,000 |
| 提供を受ける日数 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 支払利息(1.5% 簡略化されたもの) | 41.67 | 20.83 | 35.42 |
| 直接費用合計(手数料 + 金利) | 241.67 | 420.83 | 435.42 |
| 原価差異 | 74%上がる | 80%上がる | |
注意:CFD支払金利は取引ポジション全体に大して計算されますが、株式にかかる金利は借入量に対して計算されます。株式およびCFDに適用されるレートは同じです。
今度は証拠金資金として20,000ユーロのみ持ち合わせがあると考えてみます。 Unileverが前月と同じようなパフォーマンスを継続すると考えると、そこから期待される利益は以下のようになります:
| レバレッジ利益 | CFD | 株式 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 利用可能な証拠金 | 20,000 | 20,000 | 20,000 |
| 合計投資額 | 200,000 | 40,000 | 133,333 |
| 総利益(5日) | 1,600 | 320 | 1,066.66 |
| 手数料 | 200.00 | 80.00 | 266.67 |
| 支払利息(1.5% 簡略化されたもの) | 41.67 | 4.17 | 23.61 |
| 直接費用合計(手数料 + 金利) | 241.67 | 84.17 | 290.28 |
| 純利益(総利益-直接費用) | 1,358.33 | 235.83 | 776.39 |
| 証拠金投資額に対するリターン | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| 差異 | 利益が83%下がる | 利益が43%下がる | |
| レバレッジリスク | CFD | 株式 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 利用可能な証拠金 | 20,000 | 20,000 | 20,000 |
| 合計投資額 | 200,000 | 40,000 | 133,333 |
| 総利益(5日) | -1,600 | -320 | -1,066.66 |
| 手数料 | 200.00 | 80.00 | 266.67 |
| 支払利息(1.5% 簡略化されたもの) | 41.67 | 4.17 | 23.61 |
| 直接費用合計(手数料 + 金利) | 241.67 | 84.17 | 290.28 |
| 純利益(総利益-直接費用) | -1,841.67 | -404.17 | -1,356.94 |
| 差異 | 損失が78%下がる | 損失が26%下がる | |
V. CFDのリソース
以下はIB提供のCFDに関する詳細を記載したリンクです:
以下のビデオレッスンもご利用可能です:
VI. よくあるご質問
CFDとしてどのような株式が利用できますか?
米国、西ヨーロッパ、北欧および日本における大型および中型株です。 流動小型株の取り扱いのあるマーケットも多くあります。詳細はCFD商品リストをご覧ください。ご利用可能国は近い将来、さらに追加される予定です。
株式指数とFOREXにCFDは含まれていますか?
はい。詳細およびQ&AはIB株価指数CFD - 詳細およびQ&A and Forex CFD - 詳細およびQ&Aをご覧ください。
株式CFDクオートはどのように設定するのですか?
IB CFDのクオートは原資産株式に対するスマートルーティング・クオートと同じです。 IBではスプレッドを広げる、またはお客様に対抗するポジションを建てることはありません。 詳細はCFDマーケットモデルの概要をご覧ください。
取引所にての自分の指値注文は見ることができますか?
はい。IBではダイレクト・マーケット・アクセス(DMS)を提供しており、成行とならない(指値の)注文の原資産ヘッジは取引されている取引所の 板画面に直接表示されています。これはまたCFDを原資産のビッド価格で購入しオファー価格で売る注文の発注ができるということになります。また一般の市場よりも良い価格の注文が他のクライアントから出てきた場合、価格向上につながることもあります。
株式CFDの証拠金はどのように設定するのですか?
IBでは各原資産の過去のボラティリティに基づき、 リスク・ベースで証拠金を採用しています。最小証拠金は10%です。 IB CFDの証拠金はほとんどこのレートで設定されており、これによりCFDは多くの場合、原資産株式の取引に比べて効果的ですが、 リテールクライアントは欧州証券市場監督局ESMAによる追加の必要証拠金の
対象となります。 詳細はIBKRにおけるESMA CFDルールの実施をご参照ください。ポートフォリオ内の各CFDポジション間または個別のCFDポジションと原資産株式のエクスポージャー間のオフセットはありません。集中しているポジションや大型のポジションは追加の証拠金の対象の対象になる可能性があります。詳細はCFD必要証拠金をご参照ください。
売りの株式CFDは強制買い入れの対象になりますか?
はい。原資産株式の借入が困難または不可能になった場合、売りのCFDポジション保持者は買い入れの対象になります。
配当金やコーポレートアクションはどのように取り扱われますか?
一般的にIBでは、コーポレートアクションの経済的な影響を、原資産の有価証券の保持を同じようにCFDを保持しているお客様に対し反映させます。配当金は現金調整として反映され、その他のコーポレートアクションは現金またはポジションの調整、またはその両方として反映されます。例として、コーポレートアクションが株式数の変動につながった場合(株式分割や、株式の合併など)、CFD数も合わせて調整されます。アクションが上場株を持つ新法人の設立にいたり、IBがこれをCFDとして提供する場合には、これに適格な量で新規のロングおよびショート・ポジションが作成されます概要はCFDコーポレートアクションをご覧ください。
*合併などの複雑なコーポレートアクションに対しCFDが正確に調整されない場合もあることをご了承ください。このような場合、CFDは権利落ち日前に終了する可能性があります。
誰でもIB CFDの取引はできますか?
米国、カナダおよび香港以外の国の居住者はIB CFD取引が可能です。シンガポール居住者は、シンガポールに上場されている株式をベースとする以外のIB CFDをお取引いただけます。居住地に基づいて設定される例外で、特定の投資家タイプに適用されるものはありません。
IB CFDの取引はどのように始めればよいのでしょうか?
アカウント・マネジメントよりCFD用の取引許可を設定し、該当する取引開示に合意してください。 IB LLCの口座をお持ちの場合、この後、弊社が新規の口座セグメントを設定します(お客様のすでにお持ちの口座番号の末尾に「F」を追加します)。設定が承認され次第、お取引が可能になります。F口座に別途、資金をご入金いただく必要はありません。資金はCFDの必要証拠金に合わせてお客様のメイン口座より自動的に移動されます。
必要なマーケットデータはありますか?
IB株式CFD用のマーケットデータは、その原資産株式用のマーケットデータになります。 このため関連取引所に対するマーケットデータ許可が必要となります。株式取引に対し取引所のマーケットデータ許可をすでに設定されている場合には、それ以上必要なものはありません。現在マーケットデータ許可の持ち合わせがない取引所におけるCFD取引をご希望の場合には、原資産株式の取引に対する許可と同じ方法で許可を設定することができます。
CFD取引およびポジションはステートメントにどのように表示されますか?
B LLCの口座をお持ちの場合、 CFDポジションは主要口座番号の末尾に「F」を追加した形で別の口座セグメントに維持されます。アクティビティー・ステートメント上のFセグメントは、別途またはメイン口座と合わせて表示することができます。選択はアカウント・マネジメントのステートメント画面より可能です。その他の口座に関しては、通常の口座ステートメントと同じようにCFDもその他の取引商品と共に表示されます。
別のブローカーからのCFDポジションの移管はできますか?
別ブローカーとの合意の下、弊社にてCFDポジション移管作業を進めます。株式ポジションの移管に比べてCFDポジションの移管は複雑なため、通常、弊社では少なくとも100,000米ドル相当のポジションを条件としております。
株式CFDのチャートはありますか?
はい。
IBでのCFD取引にはどのような口座保護が適用しますか?
CFDはIB UKを取引先とする取引であり、取引所による取引や中央決済機関による決済はありません。IB UKをCFD取引の取引先とするため、クレジットリスクを含める、IB UKとの取引に関連する取引やビジネス上のリスクの対象となります。しかしながら、すべてのお客様の資金は法人クライアントも含め、完全に分離されています。IB UKは英国金融サービス補償計画(UK Financial Services Compensation Scheme「FSCS」)に参加しています。IB UKは、米国証券投資者保護公祉(「SIPC」)のメンバーではありません。CFD取引に関連するリスクの詳細はIB UK CFDリスク・ディスクロージャーをご参照ください。
個人、ファミリー、機関など、どのような種類のIB口座でCFD取引ができますか?
CFD取引はすべてマージン口座でご利用可能です。キャッシュまたはSIPPではご利用いただけません。
特定のCFDで保有可能の最大ポジションを教えてください。
事前に設定されている制限はありませんが、ポジションがかなり大型の場合、必要証拠金が増加する場合があることにお気をつけください。詳細はCFD必要証拠金をご参照ください。
電話によるCFDの取引はできますか?
いいえ。例外的にクロージング注文の処理をお電話にてお引き受けすることはありますが、オープニング注文はお受けしておりません。
CFDはレバレッジによる損失のリスクが高い複雑な商品です。
62%の個人投資家口座に、IBKR(UK)とのCFD取引による損失が発生しています。
お取引を開始される前に、CFDの機能の仕方および損失の際のリスクをご理解ください。
ESMAルール
欧州証券市場監督局(ESMA)は、2018年8月1日より有効となる一時的な介入策(ESMA Decision)をて発行しました。
これによる規制には以下が含まれます: 1) CFDのポジションを建てるにあたってレバレッジの上限; 2) 口座ごとの証拠金解約; 3) マイナス残高に対する口座ごとの保護; 4) CFD取引へのインセンティブに対する規制; および 5) 標準的なリスク警告。
ESMAによる決定はリテールクライアントのみに適用されます。 特定投資家のお客様への影響はありません。
CFDはレバレッジによる損失のリスクが高い複雑な商品です。
62%の個人投資家口座に、IBKR(UK)とのCFD取引による損失が発生しています。
お取引を開始される前に、CFDの機能の仕方および損失の際のリスクをご理解ください。
Allocation of Partial Fills
How are executions allocated when an order receives a partial fill because an insufficient quantity is available to complete the allocation of shares/contracts to sub-accounts?
Overview:
From time-to-time, one may experience an allocation order which is partially executed and is canceled prior to being completed (i.e. market closes, contract expires, halts due to news, prices move in an unfavorable direction, etc.). In such cases, IB determines which customers (who were originally included in the order group and/or profile) will receive the executed shares/contracts. The methodology used by IB to impartially determine who receives the shares/contacts in the event of a partial fill is described in this article.
Background:
Before placing an order CTAs and FAs are given the ability to predetermine the method by which an execution is to be allocated amongst client accounts. They can do so by first creating a group (i.e. ratio/percentage) or profile (i.e. specific amount) wherein a distinct number of shares/contracts are specified per client account (i.e. pre-trade allocation). These amounts can be prearranged based on certain account values including the clients’ Net Liquidation Total, Available Equity, etc., or indicated prior to the order execution using Ratios, Percentages, etc. Each group and/or profile is generally created with the assumption that the order will be executed in full. However, as we will see, this is not always the case. Therefore, we are providing examples that describe and demonstrate the process used to allocate partial executions with pre-defined groups and/or profiles and how the allocations are determined.
Here is the list of allocation methods with brief descriptions about how they work.
· AvailableEquity
Use sub account’ available equality value as ratio.
· NetLiq
Use subaccount’ net liquidation value as ratio
· EqualQuantity
Same ratio for each account
· PctChange1:Portion of the allocation logic is in Trader Workstation (the initial calculation of the desired quantities per account).
· Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user
· Inline Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user.
· Model1:
Roughly speaking, we use each account NLV in the model as the desired ratio. It is possible to dynamically add (invest) or remove (divest) accounts to/from a model, which can change allocation of the existing orders.
Basic Examples:
Details:
CTA/FA has 3-clients with a predefined profile titled “XYZ commodities” for orders of 50 contracts which (upon execution) are allocated as follows:
Account (A) = 25 contracts
Account (B) = 15 contracts
Account (C) = 10 contracts
Example #1:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 10 am (ET) the order begins to execute2but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 2 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 7 of the 50 contracts are filled or 14%). For each account the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 14% of 25 = 3.5 rounded down to 3
Account (B) = 14% of 15 = 2.1 rounded down to 2
Account (C) = 14% of 10 = 1.4 rounded down to 1
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.10).
A: final allocation of 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 2 contract, which is 2/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.20)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #2:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be filled3 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 1 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is executed (i.e., 5 of the 50 contracts are filled or 10%).For each account, the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 10% of 25 = 2.5 rounded down to 2
Account (B) = 10% of 15 = 1.5 rounded down to 1
Account (C) = 10% of 10 = 1 (no rounding necessary)
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. to Account B which currently has a ratio of 0.067).
A: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #3:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be executed2 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 12 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 3 of the 50 contracts are filled or 6%). Normally the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers, however for a fill size of less than 4 shares/contracts, IB first allocates based on the following random allocation methodology.
In this case, since the fill size is 3, we skip the rounding fractional amounts down.
For the first share/contract, all A, B and C have the same initial fill ratio and fill quantity, so we randomly pick an account and allocate this share/contract. The system randomly chose account A for allocation of the first share/contract.
To Summarize3:
A: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
C: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
Next, the system will perform a random allocation amongst the remaining accounts (in this case accounts B & C, each with an equal probability) to determine who will receive the next share/contract.
The system randomly chose account B for allocation of the second share/contract.
A: 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
The system then allocates the final [3] share/contract to an account(s) with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.00).
A: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Available allocation Flags
Besides the allocation methods above, user can choose the following flags, which also influence the allocation:
· Strict per-account allocation.
For the initially submitted order if one or more subaccounts are rejected by the credit checking, we reject the whole order.
· “Close positions first”1.This is the default handling mode for all orders which close a position (whether or not they are also opening position on the other side or not). The calculation are slightly different and ensure that we do not start opening position for one account if another account still has a position to close, except in few more complex cases.
Other factor affects allocations:
1) Mutual Fund: the allocation has two steps. The first execution report is received before market open. We allocate based onMonetaryValue for buy order and MonetaryValueShares for sell order. Later, when second execution report which has the NetAssetValue comes, we do the final allocation based on first allocation report.
2) Allocate in Lot Size: if a user chooses (thru account config) to prefer whole-lot allocations for stocks, the calculations are more complex and will be described in the next version of this document.
3) Combo allocation1: we allocate combo trades as a unit, resulting in slightly different calculations.
4) Long/short split1: applied to orders for stocks, warrants or structured products. When allocating long sell orders, we only allocate to accounts which have long position: resulting in calculations being more complex.
5) For non-guaranteed smart combo: we do allocation by each leg instead of combo.
6) In case of trade bust or correction1: the allocations are adjusted using more complex logic.
7) Account exclusion1: Some subaccounts could be excluded from allocation for the following reasons, no trading permission, employee restriction, broker restriction, RejectIfOpening, prop account restrictions, dynamic size violation, MoneyMarketRules restriction for mutual fund. We do not allocate to excluded accountsand we cancel the order after other accounts are filled. In case of partial restriction (e.g. account is permitted to close but not to open, or account has enough excess liquidity only for a portion of the desired position).
Footnotes:
Overview of IBKR issued Share CFDs
The following article is intended to provide a general introduction to share-based Contracts for Differences (CFDs) issued by IBKR.
For Information on IBKR Index CFDs click here. For Forex CFDs click here. For Precious Metals click here.
Topics covered are as follows:
I. CFD Definition
II. Comparison Between CFDs and Underlying Shares
III. CFD Tax and Margin Advantage
IV. US ETFs
V. CFD Resources
VI. Frequently Asked Questions
Risk Warning
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage.
61% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with IBKR.
You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
ESMA Rules for CFDs (Retail Clients of IBKRs European entities, including so-called F segments)
The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) has enacted new CFD rules effective 1st August 2018.
The rules include: 1) leverage limits on the opening of a CFD position; 2) a margin close out rule on a per account basis; and 3) negative balance protection on a per account basis.
The ESMA Decision is only applicable to retail clients. Professional clients are unaffected.
Please refer to the following articles for more detail:
ESMA CFD Rules Implementation at IBKR (UK) and IBKR LLC
ESMA CFD Rules Implementation at IBIE and IBCE
I. Overview
IBKR CFDs are OTC contracts which deliver the return of the underlying stock, including dividends and corporate actions (read more about CFD corporate actions).
Said differently, it is an agreement between the buyer (you) and IBKR to exchange the difference in the current value of a share, and its value at a future time. If you hold a long position and the difference is positive, IBKR pays you. If it is negative, you pay IBKR.
Our Share CFDs offer Direct Market Access (DMA). Our Share CFD quotes are identical to the Smart-routed quotes for shares that you can observe in the Trader Workstation. Similar to shares, your non-marketable (i.e. limit) orders have the underlying hedge directly represented on the deep book of those exchanges at which it trades. This also means that you can place orders to buy the CFD at the underlying bid and sell at the offer.
To compare IBKR’s transparent CFD model to others available in the market please see our Overview of CFD Market Models.
We currently offer approximately 8500 Share CFDs covering the principal markets in the US, Europe and Asia. Eligible shares have minimum market capitalization of USD 500 million and median daily trading value of at least USD 600 thousand. Please see CFD Product Listings for more detail.
Most order types are available for CFDs, including auction orders and IBKR Algos.
CFDs on US share can also be traded during extended exchange hours and overnight. Other CFDs are traded during regular hours.
II. Comparison Between CFDs and Underlying Shares
| BENEFITS of IBKR CFDs | DRAWBACKS of IBKR CFDs |
|---|---|
| No stamp duty or financial transaction tax (UK, France, Belgium, Spain) | No ownership rights |
| Generally lower margin rates than shares* | Complex corporate actions may not always be exactly replicable |
| Tax treaty rates for dividends without need for reclaim | Taxation of gains may differ from shares (please consult your tax advisor) |
| Exemption from day trading rules | |
| US ETFs tradable as CFDs** |
*IB LLC and IB-UK accounts.
**EEA area clients cannot trade US ETFs directly, as they do not publish KIDs.
III. CFD Tax and Margin Advantage
Where stamp duty or financial transaction tax is applied, currently in the UK (0.5%), France (0.3%), Belgium (0.35%) and Spain (0.2%), it has a substantially detrimental impact on returns, particular in an active trading strategy. The taxes are levied on buy-trades, so each time you open a long, or close a short position, you will incur tax at the rates described above.
The amount of available leverage also significantly impacts returns. For European IBKR entities, margin requirements are risk-based for both stocks and CFDs, and therefore generally the same. IB-UK and IB LLC accounts however are subject to Reg T requirements, which limit available leverage to 2:1 for positions held overnight.
To illustrate, let's assume that you have 20,000 to invest and wish to leverage your investment fully. Let's also assume that you hold your positions overnight and that you trade in and out of positions 5 times in a month.
Let's finally assume that your strategy is successful and that you have earned a 5% return on your gross (fully leveraged) investment.
The table below shows the calculation in detail for a UK security. The calculations for France, Belgium and Spain are identical, except for the tax rates applied.
| UK CFD | UK Stock | UK Stock | |
|---|---|---|---|
| All Entities |
EU Account
|
IB LLC or IBUK Acct
|
|
| Tax Rate | 0% | 0.50% | 0.50% |
| Tax Basis | N/A | Buy Orders | Buy Orders |
| # of Round trips | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Commission rate | 0.05% | 0.05% | 0.05% |
| Overnight Margin | 20% | 20% | 50% |
| Financing Rate | 1.508% | 1.508% | 1.508% |
| Days Held | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Gross Rate of Return | 5% | 5% | 5% |
| Investment | 100,000 | 100,000 | 40,000 |
| Amount Financed | 100,000 | 80,000 | 20,000 |
| Own Capital | 20,000 | 20,000 | 20,000 |
| Tax on Purchase | 0.00 | 2,500.00 | 1,000.00 |
| Round-trip Commissions | 500.00 | 500.00 | 200.00 |
| Financing | 123.95 | 99.16 | 24.79 |
| Total Costs | 623.95 | 3099.16 | 1224.79 |
| Gross Return | 5,000 | 5,000 | 2,000 |
| Return after Costs | 4,376.05 | 1,900.84 | 775.21 |
| Difference | -57% | -82% |
The following table summarizes the reduction in return for a stock investment, by country where tax is applied, compared to a CFD investment, given the above assumptions.
| Stock Return vs cfD | Tax Rate | EU Account | IB LLC or IBUK Acct |
|---|---|---|---|
| UK | 0.50% | -57% | -82% |
| France | 0.30% | -34% | -73% |
| Belgium | 0.35% | -39% | -75% |
| Spain | 0.20% | -22% | -69% |
IV. US ETFs
EEA area residents who are retail investors must be provided with a key information document (KID) for all investment products. US ETF issuers do not generally provide KIDs, and US ETFs are therefore not available to EEA retail investors.
CFDs on such ETFs are permitted however, as they are derivatives for which KIDs are available.
Like for all share CFDs, the reference price for CFDs on ETFs is the exchange-quoted, SMART-routed price of the underlying ETF, ensuring economics that are identical to trading the underlying ETF.
V. Extended and Overnight Hours
US CFDs can be traded from 04:00 to 20:00EST, and the again overnight from 20:00 to 03:30 the following day. Trades in the overnight session are attributed to the day when the session ends, even if a trade is entered before midnight the previous day. This has implications for corporate actions and financing.
Trades entered before midnight on the day before ex-date will not have a dividend entitlement. Trades before midnight will settle as if they had been traded the following day, delaying the start of financing.
VI. CFD Resources
Below are some useful links with more detailed information on IBKR’s CFD offering:
The following video tutorial is also available:
How to Place a CFD Trade on the Trader Workstation
VII. Frequently Asked Questions
What Stocks are available as CFDs?
Large and Mid-Cap stocks in the US, Western Europe, Nordic and Japan. Liquid Small Cap stocks are also available in many markets. Please see CFD Product Listings for more detail. More countries will be added in the near future.
Do you have CFDs on other asset classes?
Yes. Please see IBKR Index CFDs - Facts and Q&A, Forex CFDs - Facts and Q&A and Metals CFDs - Facts and Q&A.
How do you determine your Share CFD quotes?
IBKR CFD quotes are identical to the Smart routed quotes for the underlying share. IBKR does not widen the spread or hold positions against you. To learn more please go to Overview of CFD Market Models.
Can I see my limit orders reflected on the exchange?
Yes. IBKR offers Direct market Access (DMA) whereby your non-marketable (i.e. limit) orders have the underlying hedges directly represented on the deep books of the exchanges on which they trade. This also means that you can place orders to buy the CFD at the underlying bid and sell at the offer. In addition, you may also receive price improvement if another client's order crosses yours at a better price than is available on public markets.
How do you determine margins for Share CFDs?
IBKR establishes risk-based margin requirements based on the historical volatility of each underlying share. The minimum margin is 10%, making CFDs more margin-efficient than trading the underlying share in many cases. Retail investors are subject to additional margin requirements mandated by the European regulators. There are no portfolio off-sets between individual CFD positions or between CFDs and exposures to the underlying share. Concentrated positions and very large positions may be subject to additional margin. Please refer to CFD Margin Requirements for more detail.
Are short Share CFDs subject to forced buy-in?
Yes. In the event the underlying stock becomes difficult or impossible to borrow, the holder of the short CFD position may become subject to buy-in.
How do you handle dividends and corporate actions?
IBKR will generally reflect the economic effect of the corporate action for CFD holders as if they had been holding the underlying security. Dividends are reflected as cash adjustments, while other actions may be reflected through either cash or position adjustments, or both. For example, where the corporate action results in a change of the number of shares (e.g. stock-split, reverse stock split), the number of CFDs will be adjusted accordingly. Where the action results in a new entity with listed shares, and IBKR decides to offer these as CFDs, then new long or short positions will be created in the appropriate amount. For an overview please CFD Corporate Actions.
*Please note that in some cases it may not be possible to accurately adjust the CFD for a complex corporate action such as some mergers. In these cases IBKR may terminate the CFD prior to the ex-date.
Can anyone trade IBKR CFDs?
All clients can trade IBKR CFDs, except residents of the USA, Canada, Hong Kong, New Zealand and Israel. There are no exemptions based on investor type to the residency based exclusions.
What do I need to do to start trading CFDs with IBKR?
You need to set up trading permission for CFDs in Client Portal, and agree to the relevant disclosures. If your account is with IBKR (UK) or with IBKR LLC, IBKR will then set up a new account segment (identified with your existing account number plus the suffix “F”). Once the set-up is confirmed you can begin to trade. You do not need to fund the F-account separately, funds will be automatically transferred to meet CFD initial margin requirements from your main account.
If your account is with another IBKR entity, only the permission is required; an additional account segment is not necessary.
Are there any market data requirements?
The market data for IBKR Share CFDs is the market data for the underlying shares. It is therefore necessary to have market data permissions for the relevant exchanges. If you already have market data permissions for an exchange for trading the shares, you do not need to do anything. If you want to trade CFDs on an exchange for which you do not currently have market data permissions, you can set up the permissions in the same way as you would if you planned to trade the underlying shares.
How are my CFD trades and positions reflected in my statements?
If you are a client of IBKR (U.K.) or IBKR LLC, your CFD positions are held in a separate account segment identified by your primary account number with the suffix “F”. You can choose to view Activity Statements for the F-segment either separately or consolidated with your main account. You can make the choice in the statement window in Client Portal.
If you are a client of other IBKR entities, there is no separate segment. You can view your positions normally alongside your non-CFD positions.
Can I transfer in CFD positions from another broker?
IBKR does not facilitate the transfer of CFD positions at this time.
Are charts available for Share CFDs?
Yes.
In what type of IBKR accounts can I trade CFDs e.g., Individual, Friends and Family, Institutional, etc.?
All margin and cash accounts are eligible for CFD trading.
What are the maximum a positions I can have in a specific CFD?
There is no pre-set limit. Bear in mind however that very large positions may be subject to increased margin requirements. Please refer to CFD Margin Requirements for more detail.
Can I trade CFDs over the phone?
No. In exceptional cases we may agree to process closing orders over the phone, but never opening orders.
IBKR Stock Yield Enhancement Program
PROGRAM OVERVIEW
The Stock Yield Enhancement Program provides the opportunity to earn extra income on the fully-paid shares of stock held in your account by allowing IBKR to borrow shares from you in exchange for collateral (either U.S. Treasuries or cash), and then lend the shares to traders who want to sell them short and are willing to pay interest to borrow them. For additional information on the Stock Yield Enhancement Program please see here or review the Frequently Asked Questions page.
HOW TO ENROLL IN THE STOCK YIELD ENHANCEMENT PROGRAM
To enroll, please login to the Client Portal. Once logged in, click the User menu (head and shoulders icon in the top right corner) followed by Settings.
In the Trading section of the Settings page, click the link for the Stock Yield Enhancement Program. Select the checkbox on the next screen and click Continue. You will then be presented with the requisite forms and disclosures needed to enroll in the program. Once you have reviewed and signed the forms, your request will be submitted for processing. Please allow 24-48 hours for enrollment to become active.
.png)
.png)

India Intra-Day Shorting Risk Disclosure
Interactive Brokers currently offers the ability to short sell stocks before taking delivery on an intra-day basis. In accordance with IB’s intra-day shorting rules, traders are required to deliver shares sold or close short stock positions prior to the end of the trading session.
Should traders establish a short stock position intra-day and still hold the position ten minutes prior to the end of the trading session at 15:20 IST, Interactive Brokers may, on a best efforts basis, close the position on your behalf. If the position is not closed by the end of the day and the shares are not delivered by the customer before settlement, the loss on account of auction will be borne by the customer. Please note that prices in the auction market are highly variable and typically not favorable compared to the normal market.
It is important to note, IB will not take into consideration any closing orders for short stock positions placed by the customer which may still be working. If your account holds a short position ten minutes prior to the end of the trading session and you have placed working orders to close those positions, there is the possibility your closing order will execute and that IB will act to close out your short position. In this situation you will be responsible for both executions and will need to manage your long position accordingly.
A fee of INR 2,000 will be charged for this manual processing in addition to any external penalties in the case of short stock positions resulting in auction trades. As such, we strongly urge customers to monitor their positions and take appropriate action themselves in order to avoid this.
When I short a stock, when will the hard to borrow interest begin accruing?
Short positions will have a borrow interest/fee associated with them.
Borrow interest will begin being charged on a short position from short settlement date to buy-to-cover settlement date.
For example, you sell XYZ on Monday, and you close the position on Tuesday. Borrow interest would start to be charged upon Wednesday's settlement date (T+2). Interest would cease to be charged on Thursday, the settlement date (T+2) of the buy-to-cover order.
