U.S. Microcap Stock Restrictions
Introduction
To comply with regulations regarding the sale of unregistered securities and to minimize the manual processing associated with trading shares that are not publicly quoted, IBKR imposes certain restrictions on U.S. Microcap Stocks. A list of those restrictions, along with other FAQs relating to this topic are provided below.
Microcap Restrictions
- IBKR will only accept transfers of blocks of U.S. Microcap stocks from Eligible Clients. Eligible Clients include accounts that: (1) maintain equity (pre or post-transfer) of at least $5 million or, clients of financial advisors with aggregate assets under management of at least $20 million; and (2) have less than half of their equity in U.S. Microcap Stocks.
- IBKR will only accept transfers1 of blocks of U.S. Microcap Stocks where the Eligible Client can confirm the shares were purchased on the open market or registered with the SEC;
- IBKR will not accept transfers1 of or opening orders for U.S. Microcap Stocks designated by OTC as Caveat Emptor or Grey Market from any client. Clients with existing positions in these stocks may close the positions;
- IBKR will not accept transfers of U.S. Microcap Stocks to cover a short position established at IBKR;
- Execution-only clients (i.e., execute trades through IBKR, but clear those trades elsewhere) may not trade U.S. Microcap Stocks within their IBKR account. (IBKR may make exceptions for U.S.-registered brokers);
Microcap FAQs
What is a U.S. Microcap Stock?
The term “Microcap Stock” refers to shares (1) traded over the counter or (2) that are listed on Nasdaq and NYSE American that have a market capitalization of between $50 million to $300 million and are trading at or below $5. For purposes of this policy, the term Microcap Stock will include the shares of U.S. public companies which have a market capitalization at or below $50 million, which are sometimes referred to as nanocap stocks or trade on a market generally associated with Microcap Stocks.
To avoid situations where minor, short-term fluctuations in a stock price cause repeated reclassification, any stock classified as U.S. Microcap will remain in that classification until both its market capitalization and share price exceed $300 million and $5, respectively, for a 30 consecutive calendar day period.
As Microcap Stocks are often low-priced, they are commonly referred to as penny stocks. IBKR may make exceptions, including for stocks traded at low prices that recently had a greater market cap. In addition, IBKR will not consider ADRs on non-US companies to be Micro-Cap stocks.
Where do Microcap Stocks trade?
Microcap Stocks typically trade in the OTC market, rather than on a national securities exchange. They are often electronically quoted by market makers on OTC systems such as the OTC Bulletin Board (OTCBB) and the markets administered by the OTC Markets Group (e.g., OTCQX, OTCQB & Pink). Also included in this category are stocks which may not be publicly quoted and which are designated as Caveat Emptor, Other OTC or Grey Market.
In addition, U.S. regulators also consider stocks listed on Nasdaq or NYSE American trading at or below $5 with a market capitalization at or less than $300 million to be Microcap Stocks.
What happens if IBKR receives a transfer from an Eligible Client where one or more of the positions transferred is a Microcap Stock?
If IBKR receives a transfer containing a block of a Microcap stock, IBKR reserves the right to restrict the sale of any Microcap position(s) included in the transfer unless the Eligible Client provides appropriate documentation establishing that the shares were either purchased on the open market (i.e., on a public exchange through another broker) or were registered with the SEC pursuant to an S-1 or similar registration statement.
Eligible Clients can prove that shares were purchased on the open market by providing a brokerage statement or trade confirm from a reputable broker reflecting the purchase of the shares on a public exchange. Eligible Clients can establish that the shares are registered by providing the SEC (Edgar system) File number under which their shares were registered by the company (and any documents necessary to confirm the shares are the ones listed in the registration statement).
NOTE: All customers are free to transfer out any shares we have restricted at any time.
What restrictions will IBKR apply to Prime accounts?
Clients whose activities include Prime services are considered Eligible Clients solely for the purposes of those trades which IBKR has agreed to accept from its executing brokers. However, while Prime accounts may clear U.S. Microcap Stocks at IBKR, those shares will be restricted until such time IBKR confirms that the shares are eligible for re-sale under the procedures discussed above.
To remove the restriction for shares purchased on the open market, please have the executing broker provide a signed letter on company letterhead or an official Account Statement stating that the shares were purchased in the open market. The letter or statement must also include the below required criteria. Alternatively, if the shares were acquired through an offering the letter or statement must provide documents or links to the relevant registration statement and state that the shares were part of it.
Required Broker Letter Criteria:
1) IBKR Account Number
2) IBKR Account Title
3) Trade Date
4) Settlement Date
5) Symbol
6) Side
7) Price
8) Quantity
9) Time of Execution
10) Exchange
11) Must be signed
12) Must be on Firm's official letterhead
To summarize: Sell Long trades will be accepted if the long position is no longer restricted. Sell Short trades will be accepted. Buy Long trades will be accepted and the position will be restricted until Compliance is provided with sufficient information to remove the restriction. Buy Cover trades and intraday round trip trades will not be accepted.
What happens if a stock you purchase gets reclassified as Grey Market or Caveat Emptor?
If you purchase a stock in your IBKR account that at a later date becomes classified as a Caveat Emptor or Grey Market stock, you will be allowed to maintain, close or transfer the position but will not be able to increase your position.
What are some of the reasons why Microcap Stock trading may be restricted in my account?
There are two primary reasons why you might be restricted from trading in a Microcap Stock:
- Potential Affiliation to Issuer: U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) Rule 144 places certain limitations on trading of stocks (including Microcap Stocks) by an “affiliate” of the issuer. If IBKR observes trading activity or holdings in a Microcap Stock that are close to the trading volume thresholds under Rule 144 (“Rule 144 Thresholds”), IBKR may restrict the customer from trading the Microcap Stock until a compliance review is completed.
- Transfer of Microcap Stock: If the customer has recently transferred a Microcap Stock into their IBKR account, IBKR may restrict the customer from trading in that security until a compliance review is completed.
If one of the above reasons apply, trading will be restricted in the security and a notification will be sent to the customer’s message center in Account Management. This notification will describe the reason for the restriction and the steps the customer must take before IBKR will consider lifting the restriction.
Why does IBKR consider me to be a potential affiliate of a Microcap Stock issuer?
An “affiliate” is a person, such as an executive officer, a director or large shareholder, in a relationship of control with the issuer.
Rule 144 applies to all securities, including Microcap Stocks. However, given the heightened risks associated with trading Microcap Stocks, if a customer’s trading and/or holdings in a Microcap Stock are close to the Rule 144 Thresholds, IBKR will restrict the customer’s trading in the Microcap Stock. This restriction will remain in effect pending a compliance review into the customer’s potential affiliate status.
For the Potential Affiliate review, why do I need to ask for a new review every two weeks?
A customer’s affiliate status may change soon after IBKR completes the above-referenced Potential Affiliate review. As such, IBKR believes it is appropriate to refresh a Potential Affiliate review every two weeks if a customer’s trading activity and/or holdings in the Microcap Stock remain close to the Rule 144 Thresholds.
Where can I find a list of stocks that IBKR has designated as U.S. Microcaps?
A list of stocks designated as U.S. Microcaps by IBKR is available via the following link: www.ibkr.com/download/us_microcaps.csv
Note that this list is updated daily.
Where can I find additional information on Microcap Stocks?
Additional information on Microcap Stocks, including risks associated with such stocks may be found on the SEC website: https://www.sec.gov/reportspubs/investor-publications/investorpubsmicrocapstockhtm.html
-----------------------------------------------------------
1This includes transfers by any method (e.g., ACATS, DWAC, FOP), conversion of Canadian listings to their U.S. equivalent via “Southbound” transfer, transfers to cover existing short positions, IB Prime customers executing with other brokers and clearing to IBKR, etc.
IEX Discretionary Peg Order
IEX offers a Discretionary Peg™ (D-Peg™) order type which is a non-displayed order that is priced at either the National Best Bid (NBB for buys) or National Best Offer (NBO for sells). D-Peg™ orders passively rest on the book while seeking to access liquidity at a more aggressive price up to Midpoint of the NBBO, except when IEX determines that the quote is transitioning to less aggressive price
How to Place a D-Peg Order
Please note, the IEX D-Peg order type is only available via the TWS version 961 and above. Instructions for entering this order type are outlined below:
Step 1
Enter a symbol and choose a directed quote, selecting IEX as the destination. Right click on the data line and select Trade followed by Order Ticket to open the Order Ticket window.
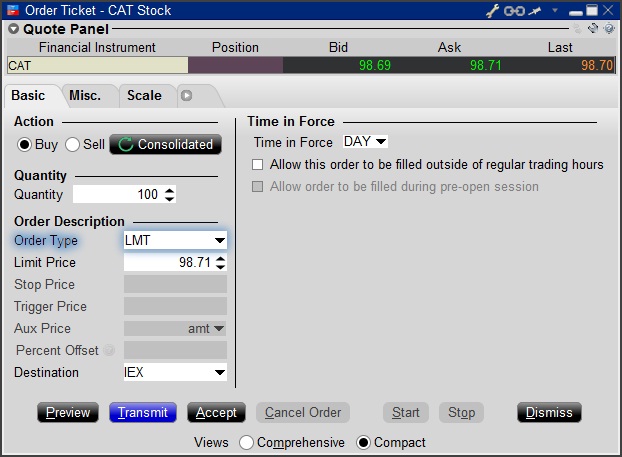
Step 2
Select the REL order type from the Order Type drop down menu.
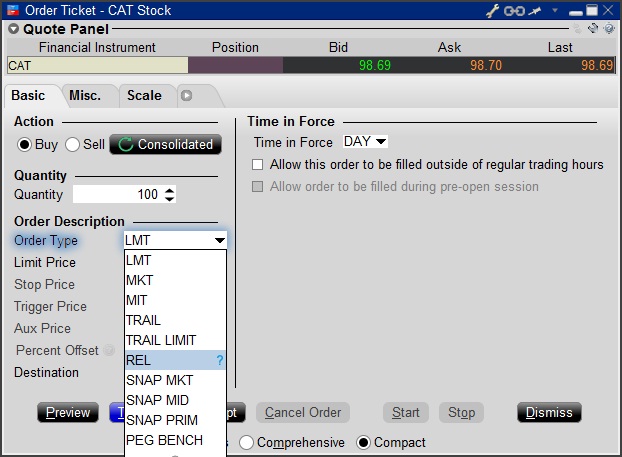
Step 3
Click on the Miscellaneous tab (Misc.) and at the bottom there will be a checkbox for "Discretionary up to limit". Check this box. The price that you set in the Limit Price field will be used at the discretionary price on the order.
.jpg)
Step 4
Hit Preview to view the Order Preview window.
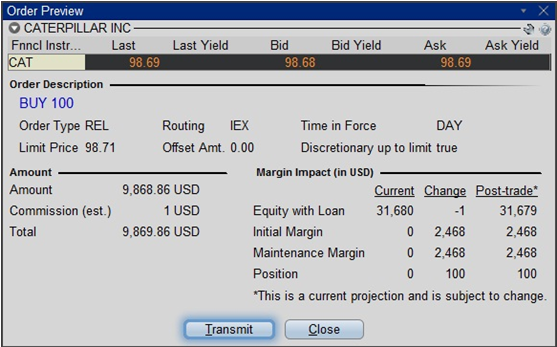
For additional information concerning this order type, please review the following exchange website link: https://www.iextrading.com/trading/dpeg/
SEC Tick Size Pilot Program
Background
Effective October 3, 2016, securities exchanges registered with the SEC will operate a Tick Size Pilot Program ("Pilot") intended to determine what impact, if any, widening of the minimum price change (i.e., tick size) will have on the trading, liquidity, and market quality of small cap stocks. The Pilot will last for 2 years and it will include approximately 1,200 securities having a market capitalization of $3 billion or less, average daily trading volume of 1 million shares or less, and a volume weighted average price of at least $2.00.
For purposes of the Pilot, these securities will be organized into groups that will determine a minimum tick size for both quote display and trading purposes. For example, Test Group 1 will consist of securities to be quoted in $0.05 increments and traded in $0.01 increments and Test Group 2 will include securities both quoted and traded in $0.05 increments. Test Group 3 will include also include securities both quoted and traded in $0.05 increments, but subject to Trade-at rules (more fully explained in the Rule). In addition, there will be a Control Group of securities that will continue to be quoted and traded in increments of $0.01. Details as to the Pilot and securities groupings are available on the FINRA website.
Impact to IB Account Holders
In order to comply with the SEC Rules associated with this Pilot, IB will change the way that it accepts orders in stocks included in the Pilot. Specifically, starting October 3, 2016 and in accordance with the phase-in schedule, IB will reject the following orders associated with Pilot Securities assigned to Test Groups:
- Limit orders having an explicit limit that is not entered in an increment of $0.05;
- Stop or Stop Limit orders having an explicit limit that is not entered in an increment of $0.05; and
- Orders having a price offset that is not entered in an increment of $0.05. Note that this does not apply to offsets which are percentage based and which therefore allow IB to calculate the permissible nickel increment
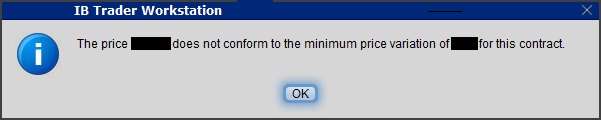
Clients submitting orders via the trading platform that are subject to rejection will receive the following pop-up message:
The following order types will continue to be accepted for Pilot Program Securities:
- Market orders;
- Benchmark orders having no impermissible offsets (e.g., VWAP, TVWAP);
- Pegged orders having no impermissible offsets ;
- Retail Price Improvement Orders routed to the NASDAQ-BX and NYSE as follows:
- Test Group 1 in .001
- Test Group 2 and 3 in .005
Other Items of Note
- GTC limit and stop orders entered prior to the start of the Pilot will be adjusted as allowed (e.g., a buy limit order at $5.01 will be adjusted to $5.00 and a sell limit at $5.01 adjusted to $5.05).
- Clients generating orders via third-party software (e.g., signal provider), order management system, computer to computer interfaces (CTCI) or through the API, should contact their vendor or review their systems to ensure that all systems recognize the Pilot restrictions.
- Incoming orders to IB that are marked with TSP exception codes from other Broker Dealers will not be acted upon by IB. For example, IB will not accept incoming orders marked with the Retail Investor Order or Trade-At ISO exception codes.
- The SEC order associated with this Pilot is available via the following link: https://www.sec.gov/rules/sro/nms/2015/34-74892-exa.pdf
- For a list of Pilot Program related FAQs, please see KB2750
Please note that the contents of this article are subject to revision as further regulatory guidance or changes to the Pilot Program are issued.
Allocation of Partial Fills
How are executions allocated when an order receives a partial fill because an insufficient quantity is available to complete the allocation of shares/contracts to sub-accounts?
Overview:
From time-to-time, one may experience an allocation order which is partially executed and is canceled prior to being completed (i.e. market closes, contract expires, halts due to news, prices move in an unfavorable direction, etc.). In such cases, IB determines which customers (who were originally included in the order group and/or profile) will receive the executed shares/contracts. The methodology used by IB to impartially determine who receives the shares/contacts in the event of a partial fill is described in this article.
Background:
Before placing an order CTAs and FAs are given the ability to predetermine the method by which an execution is to be allocated amongst client accounts. They can do so by first creating a group (i.e. ratio/percentage) or profile (i.e. specific amount) wherein a distinct number of shares/contracts are specified per client account (i.e. pre-trade allocation). These amounts can be prearranged based on certain account values including the clients’ Net Liquidation Total, Available Equity, etc., or indicated prior to the order execution using Ratios, Percentages, etc. Each group and/or profile is generally created with the assumption that the order will be executed in full. However, as we will see, this is not always the case. Therefore, we are providing examples that describe and demonstrate the process used to allocate partial executions with pre-defined groups and/or profiles and how the allocations are determined.
Here is the list of allocation methods with brief descriptions about how they work.
· AvailableEquity
Use sub account’ available equality value as ratio.
· NetLiq
Use subaccount’ net liquidation value as ratio
· EqualQuantity
Same ratio for each account
· PctChange1:Portion of the allocation logic is in Trader Workstation (the initial calculation of the desired quantities per account).
· Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user
· Inline Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user.
· Model1:
Roughly speaking, we use each account NLV in the model as the desired ratio. It is possible to dynamically add (invest) or remove (divest) accounts to/from a model, which can change allocation of the existing orders.
Basic Examples:
Details:
CTA/FA has 3-clients with a predefined profile titled “XYZ commodities” for orders of 50 contracts which (upon execution) are allocated as follows:
Account (A) = 25 contracts
Account (B) = 15 contracts
Account (C) = 10 contracts
Example #1:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 10 am (ET) the order begins to execute2but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 2 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 7 of the 50 contracts are filled or 14%). For each account the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 14% of 25 = 3.5 rounded down to 3
Account (B) = 14% of 15 = 2.1 rounded down to 2
Account (C) = 14% of 10 = 1.4 rounded down to 1
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.10).
A: final allocation of 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 2 contract, which is 2/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.20)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #2:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be filled3 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 1 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is executed (i.e., 5 of the 50 contracts are filled or 10%).For each account, the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 10% of 25 = 2.5 rounded down to 2
Account (B) = 10% of 15 = 1.5 rounded down to 1
Account (C) = 10% of 10 = 1 (no rounding necessary)
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. to Account B which currently has a ratio of 0.067).
A: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #3:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be executed2 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 12 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 3 of the 50 contracts are filled or 6%). Normally the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers, however for a fill size of less than 4 shares/contracts, IB first allocates based on the following random allocation methodology.
In this case, since the fill size is 3, we skip the rounding fractional amounts down.
For the first share/contract, all A, B and C have the same initial fill ratio and fill quantity, so we randomly pick an account and allocate this share/contract. The system randomly chose account A for allocation of the first share/contract.
To Summarize3:
A: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
C: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
Next, the system will perform a random allocation amongst the remaining accounts (in this case accounts B & C, each with an equal probability) to determine who will receive the next share/contract.
The system randomly chose account B for allocation of the second share/contract.
A: 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
The system then allocates the final [3] share/contract to an account(s) with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.00).
A: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Available allocation Flags
Besides the allocation methods above, user can choose the following flags, which also influence the allocation:
· Strict per-account allocation.
For the initially submitted order if one or more subaccounts are rejected by the credit checking, we reject the whole order.
· “Close positions first”1.This is the default handling mode for all orders which close a position (whether or not they are also opening position on the other side or not). The calculation are slightly different and ensure that we do not start opening position for one account if another account still has a position to close, except in few more complex cases.
Other factor affects allocations:
1) Mutual Fund: the allocation has two steps. The first execution report is received before market open. We allocate based onMonetaryValue for buy order and MonetaryValueShares for sell order. Later, when second execution report which has the NetAssetValue comes, we do the final allocation based on first allocation report.
2) Allocate in Lot Size: if a user chooses (thru account config) to prefer whole-lot allocations for stocks, the calculations are more complex and will be described in the next version of this document.
3) Combo allocation1: we allocate combo trades as a unit, resulting in slightly different calculations.
4) Long/short split1: applied to orders for stocks, warrants or structured products. When allocating long sell orders, we only allocate to accounts which have long position: resulting in calculations being more complex.
5) For non-guaranteed smart combo: we do allocation by each leg instead of combo.
6) In case of trade bust or correction1: the allocations are adjusted using more complex logic.
7) Account exclusion1: Some subaccounts could be excluded from allocation for the following reasons, no trading permission, employee restriction, broker restriction, RejectIfOpening, prop account restrictions, dynamic size violation, MoneyMarketRules restriction for mutual fund. We do not allocate to excluded accountsand we cancel the order after other accounts are filled. In case of partial restriction (e.g. account is permitted to close but not to open, or account has enough excess liquidity only for a portion of the desired position).
Footnotes:
SEC Tick Size Pilot Program FAQs
Tick Size Pilot ("TSP" or "Pilot") Program:
Under the TSP Program, if IBKR receives any order in a Pilot Security that does not conform to the designated pricing increment (e.g., a limit price in a $0.01 increment for a security designated as trading $0.05 increments), IBKR will REJECT that order, subject to limited exceptions. IBKR strongly encourages a thorough review of your software or your vendor’s software to understand the criteria for what causes an order in a Pilot Security to be rejected to permit you or your vendor to make changes to correctly handle orders in Test Group Pilot Securities.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS:
Q: What is the Tick Size Pilot?
A: On May 6, 2015, the SEC approved an amended TSP NMS Plan. The Pilot will be two years in length. Data collection for the Pilot began on April 4, 2016, 6 months prior to the implementation of the trading and quoting rules for the Pilot. Implementation of the trading and quoting rules for the Pilot will begin on October 3, 2016.
The Pilot will be conducted using a Control Group and three Test Groups where variations in quoting and trading rules exist between each group. Please see the TSP NMS Plan for additional information.
Q: Will the Pilot quoting and trading rules apply during regular market hours, pre-market hours and post market hours?
A: The Pilot rules apply during all operational hours (pre-market, regular hours, and post market hours trading).
Q: Will the Pilot quoting and trading rules apply to odd-lot and mixed-lot sizes?
A: Yes, the Pilot rules to all order sizes.
Q: Will orders in Control Group Securities be accepted in price increments of less than $0.05?
A: Yes, orders submitted in price increments of less than $0.05 will continue to be accepted in Control Group securities.
Q: Will orders in a Test Group 1, 2 or 3 Pilot Securities be accepted in price increments of less than $0.05?
A: No, unless covered by an exception, orders submitted in price increments of less than $0.05 will be rejected.
Q: Which Pilot Security Orders in Test Groups will Interactive Brokers accept at other than $0.05 increments?
![]() Midpoint orders with no explicitly stated limit price or impermissible offsets will be accepted
Midpoint orders with no explicitly stated limit price or impermissible offsets will be accepted
![]() VWAP orders that do not have an explicitly stated limit price or impermissible offsets will be accepted.
VWAP orders that do not have an explicitly stated limit price or impermissible offsets will be accepted.
![]() Interactive Brokers will accept Exchange operated Retail Price Improvement orders as follows:
Interactive Brokers will accept Exchange operated Retail Price Improvement orders as follows:
![]() Test Group 1 in $0.001 price increments
Test Group 1 in $0.001 price increments
![]() Test Groups 2 and 3 in $0.005 price increments.
Test Groups 2 and 3 in $0.005 price increments.
Q: Will there be any changes to the Opening / Closing processes on Exchanges?
A: Please refer to each of the exchange rules for details but in general, there will be no changes to the Opening / Closing process. All orders entered and eligible to participate in Exchange Opening / Closing Cross will be accepted in increments of $0.05. The Exchanges will begin publishing all quotes in increments of $0.05; however, Net Order Imbalance Indicator prices may be published in increments of $0.025.
Q: What will happen to my GTC order that was placed prior to October 3rd in a Pilot Stock that was priced in impermissible tick increments?
A: Interactive Brokers will adjust outstanding limit and stop GTC orders in Pilot stocks in Test Groups that are not in permissible tick increments (e.g., a buy limit order at $5.01 will be adjusted to $5.00 and a sell limit at $5.01 adjusted to $5.05).
Q: What will happen to my GTC order placed after October 3rd that was placed and accepted in a nickel tick increment but the Pilot Stock moves from a Test Group to the Control Group that permits non-nickel increments?
A: The GTC order will automatically be able to be revised by the user in non-nickel increments on the date the Pilot stock moves from the Test Group to the Control Group. Similarly, if a stock is added to Test Group due to a corporate action, IBKR will cancel the GTC order if it is priced in impermissible increments.
Q: Where can I find out more information?
A: See KB2752 or the FINRA website for additional details regarding the Pilot Program: http://www.finra.org/industry/tick-size-pilot-program
Additional Information Regarding the Use of Stop Orders
U.S. equity markets occasionally experience periods of extraordinary volatility and price dislocation. Sometimes these occurrences are prolonged and at other times they are of very short duration. Stop orders may play a role in contributing to downward price pressure and market volatility and may result in executions at prices very far from the trigger price.
Investissements admissibles dans des comptes REER ou CELI
L'Agence du revenu du Canada restreint le type de positions qui peuvent être détenues dans des comptes REER ou CELI et seuls les investissements dits "admissibles" sont acceptés. Les positions détenues sur ces comptes qui ne remplissent pas les conditions d'éligibilité sont désignées comme "investissements non-admissibles". Ces derniers sont taxés par l'Agence du revenu du Canada à hauteur de 50 % de la juste valeur de propriété au moment de l'acquisition ou au moment de la non-admissibilité.
Les investissements admissibles comprennent les instruments suivants : un investissement dans des propriétés, y compris fiduciaire, des certificats de placement garantis (CPG), des obligations d'État et d'entreprise, ou des fonds communs de placement et actions cotées sur une Bourse désignée. Veuillez noter que certains investissements, bien qu'admissibles, peuvent ne pas être offerts par IB si le type de produit ou la Bourse ne sont pas pris en charge.1
Les investissements non-admissibles comprennent toute propriété qui n'est inclut dans la catégorie Investissement admissible. Il peut s'agir par exemple de trading d'actions sur le NEX au Canada ou des actions sur le PINK ou OTCBB aux États-Unis.
Pour plus d'informations, veuillez vous référer aux liens ci-dessous du site de l'Agence du revenu du Canada :
http://www.cra-arc.gc.ca/tx/ndvdls/tpcs/rrsp-reer/glssry-eng.html
http://www.cra-arc.gc.ca/tx/ndvdls/tpcs/ntvdnc/nnqlfdnvst-eng.html
1 Veuillez noter que bien qu'IB n'offre pas d'accès au Canadian Securities Exchange (CNSX), les actions cotées sur les Bourses désignées peuvent être transférées et détenues dans un compte REER ou CELI détenu à IB mais devront être transférées ailleurs pour le débouclage.
Delivery Settings for Shareholder Materials
IBKR’s default setting for distributing shareholder communications (e.g., proxy materials and annual reports) from U.S. and Canadian issuers is electronic delivery. Under this method the account holder will receive an email notice when information becomes available for a security they hold from our processing agent, Mediant Communications. This notification will provide the necessary links for accessing the information and voting through the Internet in lieu of receiving these documents via postal service. The technology which you will need to secure the information includes access to the Internet and a web browser supporting secure connections. In addition, you will need to be able to read the documents online and print a copy provided your system supports documents in a PDF format.
Other items of note:
- The information above applies solely to shareholder communications associated with U.S. and Canadian issuers. The delivery of communications for securities issued outside of these two countries is typically electronic, but managed directly by the issuer or its agent (i.e., not Mediant).
See also: Non-Objecting Beneficial Owner (NOBO)
Répercussion de frais pour les ADR
Les titulaires de compte détenant des positions de certificats américains d'actions étrangères (ADR- American Depositary receipts), doivent savoir que ces titres font l'objet de frais périodiques qui visent à compenser le correspondant bancaire fournissant des services de garde au nom des ADR. Ces services comprennent généralement un inventaire des actions étrangères sous-jacentes et la gestion de l'enregistrement, ainsi que des services de mise en conformité et de tenue des registres.
À l'origine, les correspondants bancaires étaient uniquement en mesure de collecter les frais de garde en les soustrayant directement des dividendes des ADR. Cependant, étant donné que de nombreux ADR ne paient pas de dividendes régulièrement, ces banques se sont trouvées dans l'incapacité de collecter ces frais. Par conséquent, en 2009, la Depository Trust Company été autorisée par la SEC à collecter des frais de garde au nom des banques pour les ADR ne payant pas de dividendes réguliers. La DTC collecte ces frais auprès des courtiers participants (tels qu'IB), qui détiennent des certificats américains d'actions étrangères pour ses clients. On parle alors de répercussion des frais car ils seront collectés par le courtier auprès de ses clients.
Si vous détenez une position d'ADR ouvrant droit à un dividende, ces frais seront déduits du dividende comme par le passé. Si vous détenez une position d'ADR n'ouvrant pas droit à un dividende, cette répercussion des frais apparaîtra sur le relevé mensuel correspondant à la date d'enregistrement à laquelle il sera déterminé. Tout comme pour le traitement des dividendes en numéraire, IB s'efforcera de refléter également les frais d'allocation d'ADR dans la section Montants accumulés de vos relevés de compte. Une fois facturés, les frais apparaîtront dans la section Dépôts et retraits de votre relevé sous la description "Ajustements- Autres", avec le symbole de l'ADR auquel ils se rattachent.
Bien que le montant des frais varie généralement entre 0.01$ et 0.03$, les montants peuvent varier selon les ADR et nous vous recommandons de vous référer à la brochure relative aux ADR pour plus de détails. Vous pouvez rechercher la brochure en ligne via l'outil EDGAR Company Search de la SEC.
Qualified Investments in RSP & TFSA Accounts
Canadian Revenue Agency (“CRA”) regulations place restrictions upon the types of positions that may be held in RSP and TFSA accounts with eligibility limited to those meeting the definition of a “Qualified Investment”. Positions held in such accounts that do not meet this definition are referred to as “Non-Qualified Investments” and are subject to a CRA tax equal to 50% of the fair market value of the property at the time it was acquired or it became Non-Qualified.
Qualified Investments include the following instruments: an investment in properties, including money, guaranteed investment certificates (GICs), government and corporate bonds, mutual funds, and securities listed on a designated stock exchange. Note that certain investments, while Qualified, may not be offered by IB due to the product type itself or its designated exchange not being supported.1
Non-Qualified investments include any property that is not is not classified as a Qualified Investment. Examples include stocks trading on NEX in Canada, as well as on PINK and OTCBB shares in the US.
For additional information, please refer to the CRA website links below:
http://www.cra-arc.gc.ca/tx/ndvdls/tpcs/rrsp-reer/glssry-eng.html
http://www.cra-arc.gc.ca/tx/ndvdls/tpcs/ntvdnc/nnqlfdnvst-eng.html
