如何向盈透证券提出投诉?
如需向盈透证券提出投诉,请通过客户端提交故障咨询单:
- 登录客户端
- 点击帮助
- 选择安全消息中心
- 选择撰写,然后新咨询单
- 在类别选择账户服务,而主题为投诉
- 在简短描述中写上“投诉”,然后提交
- 选择账户,然后在空白栏位键入您的详细信息
- 提交咨询单
在咨询单主体中,IBKR要求您提供投诉的详细描述。如果您的投诉涉及交易,IBKR要求您提供交易详情,其中可能包括但不限于委托单的提交日期和时间、证券描述、执行日期和时间、执行价格,以及提供计算过程的要求补偿金额。请注意,所有与交易相关的争议必须及时提交。具体而言,交易取消请求必须在IBKR和/或交易所的时间参数范围内。
收到您的投诉后,IBKR将通过客户端确认和回覆您的投诉,并创建一张以“与咨询单#<咨询单号码>相关的投诉通信”为名的新咨询单。此后,请在通信咨询单中进行与投诉相关的所有通信往来。
通常,投诉将在三到五天内得到答覆;但是,某些复杂的问题可能需要更长的时间来评估。在这段时间,IBKR要求您管理账户中的所有委托单、交易和持仓,以确保在调查期间您的账户不会受到不必要的风险或波动的影响。
虽然所有提交的索赔也会得到公平和公正的考虑,但提出索赔并不保证能够获得部分或全额支付所要求的金额。我们鼓励索赔人查看客户协议,因为有关投诉是基于本协议中的条文进行评估。如果客户协议与IBKR网站不同,则客户协议将取代网站版本。关于与交易相关的投诉,请注意客户协议中的以下条款:(i)客户对使用客户用户名 / 密码键入的所有交易负责;(ii)取消请求并不保证;(iii)IBKR不对任何交易所、市场、交易商、清算所或监管机构的任何行动或决定负责,(iv)如果与客户的委托单一致,客户受委托单执行的约束,以及(v)客户有责任了解所交易产品的条款和条件以及相应的市场。客户有责任随时在账户内保持足够的净值,以满足保证金要求。如果客户账户的净值不足,IBKR有权利(但非必需)随时以任何方式清算客户的全部或部分持仓,而不会事前通知客户。请注意,IBKR在任何时候都不会就技术问题或机会损失对客户进行赔偿。
要查看完整的IBKR客户协议,请在IBKR主页底部选择表格和披露,然后选择适用的客户协议。
现金划转
该等法规还要求所有证券交易和相关保证金交易均在全能账户的证券账户段进行,而商品交易则在商品账户段进行。1 虽然法规允许将全额支付的证券持仓以保证金抵押品的形成存放在商品账户段进行托管,但IB并不允许这种操作,从而对抵押权应用了更为严格的SEC限制性规则。鉴于相关法规和政策已对持仓应归于哪个账户段作出了规定,现金是唯一可由客户自行决定在两个账户段之间来回转账的资产。
下方为现金划转选项、选择步骤和注意事项相关的说明。

然后,您可点击您想要的划转方式对应的单选按钮,然后选择〝继续〞按钮。您的选择将从下一个工作日起生效,并将一直有效,直到选择其它选项为止。请注意,只要满足上文中提到的交易许可设置,您可随时更改划转方式,没有次数限制。
Key Information Documents (KID)
IBKR is required to provide EEA and UK retail customers with Key Information Documents (KID) for certain financial instruments.
Relevant products include ETFs, Futures, Options, Warrants, Structured Products, CFDs and other OTC products. Funds include both UCITS and non-UCITS funds available to retail investors.
Generally KIDs must be provided in an official language of the country in which a client is resident.
However, clients of IBKR have agreed to receive communications in English, and therefore if a KID is available in English all EEA and UK clients can trade the product regardless of their country of residence.
In cases where a KID is not available in English, IBKR additionally supports other languages as follows:
| Language | Can be traded by residents or citizens* of |
| German | Germany, Austria, Belgium, Luxembourg and Liechtenstein |
| French | France, Belgium and Luxembourg |
| Dutch | the Netherlands and Belgium |
| Italian | Italy |
| Spanish | Spain |
*regardless of country of residence
Are CDs purchased through IBKR FDIC insured?
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) offered by IBKR are not FDIC insured and are subject to the credit risk of the issuing bank.
Information Regarding SIPC Coverage
1. Interactive Brokers LLC is a member of SIPC.
2. SIPC protects cash and securities held with Interactive Brokers.
3. SIPC does not generally cover commodity futures or options on futures.
4. SIPC protects cash, including US dollars and foreign currency, to the extent that the cash was "deposited with Interactive Brokers for the purpose of purchasing securities."
5. SIPC does not generally cover cash or foreign currency that is not "deposited with Interactive Brokers for the purpose of purchasing securities." For example, SIPC does not generally cover cash in commodity futures trading accounts.
6. Interactive Brokers is not able to make any statements or representations about how cash deposited into a securities account in connection with forex trading or swept from a commodities account would be treated by SIPC. SIPC protection would depend in part on whether the cash was considered to be "deposited with Interactive Brokers for the purpose of purchasing securities." Interactive Brokers expects that at least one factor in deciding this would be whether and the extent to which the customer engages in securities trading in addition to or in conjunction with forex or commodities trading.
Account holders seeking further information should refer such inquiries to their own legal counsel or SIPC.
Excess Margin Securities
The term "excess margin securities" refers to margin securities carried for the account of a customer having a market value in excess of 140 percent of the total debit balance in the customer's account. These securities are in excess of the securities held in a customer's margin account that are pledged by the customer as collateral for the margin loan and can be used to support the purchase of additional securities on margin
Example:
A customer whose account equity consists solely of a cash balance of USD 10,000 on Day 1 purchases 400 shares of stock ABC at USD 50 per share on Day 2.
| Account Balance | Day 1 | Day 2 |
| Cash | $10,000 | ($10,000) |
| Stock | $0 | $20,000 |
| Total | $10,000 | $10,000 |
On Day 2, the customer's excess margin securities total USD 6,000. This is calculated by subtracting 140% of the margin debit or loan balance from the market value of the stock position ($6,000 = $20,000 - {1.4 * $10,000}).
The term is relevant from a regulatory perspective as the SEC requires that U.S. broker dealers segregate and maintain in a good control location (e.g., DTC or bank) all customer securities which are deemed excess margin securities. Such securities cannot be pledged or loaned to finance the activities of the firm or other customers without specific written permission from the customer. The portion of the securities classified as margin securities ($20,000 - $6,000 or $14,000 in this example) are subject to a lien and may be pledged or loaned by the broker to others to assist in financing the loan made to the customer.
Note that securities which were excess margin at the date of acquisition may later be reclassified as margin securities based upon the customer's subsequent trade and/or margin borrowing activity. For example, if the loan value of excess margin securities is subsequently used to acquire additional securities on margin, a portion of securities will then be reclassified as margin securities and subject to a lien. If the customer subsequently deposits cash or sells securities to reduce or eliminate the margin loan, the securities will be reclassified as excess margin or fully paid and are required to be segregated.
See also "fully paid securities".
Fully Paid Securities
The term "fully paid securities" refers to securities held in a customer's margin or cash account that have been completely paid for and are not being pledged as collateral to support the purchase of other securities on margin. The term is relevant from a regulatory perspective as the SEC requires that U.S. broker dealers segregate and maintain in a good control location (e.g., DTC or bank) all customer securities which are fully paid. Such securities cannot be pledged or loaned to finance the activities of the firm or other customers.
Note that securities which were fully paid at the date of acquisition may later be reclassified as margin or excess margin securities based upon the customer's subsequent trade and/or borrowing activity. For example, if the loan value of fully paid securities is subsequently used to acquire additional securities on credit, a portion of securities will then be classified as margin securities and subject to a lien and potential pledge or hypothecation by the broker.
See also "excess margin securities".
Comparison of U.S. Segregation Models
INTRODUCTION
The regulation of securities and commodities products and brokers1 in the U.S. is administered by two distinct federal agencies, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) for securities including stocks, ETFs, bonds, options and mutual funds and the Commodities Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) for commodities including futures and options on futures.2 While both agencies seek to safeguard customer assets by restricting their use and “segregating” them from assets of the broker, the regulations and manner in which they accomplish this differs. The following article provides a basic overview of two segregation models and additional considerations relating to IB accounts.
OVERVIEW
Differences between the CFTC and SEC segregation models originate largely from the products themselves, whose characteristics are fundamentally unique. Commodity products, by nature, do not involve an extension of credit by the broker to the customer as a futures contract is not an asset but rather a contingent liability which is marked-to-market and a long futures option, while an asset, must be paid for in-full. Consequently, non-option assets in a commodities account are generally comprised of funds deposited as margin to secure performance on the contracts therein. Since the broker may not use the funds of one customer to margin or guarantee the transactions of another, the commodities segregation requirement (CFTC Rules 1.20 – 1.30) is equal to the gross assets of all customers and the broker needs to add its own funds to segregation to cover customers whose net equity is in deficit.
A securities margin account, in contrast, can facilitate the extension of credit for the purpose of long securities (e.g., stocks, bonds) purchases or short securities sales on a secured basis. The segregation or reserve requirement rules recognize this through special provisions for the protection of each of the cash and securities components, further distinguishing fully-paid securities from those whose purchase the broker has financed and maintains a lien upon. Here, the broker must deposit into a separate bank account the net amount of customer cash balances3, in accordance with a formula set forth in SEC Rule 15c3-3. In addition, the broker must identify and segregate in a good control location (e.g., depository, bank) customer securities which meet the definition of “fully paid” or “excess margin”.
The table below provides a comparison of the main principals of each model.
| COMPARISON OF CFTC & SEC SEGREGATION MODELS | ||
| PRINCIPAL | CFTC | SEC |
|
Separation of Customer Balances
|
Commodity customer balances must be maintained separate from firm assets and cannot be used to finance proprietary business activities or to satisfy firm debts.
Funds used for trading on non-US commodity exchanges must be kept separate from those used for trading on U.S. exchanges (even for the same customer). Commodity customer balances must also be maintained separate from securities customer balances (even for the same customer). |
Securities customer balances must be maintained separate from firm assets and cannot be used to finance proprietary business activities or to satisfy firm debts. Securities customer balances must also be maintained separate from commodity customer balances (even for the same customer).
|
|
Priority in the Event of Broker Default
|
Commodity customers maintain priority and equal claim over assets in each of their respective U.S. segregated and non-U.S. secured pools.
No claim on assets in a commodity pool in which one is not a participant and no claim on securities customer assets. If commodity segregated assets are insufficient to meet claims and broker is insolvent, customers share equally in shortfall and become general creditors for residual claims. |
Securities customers maintain priority and equal claim over assets.4
No claim on commodity segregated assets. If securities segregated assets are insufficient to meet claims, broker is insolvent and claims exceed SPIC coverage, customers share equally in shortfall and become general creditors for residual claims.
|
| Segregation Style |
Gross – the broker may not use the funds of one customer to margin or guarantee the transactions of another and must segregate assets in an amount at least equal to the sum of all customer credit balances. |
Net – broker may use customer cash credit balances to finance, on a secured basis, margin loans to other customers and may lend or pledge a portion of customer securities purchased on margin to other customers selling short.
|
| Investment of Cash Balances |
Broker is allowed to reinvest commodity customer’s cash balances and retain an interest in the income generated. Permissible investments include: U.S. government securities, municipal securities, government sponsored enterprise securities, bank CDs, corporate obligations (commercial paper, notes and bonds) fully guaranteed as to principal and interest by the U.S. under the Temporary Liquidity Guarantee Program and money market mutual funds. Securities which are the subject of reinvestment must be maintained in a segregated account. |
Broker is allowed to reinvest securities customer’s cash balances and retain an interest in the income generated. Permissible investments limited to “qualified securities” defined as securities which are guaranteed as to both interest and principal by the U.S. government. Securities which are the subject of reinvestment must be held in Special Reserve Bank Account (i.e., segregated). |
| Computation Frequency | Daily | Weekly |
| Insurance | None | Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC) provides insurance of up to USD 500,000 with a cash sublimit of USD 250,000. |
ADDITIONAL CONSIDERATIONS
In addition to the safeguards afforded through segregation, IB employs a number of policies and practices which serve to enhance the safety and security of accounts beyond that outlined above. These include the following:
- IB computes its securities segregation or reserve requirement on a daily rather than weekly basis as allowed by regulation, thereby ensuring timely determination as to the amount required to be reserved and the deposit of funds necessary to satisfy the requirement.
- IB’s does not avail itself of the generally more permissive rules with respect to the investment of commodity customer cash balances. These balances are instead invested in a manner similar to that of securities cash balances (i.e., U.S. government securities) with the exception of an occasional investment in money market funds.
- All customer securities positions are held in the securities segment of the Universal Account as opposed to the commodities (commodities margin met with cash and/or futures options), thereby limiting their hypothecation to the more restrictive rules of the SEC.
- In addition to SIPC coverage, IB maintains an excess SIPC policy with Lloyd's of London which, in aggregate with SIPC, offers insurance totaling $30 million (with a cash sublimit of $900,000), subject to an aggregate firm limit of $150 million.
- IB offers account holders the ability to sweep cash balances in excess of that required for margin purposes in either the securities or commodities segment to the other segment. Details as to this feature may be found in KB1851.
- For additional information regarding IB strength and security, please review the following website page.
Other Relevant Knowledge Base Articles:
Information Regarding SIPC Coverage
Footnotes:
1The term broker as used in this article is intended to refer to an organization registered with both the SEC as a Broker-Dealer and the CFTC as a Futures Commission Merchant for the purpose of conducting customer transactions
2Single stock futures are a hybrid product jointly regulated by the SEC and CFTC and allowed to be carried in either account type.
3Including cash obtained through the use of customer securities such bank pledges or stock loans less cash required to finance customer transactions (e.g., stock borrows, customer fails to deliver of securities, or margin deposited for short option positions with OCC).
4Assets, or customer property, which securities customers share in proportion to their net equity claim, include cash, margin securities and fully-paid securities held in “street name”. IB does not hold securities in the customer’s name which are not considered bulk customer property.
如何申请替换数码安全卡+(DSC+)
进行下方操作需遵循以下步骤:
- 更换遗失、被盗或无法使用的数码安全卡+
- 持有当前安全设备的同时申请数码安全卡+(账户资产不低于100万美元)
1. 通知IBKR客户服务- 联系IBKR客户服务获取临时账户访问。此服务只可通过电话提供,并且需要核实账户持有人的身份,详情请见IBKR知识库。
2. 获取在线安全代码卡 - 激活在线安全代码卡,此卡可供您在21天内安全地访问客户端全部功能。如需相关指南,请参见IBKR知识库。
3. 申请替换DSC+ - 完成在线安全代码卡激活后,请前往客户端的安全登录系统界面,申请替换DSC。
申请DSC+
1. 点击请求实物设备按钮。
.png)
.png)
3. 为您的DSC+输入四位Soft PIN码1。请牢记输入的PIN码,之后激活和操作设备需要用到。 如需要,您可更改将暂扣20美元设备预备金的账户2。点击继续完成此步。
.png)
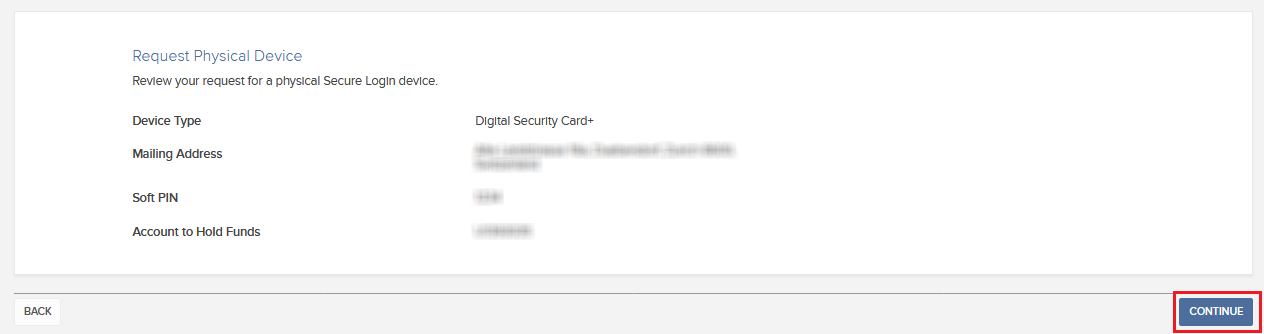
4. 系统将显示概览信息。请确保显示的信息均准确无误。如果需要修改,请点击页面底部的返回按钮(不是浏览器的返回按钮);如无需修改,请点击继续提交申请。
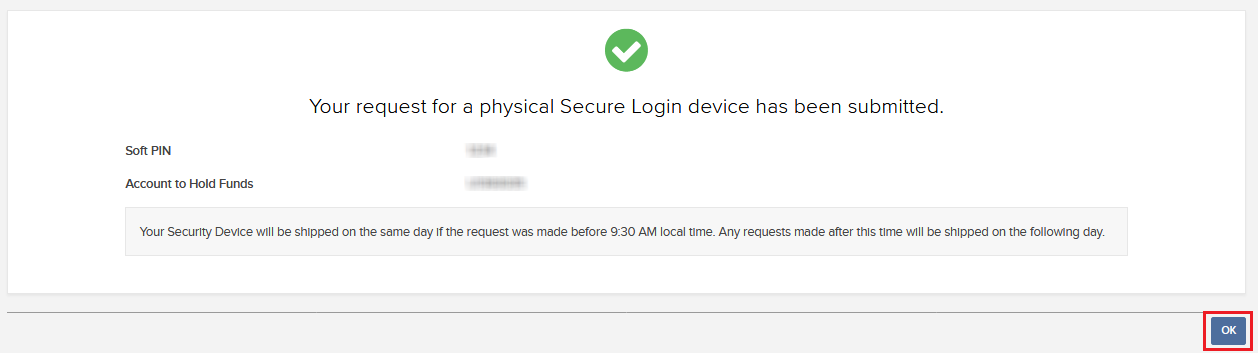
5. 您会看到最终的确认信息,其中会给出预估的寄件日期3。点击确定完成程序。
1. PIN码相关指南请参见IBKR知识库。
2. 安全设备和设备邮寄均为免费。 但是,在您申请设备时,我们会冻结您的一小笔资金(20美元)。 如果设备遗失、故意损坏、被盗或者如果您关闭账户时未能将设备退回IBKR,我们将扣除该笔资金以补偿硬件损失。任何其它情况下,在您将设备退回IBKR后,该笔资金便会解除冻结。更多信息请参见IBKR知识库。
3. 出于安全考虑,替换设备会在寄出之日起三周内自动激活。 临近自动激活时,IBKR会通知您。
IBKR知识库参考
- KB1131:安全登录系统概述
- KB2636:安全设备相关信息与程序
- KB2481:如何在多个使用者之间共享安全登录设备的说明
- KB2545:如何在退出后重新加入安全登录系统的说明
- KB975:如何将安全设备退回IBKR的说明
- KB2260:通过移动IBKR激活IB Key验证的说明
- KB2895:多重双因素系统(M2FS)
- KB1861:安全设备费用信息
- KB69:临时密码有效期的相关信息
How to request a Digital Security Card+ (DSC+) replacement
The below steps are required in order to:
- Replace a Digital Security Card+ which has been lost, stolen or has become inoperable
- Request a Digital Security Card+ alongside your current security device (if you are a new or existing Client with equity above $1,000,000, or equivalent)
1. Notify IBKR Client Services- Contact IBKR Client Services to obtain a temporary account access. This service can only be provided via telephone and requires the identity of the account holder to be verified, as detailed in the IBKR Knowledge Base.
2. Obtain an Online Security Code Card - Activate an Online Security Code Card, which offers enhanced protection and full Client Portal functionality for an extended period of 21 days. Please consult the IBKR Knowledge Base should you need guidance for this specific step.
3. Request the DSC+ replacement - Once you have completed the Online Security Code Card activation, please remain in the Secure Login System section of the Client Portal and order your replacement DSC.
Request a DSC+
1. Click on the button Request Physical Device.
.png)
.png)
3. Enter a four-digit Soft PIN1 for your DSC+. Please make sure to remember the PIN you are typing since it will be necessary to activate and to operate your device. When applicable and desired, you may change the account on which the 20 USD deposit will be kept on hold2. Complete this step by clicking on Continue..png)
4. The system will show you a summary of your selection. Please make sure the information displayed is correct. Should you need to perform changes, click on the white Back button under the information field (not your browser back button), otherwise submit the request by clicking on Continue.
5. You will receive a final confirmation containing the estimated shipment date3. Click on Ok to finalize the procedure.
1. For PIN guidelines, please consult the IBKR Knowledge Base.
2. The Security token and the shipment are both free of charge. Nevertheless, when you order your device, we will freeze a small amount of your funds (20 USD). If your device is lost, intentionally damaged, stolen or if you close your account without returning it to IBKR, we will use that amount as a compensation for the loss of the hardware. In any other case, the hold will be released once your device has been returned to IBKR. More details on the IBKR Knowledge Base.
3. For security reasons, the replacement device is set to auto-activate within three weeks from the shipment date. IBKR will notify you when the auto-activation is approaching and when it is imminent.
IBKR Knowledge Base References
- See KB1131 for an overview of the Secure Login System
- See KB2636 for information and procedures related to Security Devices
- See KB2481 for instructions about sharing the Security Login Device between two or more users
- See KB2545 for instructions on how to opt back in to the Secure Login System
- See KB975 for instructions on how to return your security device to IBKR
- See KB2260 for instructions on activating the IB Key authentication via IBKR Mobile
- See KB2895 for information about Multiple 2Factor System (M2FS)
- See KB1861 for information about charges or expenses associated with the security devices
- See KB69 for information about Temporary passcode validity
