賣空的操作風險
費率風險
賣出看漲期權的持有者可能會在期權到期前被行權。期權多頭持有者輸入提早行權請求時,期權清算公司(OCC)會將其隨機分配給其會員(包括盈透證券)。期權清算公司將在多頭看漲期權行權當天(T)的美國收市後將其報給IBKR。因此,期權被行權將在下一個工作日(T+1)反映在IBKR客戶賬戶之中,幷于T+2結算。被行權會導致底層股票在T日賣出,如果在那之前沒有持有相應的底層股票,則會導致出現空頭倉位。已結算空頭倉位持有者需繳納借券費用,且費用可能會很高。此外,如果IBKR因爲沒有足够的可供借用證券庫存而無法在結算日履行賣空交付義務,則空頭倉位可能會面臨被迫補進平倉。
由于上文提到的T+2結算機制,傳統的在T+1買入股票填平空頭倉位的操作會使賬戶至少有1個晚上(如果碰上周末或節假日可能更長)會持有已結算的空頭股票持倉。
多頭價內看跌期權會在到期日自動行權。行權産生的空頭倉位與被行權的空頭看漲期權具有同樣的風險。
| 日期 | 賣空 | 買入回補 | 已結算空頭倉位 | 有無借券費用? | |
| 周一 | 期權清算公司盤後向IBKR報告空頭看漲期權被行權。 | -100股XYZ股票 交易日(T) |
不變 | 否 | |
| 周二 | 看漲期權被行權和股票賣出反映在IBKR客戶賬戶中 | T+1 | +100股XYZ股票 交易日(T) |
不變 | 否 |
| 周三 | T+2結算日 | T+1 | -100 | 是 | |
| 周四 | T+2結算日 | 不變 | 否 |
賣空股票收入的貸方利息
如何確定與股票借入倉位相關的貸方利息或費用
賬戶持有人賣空股票時,IBKR會代賬戶持有人借入相應數量的股票,以履行向買方交付股票的義務。根據借入股票的股票借貸協議,IBKR需向股票出借方提供現金抵押品。現金抵押品的金額基于股票價值的行業標準計算,稱爲抵押品標記。
股票出借方就現金抵押品向IBKR提供利息,利率通常會低于現金抵押存款的現行市場利率(通常與美元計價現金存款的聯邦基金有效利率挂鈎),其中的差額即作爲出借方提供此服務收取的費用。對于難以借入的股票,出借方所收取的費用會相應提高,可能會導致淨利率變爲負,IBKR反而被倒扣費用。
許多經紀商只會向機構客戶提供部分利息返還,但所有IBKR客戶其賣空股票收入超出10萬美元或等值其它貨幣的部分都可以獲得利息。當某證券可供借用的供應量高于借用需求時,賬戶持有人可就其賣空股票餘額獲得的利息利率相當于基準利率(例如,美元餘額采用聯邦基金有效隔夜利率)减去一個利差(目前介于1.25%(10萬美元檔的餘額)至0.25%(300萬美元以上的餘額)之間)。利率可能會在無事先通知的情况下發生變化。
當某特定證券的供求不平衡導致其難以借入時,借出方提供的利息返還將會减少,甚至可能導致向賬戶倒扣費用。該等利息返還或倒扣費用會以更高的借券費用的形式轉嫁給賬戶持有人,這可能會超過賣空收入所得的利息,導致賬戶最終算下來還付出了費用。由于利率因證券和日期而异,IBKR建議客戶通過客戶端/賬戶管理中的支持部分,訪問〝可供賣空股票〞工具,查看賣空的指示性利率。請注意,該等工具中反映的指示性利率對應的是IBKR向第三等級餘額支付的賣空收入利息,即賣空收入爲300萬美元或以上。對于較低的餘額,其利率將根據餘額等級和交易貨幣對應的基準利率進行調整。可使用“對賣空收益現金餘額向您支付的利息”計算器計算適用的利率。
請參閱證券融資(融券)頁面的更多範例和計算機。
重要提示
“可供賣空股票”工具和TWS中關于可供借用股票和指示性利率的信息,是在盡最大努力的基礎上提供,不保證其準確性或有效性。 “可供賣空股票”包括來自第三方的信息,不會實時更新。利率信息僅爲指示性質。在當前交易時段執行的交易通常在2個工作日內結算,實際供應和借入成本在結算日確定。交易者應注意,在交易和結算日之間,利率和供應可能會發生重大變化,尤其是交易稀少的股票、小盤股和即將發生公司行動(包括股息)的股票。詳情請參閱賣空的操作風險(Operational Risks of Short Selling) 。
IBKR股票收益提升計劃
計劃概覽
股票收益提升計劃(Stock Yield Enhancement Program)讓客戶有機會用賬戶中全額支付的股票賺取額外收益。該計劃允許IBKR通過抵押(美國國債或現金)從您那裡借入股票,然後將股票借給希望做空股票並願意支付借券利息的交易者。有關股票收益提升計劃的更多信息,請參見此處或查看常見問題頁面。
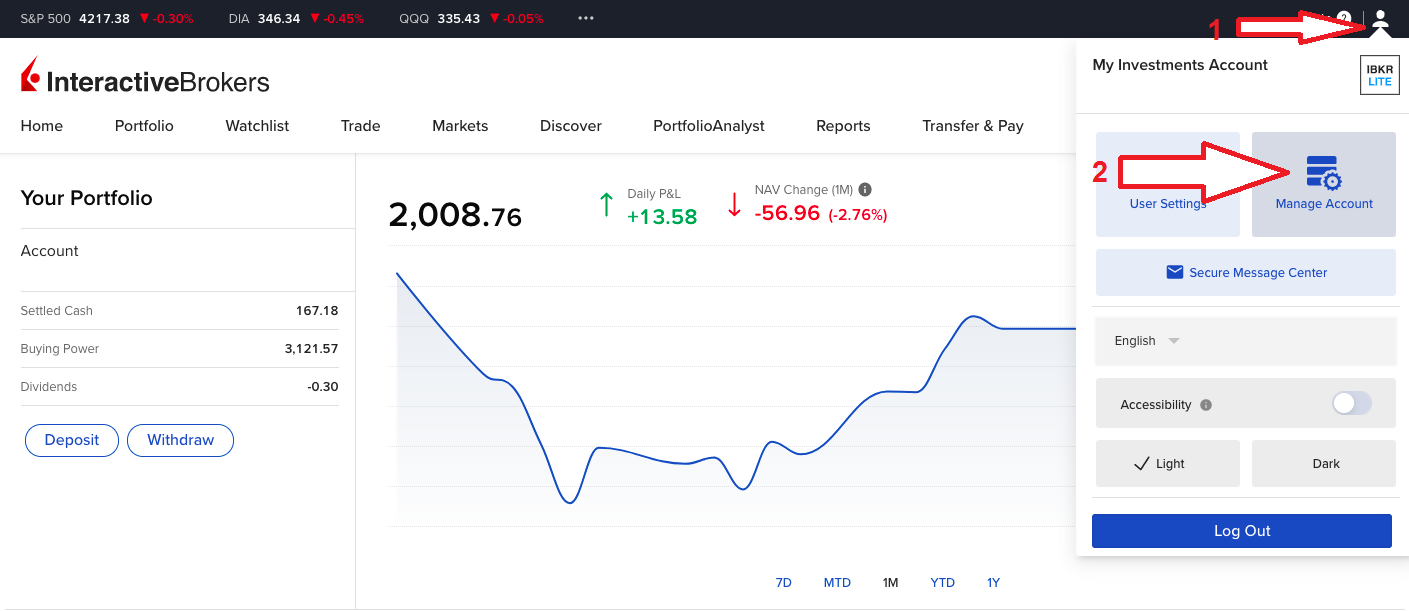
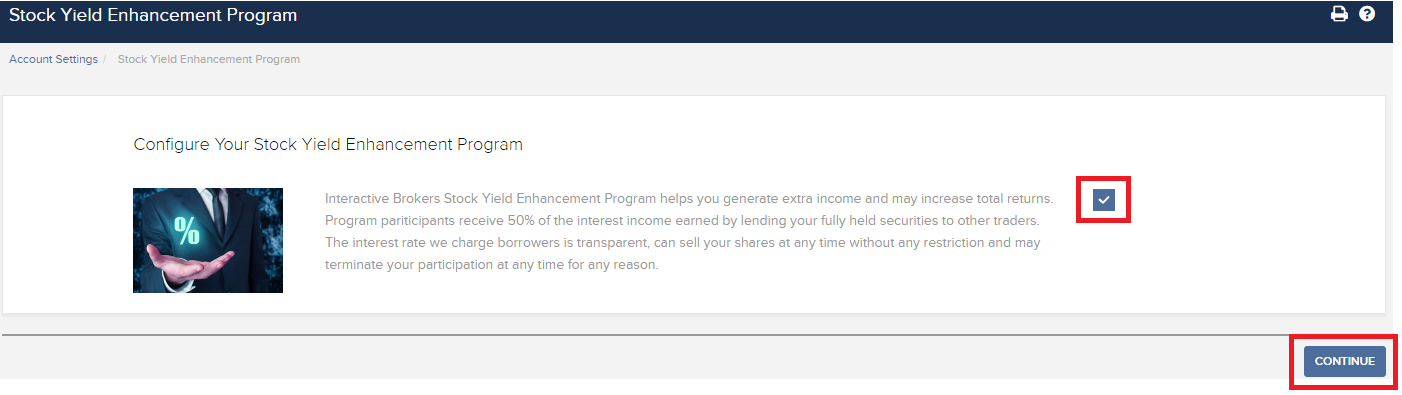
要參加計劃,請登錄客戶端。登錄後,點擊使用者菜單(右上角的頭像圖標),然後點擊管理賬戶。在配置部分,點擊股票收益提升計劃旁邊的配置(齒輪)圖標。在下一個界面勾選複選框然後點擊繼續。您將會看到參加計劃必需的表格和披露。查看並簽署表格後,您的申請便會提交處理。需要24到48小時才會激活生效。
.png)
For enrollment via Classic Account Management, please click on the below buttons in the order specified.
為什麼難以借到的股票其“價格”與收盤價不一致?
在確定借用股票頭寸所需存入的現金抵押金額時,通用的行業慣例是用股票前一個交易日**的收盤價乘以102%,向上取整到最近的美元,然後再乘以所借股數。由於借股費用根據現金抵押金額確定,這一慣例直接影響到維持空頭頭寸的成本,尤其是對那些股價不高但難以借到的股票。注意,不是以美元計價的股票,計算會有所不同。下表為各個幣種對應的行業慣例:
| 幣種 | 計算方法 |
| USD | 102%;向上取整到最近的元 |
| CAD | 102%;向上取整到最近的元 |
| EUR | 105%;向上取整到最近的分 |
| CHF | 105%;向上取整到最近的生丁 |
| GBP | 105%;向上取整到最近的便士 |
| HKD | 105%;向上取整到最近的分 |
賬戶持有人可在每日賬戶報表的“非直接難以借用股票詳情(Non-Direct Hard to Borrow Details)”部分查看借股價格。下方通過舉例說明了現金抵押金額的計算及其對借股費用的影響。
例 1
以$1.50美元的價格賣空100,000股ABC
賣空所得 = $150,000.00美元
假設ABC股價跌至$0.25美元,股票借貸費率為50%
賣空股票抵押金額計算
價格 = 0.25 x 102% = 0.255; 向上取整至$1.00美元
總金額 = 100,000股 x $1.00 = $100,000.00美元
借股費用 = $100,000 x 50% / 360天 = $138.89美元/天
假設賬戶持有人的現金餘額中沒有任何其它賣空交易所得,由於餘額沒有超過可以開始計息的最低門檻要求$100,000美元,將不會有任何賣空收益的利息收入可用於沖抵此借股費用。
例 2(以歐元計價的股票)
以1.50歐元的價格賣空100,000股ABC
假設前一個交易日收盤價為1.55歐元,股票借貸費率為50%
賣空股票抵押金額計算
價格 = 1.55歐元 x 105% = 1.6275; 向上取整至1.63歐元
總金額 = 100,000股 x 1.63 = 163,000.00歐元
借股費用 = 163,000歐元 x 50% / 360天 = 226.38歐元/天
** 請注意,週六和周天與週五一樣將採用週四的收盤價計算抵押金額。
股票收益提升計劃(SYEP)常見問題
股票收益提升計劃推出的目的是什麽?
股票收益提升計劃可供客戶通過允許IBKR將其賬戶內原本閑置的證券頭寸(即全額支付和超額保證金證券)出借給第三方來賺取額外收益。參與此計劃的客戶會收到用以確保股票在借貸終止時順利歸還的抵押(美國國債或現金)。
什麽是全額支付和超額保證金證券?
全額支付證券是客戶賬戶中全款付清的證券。超額保證金證券是雖然沒有全款付清但本身市場價值已超過保證金貸款餘額的140%的證券。
客戶股票收益提升計劃的借出交易收益如何計算?
客戶借出股票的收益取决于場外證券借貸市場的借貸利率。借出的股票不同,出借的日期不同,都會對借貸利率造成很大差异。通常,IBKR會按自己借出股票所得金額的大約50%向參與計劃的客戶支付利息。
借貸交易的抵押金額如何確定?
證券借貸的抵押(美國國債或現金)金額採用行業慣例確定,即用股票的收盤價乘以特定百分比(通常爲102-105%),然後向上取整到最近的美元/分。每個幣種的行業慣例不同。例如,借出100股收盤價爲$59.24美元的美元計價股票,現金抵押應爲$6,100 ($59.24 * 1.02 = $60.4248;取整到$61,再乘以100)。下表爲各個幣種的行業慣例:
| 美元 | 102%;向上取整到最近的元 |
| 加元 | 102%;向上取整到最近的元 |
| 歐元 | 105%;向上取整到最近的分 |
| 瑞士法郎 | 105%;向上取整到最近的生丁 |
| 英鎊 | 105%;向上取整到最近的便士 |
| 港幣 | 105%;向上取整到最近的分 |
更多信息,請參見KB1146。
股票收益提升計劃下的抵押如何保管以及保管在何處?
對於IBLLC的客戶,抵押將採用現金或美國國債的形式,並將轉入IBLLC的聯營公司IBKR Securities Services LLC (“IBKRSS”)進行保管。您在該計劃下借出股票的抵押會由IBKRSS以您爲受益人保管在一個賬戶中,您將享有第一優先級擔保權益。如果IBLLC違約,您將可以直接從IBKRSS取得抵押,無需經過IBLLC。請參見 此處的《證券賬戶控制協議》瞭解更多信息。對于非IBLLC的客戶,抵押將由賬戶所在實體保管。例如,IBIE的賬戶其抵押將由IBIE保管。
退出IBKR股票收益提升計劃或賣出/轉帳通過此計劃借出的股票會對利息造成什麽影響?
交易日的下一個工作日(T+1)停止計息。對於轉帳或退出計劃,利息也會在發起轉帳或退出計劃的下一個工作日停止計算。
參加IBKR股票收益提升計劃有什麽資格要求?
| 可參加股票收益提升計劃的實體* |
| 盈透證券有限公司(IB LLC) |
| 盈透證券英國有限公司(IB UK)(SIPP賬戶除外) |
| 盈透證券愛爾蘭有限公司(IB IE) |
| 盈透證券中歐有限公司(IB CE) |
| 盈透證券香港有限公司(IB HK) |
| 盈透證券加拿大有限公司(IB Canada)(RRSP/TFSA賬戶除外) |
| 盈透證券新加坡有限公司(IB Singapore) |
| 可參加股票收益提升計劃的賬戶類型 |
| 現金帳戶(申請參加時賬戶資産超過$50,000美元) |
| 保證金賬戶 |
| 財務顧問客戶賬戶* |
| 介紹經紀商客戶賬戶:全披露和非披露* |
| 介紹經紀商綜合賬戶 |
| 獨立交易限制賬戶(STL) |
*參加的賬戶必須是保證金賬戶或滿足上述現金帳戶最低資産要求的現金帳戶。
盈透證券日本、盈透證券盧森堡、盈透證券澳大利亞和盈透證券印度公司的客戶不能參加此計劃。賬戶開在IB LLC下的日本和印度客戶可以參加。
此外,滿足上方條件的財務顧問客戶賬戶、全披露介紹經紀商客戶和綜合經紀商可以參加此計劃。如果是財務顧問和全披露介紹經紀商,必須由客戶自己簽署協議。綜合經紀商由經紀商簽署協議。
IRA賬戶可以參加股票收益提升計劃嗎?
可以。
IRA賬戶由盈透證券資産管理公司(Interactive Brokers Asset Management)管理的賬戶分區可以參加股票收益提升計劃嗎??
不是。
英國SIPP賬戶可以參加股票收益提升計劃嗎?
不是。
如果參加計劃的現金帳戶資産跌破最低資産要求$50,000美元會怎麽樣?
現金帳戶只有在申請參加計劃當時必須滿足這一最低資産要求。之後資産跌破此要求並不會對現有借貸造成任何影響,也不影響您繼續借出股票。
如何申請參加IBKR股票收益提升計劃?
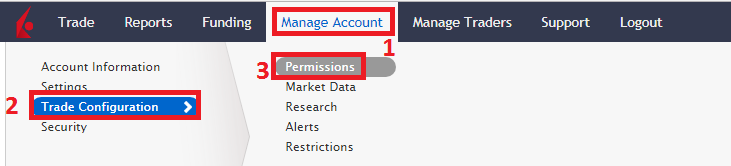
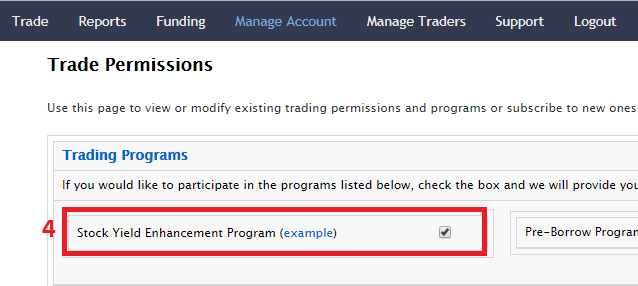
要參加股票收益提升計劃,請登錄客戶端。登錄後,點擊 使用者菜單(右上角的小人圖標),然後點擊設置。然後,在賬戶設置內,尋找交易板塊並點擊股票收益提升計劃 以申請參加。您將會看到參加該計劃所需填寫的表格和披露。閱讀並簽署表格後,您的申請便會提交處理。可能需要24到48小時才能完成激活。
如何終止股票收益提升計劃?
要退出股票收益提升計劃,請登錄客戶端。登錄後,點擊使用者菜單 (右上角的小人圖標),然後點擊 設置。在賬戶 設置板塊內會找到交易,然後點擊股票 收益 提升 計劃,然後依照所需步驟。您的申請便會提交處理。 中止參加的請求通常會在當日結束時進行處理。
如果一個賬戶參加了計劃然後又退出,那麽該賬戶多久可以重新參加計劃?
退出計劃後,賬戶需要等待90天才能重新參加。
哪些證券頭寸可以出借?
| 美國市場 | 歐洲市場 | 香港市場 | 加拿大市場 |
| 普通股(交易所掛牌、粉單和OTCBB) | 普通股(交易所掛牌) | 普通股(交易所掛牌) | 普通股(交易所掛牌) |
| ETF | ETF | ETF | ETF |
| 優先股 | 優先股 | 優先股 | 優先股 |
| 公司債券* |
*市政債券不適用。
借出IPO後在二級市場交易的股票有什麽限制嗎?
沒有,只要賬戶本身沒有就相應的證券受到限制就可以。
IBKR如何確定可以借出的股票數量?
第一步是確定IBKR有保證金扣押權從而可以在沒有客戶參與的情况下通過股票收益提升計劃借出的證券的價值(如有)。根據規定,通過保證金貸款借錢給客戶購買證券的經紀商可以將該客戶的證券借出或用作抵押,金額最高不超過貸款金額的140%。例如,如果客戶現金餘額爲$50,000美元,買入市場價值爲$100,000美元的證券,則貸款金額爲$50,000美元,那麽經紀商對$70,000美元($50,000的140%)的證券享有扣押權。客戶持有的證券超出這一金額的部分被稱爲超額保證金證券(此例子中爲$30,000),需要記在隔離賬戶,除非客戶授權IBKR通過股票收益提升計劃將其借出。
計算貸款金額首先要將所有非美元計價的現金餘額轉換成美元,然後减去股票賣空所得(轉換成美元)。如果結果爲負數,則我們最高可抵押此數目的140%。此外,商品賬戶段中持有的現金餘額和現貨金屬和差價合約相關現金不納入考慮範圍。 詳細說明請參見此處。
例1: 客戶在基礎貨幣爲美元的賬戶內持有100,000歐元,歐元兌美元匯率爲1.40。客戶買入價值$112,000美元(相當於80,000歐元)的美元計價股票。由於轉換成美元後現金餘額爲正數,所有證券被視爲全額支付。
| 項目 | 歐元 | 美元 | 基礎貨幣(美元) |
| 現金 | 100,000 | (112,000) | $28,000 |
| 多頭股票 | $112,000 | $112,000 | |
| 淨清算價值 | $140,000 |
例2: 客戶持有80,000美元、多頭持有價值$100,000美元的美元計價股票並且做空了價值$100,000美元的美元計價股票。總計$28,000美元的多頭證券被視爲保證金證券,剩餘的$72,000美元爲超額保證金證券。計算方法是用現金餘額减去賣空所得($80,000 - $100,000),所得貸款金額再乘以140% ($20,000 * 1.4 = $28,000)
| 項目 | 基礎貨幣(美元) |
| 現金 | $80,000 |
| 多頭股票 | $100,000 |
| 空頭股票 | ($100,000) |
| 淨清算價值 | $80,000 |
IBKR會把所有符合條件的股票都借出去嗎?
不保證賬戶內所有符合條件的股票都能通過股票收益提升計劃借出去,因爲某些證券可能沒有利率有利的市場,或者IBKR無法接入有意願的借用方所在的市場,也有可能IBKR不想借出您的股票。
通過股票收益提升計劃借出股票是否都要以100爲單位?
不是。只要是整股都可以,但是借給第三方的時候我們只以100爲倍數借出。這樣,如果有第三方需要借用100股,就可能發生我們從一個客戶那裏借出75股、從另一個客戶那裏借出25股的情况。
如果可供借出的股票超過借用需求,如何在多個客戶之間分配借出份額?
如果我們股票收益提升計劃的參與者可用以借出的股票數量大於借用需求,則借出份額將按比例分配。例如,可供借出XYZ數量爲20,000股,而對於XYZ的需求只有10,000股的情况下,每個客戶可以借出其所持股數的一半。
股票是只借給其它IBKR客戶還是也會借給其它第三方?
股票可以借給IBKR客戶和第三方。
股票收益提升計劃的參與者可以自行决定哪些股票IBKR可以借出嗎?
不是。此計劃完全由IBKR管理,IBKR在確定了自己因保證金貸款扣押權可以借出的證券後,可自行决定哪些全額支付或超額保證金證券可以借出,並發起借貸。
通過股票收益提升計劃借出去的證券其賣出是否會受到限制?
借出去的股票可隨時賣出,沒有任何限制。賣出交易的結算並不需要股票及時歸還,賣出收益會按正常結算日記入客戶的賬戶。此外,借貸會於證券賣出的下一個工作日開盤終止。
客戶就通過股票收益提升計劃借出去的股票沽出持保看張期權還能享受持保看漲期權保證金待遇嗎?
可以。由於借出去的股票其盈虧風險仍然在借出方身上,借出股票不會對相關保證金要求造成任何影響。
借出去的股票由於看漲期權被行權或看跌期權行權被交付會怎麽樣?
借貸將於平倉或减倉操作(交易、被行權、行權)的T+1日終止。
借出去的股票被暫停交易會怎麽樣?
暫停交易對股票借出沒有直接影響,只要IBKR能繼續借出該等股票,則無論股票是否被暫停交易,借貸都可以繼續進行。
借貸股票的抵押可以劃至商品賬戶段沖抵保證金和/或應付行情變化嗎?
不是。股票借貸的抵押不會對保證金或融資造成任何影響。
計劃參與者發起保證金貸款或提高現有貸款金額會怎麽樣?
如果客戶有全額支付的證券通過股票收益提升計劃借出,之後又發起保證金貸款,則不屬於超額保證金證券的部分將被終止借貸。同樣,如果客戶有超額保證金證券通過此計劃借出,之後又要增加現有保證金貸款,則不屬於超額保證金證券的部分也將被終止借貸。
什麽情况下股票借貸會被終止?
發生以下情况(但不限于以下情况),股票借貸將被自動終止:
- 客戶選擇退出計劃
- 轉帳股票
- 以股票作抵押借款
- 賣出股票
- 看漲期權被行權/看跌期權行權
- 賬戶關閉
股票收益提升計劃的參與者是否會收到被借出股票的股息?
通過股票收益提升計劃借出的股票通常會在除息日前召回以獲取股息、避免股息替代支付。但是仍然有可能獲得股息替代支付。
股票收益提升計劃的參與者是否對被借出的股票保有投票權?
不是。如果登記日或投票、給予同意或採取其它行動的截止日期在貸款期內,則證券的借用者有權就證券相關事項進行投票或决斷。
股票收益提升計劃的參與者是否能就被借出的股票獲得權利、權證和分拆股份?
可以。被借出股票分配的任何權利、權證和分拆股份都將屬於證券的借出方。
股票借貸在活動報表中如何呈現?
借貸抵押、借出在外的股數、活動和收益在以下6個報表區域中反映:
1. 現金詳情 – 詳細列出了期初抵押(美國國債或現金)餘額、借貸活動導致的淨變化(如果發起新的借貸則爲正;如果股票歸還則爲負)和期末現金抵押餘額。
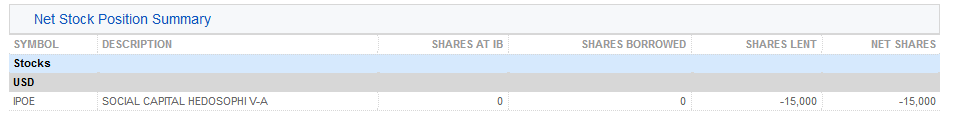
2. 淨股票頭寸總結 – 按股票詳細列出了在IBKR持有的總股數、借入的股數、借出的股數和淨股數(=在IBKR持有的總股數 + 借入的股數 - 借出的股數)。
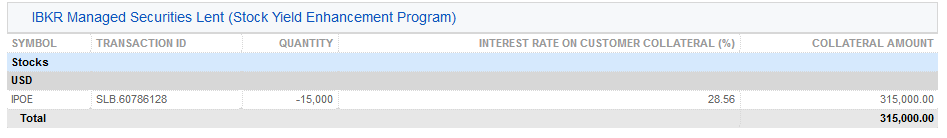
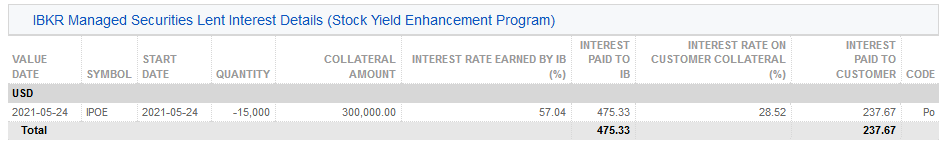
3. 借出的IBKR管理證券(股票收益提升計劃) – 對通過股票收益提升計劃借出的股票按股票列出了借出的股數以及利率(%)。
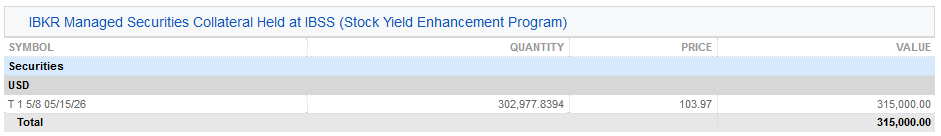
3a. 在IBSS保管的IBKR管理證券的抵押(股票收益提升計劃) – IBLLC的客戶會看到其報表中多出來一欄,顯示作爲抵押的美國國債以及抵押的數量、價格和總價值。
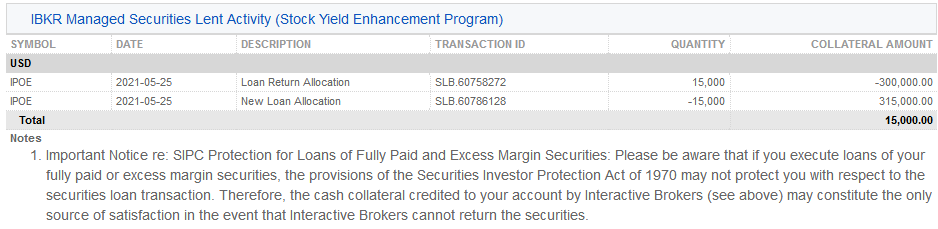
4. IBKR管理證券借出活動 (股票收益提升計劃)– 詳細列出了各證券的借貸活動,包括歸還份額分配(即終止的借貸);新借出份額分配(即新發起的借貸);股數;淨利率(%);客戶抵押金額及其利率(%)。
5. IBKR管理的證券借出活動利息詳情 (股票收益提升計劃)– 按每筆借出活動詳細列出了IBKR賺取的利率(%);IBKR賺取的收益(爲IBKR從該筆借出活動賺取的總收益,等于{抵押金額 * 利率}/360);客戶抵押的利率(爲IBKR從該筆借出活動賺取的收益的一半)以及支付給客戶的利息(爲客戶的現金抵押賺取的利息收入)
注:此部分只有在報表期內客戶賺取的應計利息超過1美元的情况下才會顯示。
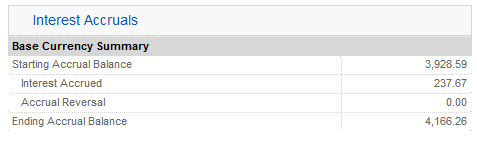
6. 應計利息 – 此處利息收入列爲應計利息,與任何其它應計利息一樣處理(累積計算,但只有超過$1美元才會顯示並按月過帳到現金)。年末申報時,該筆利息收入將上報表格1099(美國納稅人)。
Shorting US Treasuries
Interactive Brokers clients have the ability to gain direct exposure to US Treasuries on both the short and long side of the market.
Order Entry
Orders can be entered via TWS.
Cost to Borrow
The borrow fee to short US Treasuries is based on IBKR’s borrow cost and is subject to daily change. If the Treasury is borrowed by Interactive Brokers at the General Collateral rate, the customer does not incur a borrow fee.
Interest Income
Customers earn Short Credit Interest on their short US Treasury positions based on IBKR’s standard tiered rates.
.png)
Margin Requirements
Margin1 requirements on Short US Treasury positions are the same as Long US Treasury positions. The requirement is between 1% and 9%, depending on time to maturity. The proceeds of the short sale are not available for withdrawal. The amount available for withdrawal is generally Equity with Loan Value – Initial Margin.
Additional information on fixed income margin requirements can be found here.
Commissions
Selling short US Treasuries incurs the same commission cost as buying US Treasuries. IBKR’s commission schedule can be found here.
Trading Policy
Minimum short position size is $250,000 face value per CUSIP due to limitations of the US Treasury borrow market. Once the minimum position size is met, the minimum order increment is $250,000 for both short sales and buy to covers (as long as the resulting short position remains higher than the $250,000 face value minimum).
Short Sale Order Examples
| Existing US Treasury Short Position Face Value in Account (per CUSIP) | Face Value of Short Sale Order | Face Value of Resulting Position | Order Accepted? | Reason |
| Flat | $250,000 | $250,000 | Yes | Face Value of resulting position is => $250,000 |
| Flat | $100,000 | $100,000 | No | Face Value of resulting position is < $250,000 |
| $250,000 | $50,000 | $300,000 | No | Order increment < $250,000 |
| $250,000 | $250,000 | $500,000 | Yes | Order increment =>$250,000 |
Buy-to-cover orders that will result in a short US Treasury position of less than $250,000 face value will not be accepted.
Buy to Cover Order Examples
| Existing US Treasury Short Position Face Value in Account (per CUSIP) | Face Value of Buy to Cover Order | Face Value of Resulting Position | Order Accepted? | Reason |
| $500,000 | $250,000 | $250,000 | Yes | Face Value of resulting position is => $250,000 |
| $500,000 | $300,000 | $200,000 | No | Face Value of resulting position is < $250,000 |
| $500,000 | $500,000 | Flat | Yes | Order increment => $250,000 |
Payment in Lieu
When a short US Treasury position is held over the record date of an interest payment, the borrower’s account will be debited a payment-in-lieu of interest equal to the interest payment owed to the lender.
Eligible US Treasuries for Shorting
Only accounts carried under Interactive Brokers LLC and Interactive Brokers UK are eligible to short sell US Treasuries.
US Treasury Notes and Bonds with an outstanding value greater than $14 Billion can be sold short.
US Treasury Bills, TIPs, STRIPs, TF (Floating Rate Notes) and WITFs (When-Issued Floating Rate Notes) are not available for shorting.
Non-US sovereign debt is also not available for shorting.
1Trading on margin is only for sophisticated investors with high risk tolerance. You may lose more than your initial investment.
For more information regarding margin loan rates, see ibkr.com/interest
Regulation SHO Rule 204, Closeouts, and Introducing Brokers
As a US registered broker-dealer, Interactive Brokers LLC (“IBKR”) is subject to Regulation SHO, a collection of US Securities & Exchange Commission rules relating to short-selling of equity securities. Rule 204 of Regulation SHO places certain requirements on clearing brokers in the event that they fail to deliver securities on settlement date in connection with a sale of those securities. This can happen for a variety of commonplace operational reasons, and does not indicate a problem at the clearing broker. In certain circumstances, Rule 204 may require a clearing broker to not permit shorting a security for a certain period of time (unless sufficient shares of that security are pre-borrowed to cover the order marked as a short sale).
Rule 204(a) requires that a clearing broker, if it fails to deliver on a sale trade on the settlement date, must closeout its fail by buying or borrowing the relevant security a specified number of trading days later (depending on whether the sale was long or short), prior to the opening of the regular trading session on that day.
Rule 204(b) provides that if the clearing broker does not closeout its fail in accordance with Rule 204(a), the broker may not accept short sale orders from its customers in the relevant stock (the stock in which the unclosed-out fail has occurred), or place such orders for its own account, unless it has first borrowed the shares of the relevant stock to cover the new short sale order. This is colloquially known in the securities industry as being in the “penalty box” for the relevant security. This restriction exists until the clearing broker has purchased shares in the amount of the unclosed-out fail, and that purchase has settled.
Any broker that executes trades through that clearing broker, and clears and settles those trades through that clearing broker, is subject to the same Rule 204(b) restriction, as is any broker that executes away from that clearing broker, but intends to clear and settle those trades through the clearing broker.
Rule 204(c) requires clearing brokers to notify brokers from whom they receive trades for clearance and settlement of when they become subject to a short-sale restriction under Rule 204(b), and when that restriction ends. This is so that the notified brokers can avoid executing trades away from the clearing broker that are not permitted under the clearing broker’s short-sale restriction. If you have received a notice from IBKR regarding Rule 204(c), it generally means that IBKR's books and records show that you are an introducing broker or dealer that clears and settles trades through IBKR, and that also has the capability (or your client has such capability) of executing trades at away brokers or dealers for settlement through IBKR. You should not execute any short-sale order at an away broker-dealer in a security which we have notified you is shortsale restricted, unless you have first arranged to pre-borrow sufficient shares of that security through IBKR. For more information on pre-borrowing, please click here or contact us.
The above is a general description of Rule 204 of Regulation SHO, to aid our broker-dealer clients in understanding IBKR's obligations and why certain stocks may become unshortable at certain times irrespective of their availability to be borrowed. It is not legal advice and should not be used as such.
Operational Risks of Short Selling
Rate Risk
Holders of short call options can be assigned before option expiration. When the long holder of an option enters an early exercise request, the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) allocates assignments to its members (including Interactive Brokers) at random. The OCC reports assignments to IBKR on the day of the long call exercise (T) but after US market hours. As such, option assignments are reflected in IBKR client accounts on the next business day (T+1), which is also the settlement date. The assignment causes a sale of the underlying stock on T, which can result in a short position if no underlying shares are held beforehand. Settled short position holders are subject to borrow fees, which can be high. Additionally, if IBKR cannot fulfil the short sale delivery obligation due to a lack of securities lending inventory on settlement date, the short position can be subject to a closeout buy-in.
Due to T+1 settlement mechanics described previously, traditional purchases to cover a short position on T+1 will leave the account with a settled short stock position for at least 1 night (or longer in case of a weekend or holiday).
Long in-the-money Puts are automatically exercised on expiration date. A short position as a result of the exercise carries the same risks as assigned short calls.
| Day | Short Sale | Buy to Cover | Settled Short Position | Borrow Fee Charged? | |
| Monday | OCC reports short call assignment to IBKR after market hours. | -100 XYZ stock Trade Date (T) |
Flat | No | |
| Tuesday | Call assignment and stock sale are reflected in the account | T+1 Settlement Date | +100 XYZ stock Trade Date (T) |
Yes | Yes |
| Wednesday | T+1 Settlement Date | Flat | No |
Special Risks Associated with ETN & Leveraged ETF Short Sales
Introduction
While account holders are always at risk of having a short security position closed out if IB is unable to borrow shares at settlement of the initial trade or bought in if the trade settles and the shares are recalled by the lender thereafter, certain securities have characteristics which may increase the likelihood of these events occurring. Two examples are leveraged Exchange Traded Funds (ETF) and Exchange Traded Notes (ETN), where the supply of shares available to borrow can be influenced by a number of factors not found with shares of common stock. An overview of these securities and these factors is provided below.
Overview
As background, an ETF is a security organized as a pooled investment vehicle that can offer diversified exposure or track a particular index by investing in stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, options or a blend of assets. An ETF is similar to a mutual fund in that each share of an ETF represents an undivided interest in the underlying assets of the fund. However, unlike a mutual fund in which orders are only processed at a price determined at the end of the day, ETF shares are repriced and trade throughout the day on an exchange. To balance the supply and demand of shares and ensure that secondary market prices approximate the market value of the underlying assets, ETF issuers allow Authorized Participants (typically large broker-dealers) to create and redeem ETF shares in large blocks, typically 50,000 to 100,000 shares. While many ETFs invest solely in securities, others use debt or derivatives to track and/or magnify exposure to an index. The ProShares Ultra VIX Short-Term Futures ETF ( symbol: UVXY) is one example of a widely traded leveraged ETF.
ETNs are also securities that are repriced and trade throughout the day on an exchange and are designed to provide investors with a return that corresponds to an index. Unlike ETFs, however, ETNs are unsecured debt instruments and do not represent an interest in an underlying pool of assets. They do not pay interest like traditional debit instruments, but rather a promise to pay a specific return that typically corresponds to an index or benchmark. The Barclays iPath® S&P 500 VIX Short-Term Futures™ ETN (symbol: VXX) is one example of a widely traded ETN.
The supply of shares available to borrow in order to initiate or maintain a short sale position may be less stable for certain leveraged ETFs and ETNs, including UVXY and VXX, due to the following factors:
- Limited Authorized Participants: The number of Authorized Participants willing to issue ETFs, particularly those that invest in derivatives (e.g., futures contracts, swap agreements and forward contracts) rather than securities and seek performance equal to a multiple (i.e., 2x) or an inverse multiple (i.e., -2x) of a benchmark may be limited. Moreover, Authorized Participants have no legal obligation to create shares and may elect not to do so to minimize their exposure as a dealer.
- No Authorized Participants: As ETN shares represent credit instruments, the supply of such shares is determined solely by the issuing financial institution and Authorized Participants are not involved with the creation or redemption of shares. The ETN issuer typically reserves the right to limit, restrict or stop selling additional shares at any time.
- Limited Holding Period: Certain leveraged ETFs and ETNs seek to match the performance of a benchmark index for a single day rather than an extended period. They are principally used by institutional investors and other traders looking to obtain short-term exposure to an asset class, hedge other investments in a portfolio or invest as a way to gain interim exposure to a particular market while gradually investing directly in that market. These factors can result in a higher rate of turnover and less stability of share inventory available to lend for short sales.
- Margin Considerations: Shares made available for lending to short sellers often originate from brokers who maintain a lien on the shares as they’ve financed the purchase of the shares on behalf of clients via margin loans. Clients purchasing shares using borrowed funds are subject to regulatory margin requirements, compliance to which depends in part upon the value of the shares supporting the loan. As certain leveraged ETFs/ETNs are designed to provide returns in multiples of their benchmark, the inherent volatility of these products may diminish clients’ ability to maintain the position and, in turn, the broker’s ability to lend the shares.
空頭股票補倉與平倉概述
簡介
持有空頭股票頭寸的客戶會面臨頭寸通常會在IB無事先通知的情況下被補倉、平倉的風險。這是賣空交易所固有的風險,通常不受客戶控制。這還受到監管法規的限制,這些法規指定了經紀商必須遵守的時間安排。
雖然效果相同,但補倉是指第三方採取的行動,而平倉則由IB操作。這些行動通常由以下三種情況導致:
1. 賣空交易結算時需要交割的股票無法借到;
2. 結算時成功借到並交割的股票隨後被召回;或
3. 無法完成清算所交割。
下方列出了三種情況的概述及相關注意事項。
補倉/平倉概述
1. 賣空交易結算 – 賣空股票時,經紀商必須安排結算時需借用的股票,如果是美國證券,結算日是指成交日之後的第二個工作日(T+2)。執行賣空交易前,經紀商必須通過驗證股票當前的可用性來確定在需要時會有股票可用於借用。請注意,如果沒有預先安排,便無法確保成交當天可用於借用的股票在兩天后仍然可用,而如果沒有可用股票,賣空將面臨強制平倉。確定平倉的處理時間安排如下:
T+2(美國東部時間全天)
14:30 - 如果IB到目前為止仍未能借入股票滿足結算要求,且預料到其極有可能無法借到股票,IB將會在盡最大努力的基礎上發送消息通知客戶潛在的平倉風險。客戶需要在當日延長交易時段結束前自己平倉空頭頭寸以避免被強制平倉。如果在任何時候能夠借到股票,IB也會通知客戶。
15:15 – 如果客戶未平倉空頭頭寸而IB也未能借到股票,IB將在盡最大努力的基礎上向客戶發送消息。客戶仍需要在當日延長交易時段結束前平倉空頭頭寸以避免被強制平倉。
16:50 – 如果未能借到股票滿足結算要求,IB將在盡最大努力的基礎上發送消息通知客戶如果在T+2工作日收盤前仍未能借到股票,其會在T+3工作日09:00之前進行最後嘗試。
T+3
09:00 – 如果IB在09:00之前未能借到股票,平倉將在東部時間09:30開盤時開始。平倉將以參考價格反映在TWS交易窗口。
09:30 – IB採用交易量加權平均價定單(VWAP)發起平倉,時間覆蓋整個交易日。TWS交易窗口中反映的參考價格將在平倉完成後更新為實際價格。
2. 召回– 一旦賣空交易完成結算(即已借入股票向買方進行了交割),股票的出借人便有權隨時要求返還股票。如果發生召回,IB會嘗試用從另一個出借人處借到的股票來替換先前借到的股票。如果無法借到股票,出借人有權發起正式召回,如果IB不歸還被召回的股票,則會在正式召回發出後三個工作日內進行補倉。雖然發出正式召回為出借人提供了補倉的選擇,但真正會導致補倉的比率很低(通常是因為IB能夠從別處獲得股票)。鑑於我們收到但不會採取針對性行動的正式召回通過太多,IB不會就這些召回通知向客戶發出提前警告。
一旦交易對方向IB發送了補倉警告,其便能在對應交易日隨時補進IB正在借入的股票。如果召回導致了補倉,出借人可執行補倉交易並通知IB交易的執行價格。IB會對交易對方的補倉價格進行審核看其是否符合當天的交易活動。
反過來,IB也會根據客戶已結算的空頭股票頭寸將補倉分配給客戶,而在確定負債時,未結算的交易是不納入考慮的。一旦記入賬戶,客戶便可在TWS交易窗口查看召回補倉交易,IB會在盡最大努力的基礎上於東部時間約17:30之前向客戶發出通知。
3. 無法交割– 當經紀商在清算所有一項淨空頭結算義務但盤存沒有可用股票或無法從另一經紀商處借入股票滿足交割義務時,便會發生無法交割的情況。無法交割係因賣出交易導致,雖不限於賣空,但很可能是以保證金持有且可出借給其他客戶之多頭頭寸的平倉交易所導致。
如果是美國股票,經紀商必須在下一個結算日常規交易時段開始之前處理無法交割的頭寸。這可通過購買或借用股票來完成;但是,如果可用股票借入並不足以滿足交割義務,IB將會以交易量加權平均價(VWAP)定單來平倉客戶的空頭頭寸。
重要注意事項:
* 客戶需注意,在被平倉的當天,客戶須為被平倉之股票的淨買入者,買入數量(其在公司所有賬戶總計)至少為其被平倉之股票的數量。在被平倉之交易日剩下的時間裡,其將不能 (i) 賣空其被平倉的股票; (ii) 沽出其被平倉之股票的價內看漲期權;或 (iii) 行使其被平倉之股票的看跌期權(“交易限制”)。如果客戶未能買入其被平倉之股票的規定股數(客戶在公司所有賬戶總計)成為淨買入者(例如,由於先前沽出的看漲期權被行權),公司將會在下一個交易日再進行一次平倉,平倉股數為在平倉當天客戶距離成為該股票淨買入者還需要再買入的股票數量,而客戶也再次需要買入規定數額股票成為淨買入者,並且在當日剩下的時間還會受到交易限制。
* 客戶需注意,根據IB需要執行平倉和第三方可執行補倉的方式,可能會導致交易執行的價格和前一日收盤價之間出現巨大差距。對於流動性差的證券,這種差距會尤為明顯。客戶需隨時注意這類風險,並對投資組合進行相應的管理。
持有空頭股票頭寸的客戶會面臨頭寸通常會在IB無事先通知的情況下被補倉、平倉的風險。這是賣空交易所固有的風險,通常不受客戶控制。這還受到監管法規的限制,這些法規指定了經紀商必須遵守的時間安排。
雖然效果相同,但補倉是指第三方採取的行動,而平倉則由IB操作。這些行動通常由以下三種情況導致:
1. 賣空交易結算時需要交割的股票無法借到;
2. 結算時成功借到並交割的股票隨後被召回;或
3. 無法完成清算所交割。
下方列出了三種情況的概述及相關注意事項。
補倉/平倉概述
1. 賣空交易結算 – 賣空股票時,經紀商必須安排結算時需借用的股票,如果是美國證券,結算日是指成交日之後的第二個工作日(T+2)。執行賣空交易前,經紀商必須通過驗證股票當前的可用性來確定在需要時會有股票可用於借用。請注意,如果沒有預先安排,便無法確保成交當天可用於借用的股票在兩天后仍然可用,而如果沒有可用股票,賣空將面臨強制平倉。確定平倉的處理時間安排如下:
T+2(美國東部時間全天)
14:30 - 如果IB到目前為止仍未能借入股票滿足結算要求,且預料到其極有可能無法借到股票,IB將會在盡最大努力的基礎上發送消息通知客戶潛在的平倉風險。客戶需要在當日延長交易時段結束前自己平倉空頭頭寸以避免被強制平倉。如果在任何時候能夠借到股票,IB也會通知客戶。
15:15 – 如果客戶未平倉空頭頭寸而IB也未能借到股票,IB將在盡最大努力的基礎上向客戶發送消息。客戶仍需要在當日延長交易時段結束前平倉空頭頭寸以避免被強制平倉。
16:50 – 如果未能借到股票滿足結算要求,IB將在盡最大努力的基礎上發送消息通知客戶如果在T+2工作日收盤前仍未能借到股票,其會在T+3工作日09:00之前進行最後嘗試。
T+3
09:00 – 如果IB在09:00之前未能借到股票,平倉將在東部時間09:30開盤時開始。平倉將以參考價格反映在TWS交易窗口。
09:30 – IB採用交易量加權平均價定單(VWAP)發起平倉,時間覆蓋整個交易日。TWS交易窗口中反映的參考價格將在平倉完成後更新為實際價格。
2. 召回– 一旦賣空交易完成結算(即已借入股票向買方進行了交割),股票的出借人便有權隨時要求返還股票。如果發生召回,IB會嘗試用從另一個出借人處借到的股票來替換先前借到的股票。如果無法借到股票,出借人有權發起正式召回,如果IB不歸還被召回的股票,則會在正式召回發出後三個工作日內進行補倉。雖然發出正式召回為出借人提供了補倉的選擇,但真正會導致補倉的比率很低(通常是因為IB能夠從別處獲得股票)。鑑於我們收到但不會採取針對性行動的正式召回通過太多,IB不會就這些召回通知向客戶發出提前警告。
一旦交易對方向IB發送了補倉警告,其便能在對應交易日隨時補進IB正在借入的股票。如果召回導致了補倉,出借人可執行補倉交易並通知IB交易的執行價格。IB會對交易對方的補倉價格進行審核看其是否符合當天的交易活動。
3. 無法交割– 當經紀商在清算所有一項淨空頭結算義務但盤存沒有可用股票或無法從另一經紀商處借入股票滿足交割義務時,便會發生無法交割的情況。無法交割係因賣出交易導致,雖不限於賣空,但很可能是以保證金持有且可出借給其他客戶之多頭頭寸的平倉交易所導致。
如果是美國股票,經紀商必須在下一個結算日常規交易時段開始之前處理無法交割的頭寸。這可通過購買或借用股票來完成;但是,如果可用股票借入並不足以滿足交割義務,IB將會以交易量加權平均價(VWAP)定單來平倉客戶的空頭頭寸。
重要注意事項:
* 客戶需注意,在被平倉的當天,客戶須為被平倉之股票的淨買入者,買入數量(其在公司所有賬戶總計)至少為其被平倉之股票的數量。在被平倉之交易日剩下的時間裡,其將不能 (i) 賣空其被平倉的股票; (ii) 沽出其被平倉之股票的價內看漲期權;或 (iii) 行使其被平倉之股票的看跌期權(“交易限制”)。如果客戶未能買入其被平倉之股票的規定股數(客戶在公司所有賬戶總計)成為淨買入者(例如,由於先前沽出的看漲期權被行權),公司將會在下一個交易日再進行一次平倉,平倉股數為在平倉當天客戶距離成為該股票淨買入者還需要再買入的股票數量,而客戶也再次需要買入規定數額股票成為淨買入者,並且在當日剩下的時間還會受到交易限制。
* 客戶需注意,根據IB需要執行平倉和第三方可執行補倉的方式,可能會導致交易執行的價格和前一日收盤價之間出現巨大差距。對於流動性差的證券,這種差距會尤為明顯。客戶需隨時注意這類風險,並對投資組合進行相應的管理。
