Risk Based Margin Considerations
| LLC Risk Based (i.e. Portfolio Margin) | Non-LLC Risk Based Margin | |
| $110,000 initial value requirement | Yes | N/A |
| Minimum equity to operate on margin | USD 100,000 | IB-HK: USD 2,000 IB-AU: AUD 2,000 IB-LUX, IB-IE and IB-CE: EUR 2,000 IB-SG: SGD 2,000 |
| Full options trading approval | Yes | N/A |
| PDT | Yes | N/A |
| Stress testing | Yes | Yes |
| Dynamic House Scanning Charges (TOMS) ¹ | Yes | Yes |
| Shifts in option Implied Volatility (IV) | Yes | Yes |
| A $0.375 multiplied by the index per contract minimum is computed (Only applied to Portfolio Margin eligble products) | Yes | Yes |
| Initial margin will be 110% of Maintenance Margin (US securities only) | Yes | Yes |
| Initial margin will be 125% of Maintenance Margin (Non-US securities) | Yes | Yes |
| Extreme Price Scans | Yes | Yes |
| Large Position Charge (A position which is 1% or more of shares outstanding) | Yes | Yes |
| Days to Liquidate (A large position in relation to the average daily trading volume, which may result in higher initial margin requirements) | Yes | Yes |
| Global Concentration Charge (2 riskiest position stressed +/-30% remaining assets +/-5%) | Yes | Yes |
| Singleton Margin Method for Small Cap Stocks (Stress Test which simulates a price change reflective of a $500 million USD in market capitalization)² | Yes | Yes |
| Singleton Margin Method for stocks domiciled in China (Stress Test which simulates a price change reflective of a $1.5 billion USD in market capitalization)² | Yes | Yes |
| Default Singleton Margin Method (Stress Test which simulates a price change +30% and down -25%)² | Yes | Yes |
| Singleton Margin Method for HK Real Estate Stocks (Stress test +/-50%)² | Yes | Yes |
1 Dynamic House Scanning Charges are available only on select exchanges (Asian Exchanges and MEXDER)
2 IBKR will calculate the potential loss for each stock and its derivates by subjecting them to a stress test. The requirement for the stock (and its derivatives) which projects the greatest loss in the above scenario will be compared to what would otherwise be the aggregate portfolio margin requirement, and the greater of the two will be the margin requirement for the portfolio
U.S. 2020 Election Margin Increase
In light of the potential market volatility associated with the upcoming United States presidential election, Interactive Brokers will implement an increase in the margin requirement for all U.S. traded equity index futures and derivatives and Dow Jones Futures listed on the OSE.JPN exchange.
Clients holding a position in a U.S. equity index future and their derivatives and/or Down Jones Futures listed on the OSE.JPN exchange should expect the margin requirement to increase by approximately 35% above the normal margin requirement. The increase is scheduled to be implemented gradually over a 20-calendar day period with the maintenance margin increase starting on October 5, 2020 through October 30, 2020.
The table below provides examples of the margin increases projected for some of the more widely held products
| Future Symbol |
Description | Listing Exchange | Trading Class | Current Rate (Price scan range)* | Projected Rate (Price scan range) |
| ES | E-mini S&P 500 | CME | ES | 7.13 | 9.63 |
| YM | MINI DJIA | CBOT | YM | 6.14 | 8.29 |
| RTY | Russell 2000 | CME | RTY | 6.79 | 9.17 |
| NQ | NASDAQ E-MINI | CME | NQ | 6.57 | 8.87 |
| DJIA | OSE Dow Jones Industrial Average | OSE.JPN | DJIA | 5.14 | 6.94 |
*As of 10/2/20 open.
NOTE: IBKR's Risk Navigator can help you determine the impact the new maintenance margin requirements will have on your current portfolio or any other portfolio you would like to construct or test. For more information about the Alternative Margin Calculator feature, please see KB Article 2957: Risk Navigator: Alternative Margin Calculator and from the margin mode setting in Risk Navigator, select " US Election Margin".
Overview of Central Bank of Ireland CFD Rules Implementation for Retail Clients at IBIE
|
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 61% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with IBKR. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money. |
The Central Bank of Ireland (CBI) enacted new rules applicable to retail clients trading CFDs, effective 1st August 2019. Professional clients are unaffected.
The rules consist of: 1) leverage limits; 2) a margin close out rule on a per account basis; 3) negative balance protection on a per account basis; 4) a restriction on the incentives offered to trade CFDs; and 5) a standardized risk warning.
Most clients (excepting regulated entities) are initially categorised as Retail Clients. IBKR may in certain circumstances agree to reclassify a Retail Client as a Professional Client, or a Professional Client as a Retail Client. Please see MiFID Categorisation for further detail.
The following sections detail how IBKR has implemented the CBI Decision.
1 Leverage Limits
1.1 Margins
Leverage limits were set by CBI at different levels depending on the underlying:
- 3.33% for major currency pairs; Major currency pairs are any combination of USD; CAD; EUR; GBP; CHF; JPY
- 5% for:
- Non-major currency pairs are any combination that includes a currency not listed above, e.g., USD.CNH
- Major indices are IBUS500; IBUS30; IBUST100; IBGB100; IBDE40; IBEU50; IBFR40; IBJP225; IBAU200
- Gold
- 10% for non-major equity indices; IBES35; IBCH20; IBNL25; IBHK50
- 20% for individual equities
1.2 Applied Margins - Standard Requirement
In addition to the CBI Margins, IBKR establishes its own margin requirements (IB Margins) based on the historical volatility of the underlying, and other factors. We will apply the IB Margins if they are higher than those prescribed by CBI .
Details of applicable IB and CBI margins can be found here.
1.2.1 Applied Margins - Concentration Minimum
A concentration charge is applied if your portfolio consists of a small number of CFD and/or Stock positions, or if the three largest positions have a dominant weight. We stress the portfolio by applying a 30% adverse move on the three largest positions and a 5% adverse move on the remaining positions. The total loss is applied as the maintenance margin requirement if it is greater than the standard requirement for the combined Stock and CFD positions. Note that the concentration charge is the only instance where CFD and Stock positions are margined together.
1.3 Funding of Initial Margin Requirements
You can only use cash to post initial margin to open a CFD position.
Initially all cash used to fund the account is available for CFD trading. Any initial margin requirements for other instruments and cash used to purchase cash stock reduce the available cash. If your cash stock purchases have created a margin loan, no funds are available for CFD trades even if your account has significant equity. We cannot increase a margin loan to fund CFD margin under the CBI rules.
Realized CFD profits are included in cash and are available immediately; the cash does not have to settle first. Unrealized profits however cannot be used to meet initial margin requirements.
2 Margin Close Out Rule
2.1 Maintenance Margin Calculations & Liquidations
The CBI requires IBKR to liquidate CFD positions latest when qualifying equity falls below 50% of the initial margin posted to open the positions. IBKR may close out positions sooner if our risk view is more conservative. Qualifying equity for this purpose includes CFD cash and unrealized CFD P&L (positive and negative). Note that CFD cash excludes cash supporting margin requirements for other instruments.
The basis for the calculation is the initial margin posted at the time of opening a CFD position. In other words, and unlike margin calculations applicable to non-CFD positions, the initial margin amount does not change when the value of the open position changes.
2.1.1 Example
You have EUR 2000 cash in your account and no open positions. You want to buy 100 CFDs of XYZ at a limit price of EUR 100. You are first filled 50 CFDs and then the remaining 50. Your available cash reduces as your trades are filled:
|
|
Cash |
Equity* |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Pre Trade |
2000 |
2000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2000 |
|
|
Post Trade 1 |
2000 |
2000 |
50 |
100 |
5000 |
0 |
1000 |
500 |
1000 |
No |
|
Post Trade 2 |
2000 |
2000 |
100 |
100 |
10000 |
0 |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
No |
*Equity equals Cash plus Unrealized P&L
The price increases to 110. Your equity is now 3000, but you cannot open additional positions because your available cash is still 0, and under the CBI rules IM and MM remain unchanged:
|
|
Cash |
Equity |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Change |
2000 |
3000 |
100 |
110 |
11000 |
1000 |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
No |
The price then drops to 95. Your equity declines to 1500 but there is no margin violation since it is still greater than the 1000 requirement:
|
|
Cash |
Equity |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Change |
2000 |
1500 |
100 |
95 |
9500 |
(500) |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
No |
The price falls further to 85, causing a margin violation and triggering a liquidation:
|
|
Cash |
Equity |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Change |
2000 |
500 |
100 |
85 |
8500 |
(1500) |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
Yes |
3 Negative Equity Protection
The CBI Decision limits your CFD-related liability to the funds dedicated to CFD-trading. Other financial instruments (e.g., shares or futures) cannot be liquidated to satisfy a CFD margin-deficit.*
Therefore, non-CFD assets are not part of your capital at risk for CFD trading.
Should you lose more than the cash dedicated to CFD trading, IB must write off the loss.
As Negative Equity Protection represents additional risk to IBKR, we will charge retail investors an additional financing spread of 1% for CFD positions held overnight. You can find detailed CFD financing rates here.
*Although we cannot liquidate non-CFD positions to cover a CFD deficit, we can liquidate CFD positions to cover a non-CFD deficit.
Margin Considerations for Intramarket Futures Spreads
Background
Clients who simultaneously hold both long and short positions of a given futures contract having different delivery months are often provided a spread margin rate that is less than the margin requirement for each position if considered separately. However, as the settlement prices of each contract may deviate significantly as the front month contract approaches its close out date, IBKR will reduce the benefit of the spread margin rate to reflect the risk of this price deviation.
Spread Margin Adjustment
This reduction is accomplished by effectively decoupling or breaking the spread in phases on each of the 3 business days preceding the close out date of the front contract month, as follows:
- On the 3rd business day prior to close out, the initial and maintenance margin requirements will be equal to 10% of their respective requirements on each contract month as if there was no spread, plus 90% of the spread requirement;
- On the 2nd business day prior to close out, the initial and maintenance margin requirements will be equal to 20% of their respective requirements on each contract month as if there was no spread, plus 80% of the spread requirement;
- On the business day prior to close out, the initial and maintenance margin requirements will be equal to 30% of their respective requirements on each contract month as if there was no spread, plus 70% of the spread requirement.
Working Example
Assume a hypothetical futures contract XYZ with the margin requirements as outlined in the table below:
| XYZ | Front Month - 1 Short Contract (Uncovered) | Back Month - 1 Long Contract (Uncovered) | Spread - 1 Short Front Month vs. 1 Long Back Month |
| Initial Margin | $1,250 | $1,500 | $500 |
| Maintenance Margin | $1,000 | $1,200 | $400 |
Further assume a position consisting of 1 short front month contract and 1 long back month contract with the front month contract close out date = T. using this hypothetical example, the initial margin requirement over the 3 business day period preceding close out date is outlined in the table below:
| Day | Initial Margin Requirement | Calculation Details |
| T-4 | $500 | Unadjusted |
| T-3 | $725 | .1($1,250 + $1,500) + .9($500) |
| T-2 | $950 | .2($1,250 + $1,500) + .8($500) |
| T-1 | $1,175 | .3($1,250 + $1,500) + .7($500) |
| T | $1,175 | Positions not in compliance with close out requirements are subject to liquidation. |
Concentrated Positions in Low Cap Stocks
The margin requirement for accounts holding concentrated positions in low cap stocks is as follows:
- An alternative stress test will be considered following the margin calculation currently in place. Here, each stock and its derivatives will be subject to a stress test which simulates a price change reflective of a $500 million decrease in capitalization (e.g., 25% in the case of a stock with a market capitalization of $2 billion; 30% for a stock with a market capitalization of $1.5 billion; etc.). Stocks with a market capitalization of $500 million or below will be subject to a stress test as if the price has fallen to $0.
- For the stock which projects the greatest loss assuming a $500 million decrease in capitalization, that loss will be compared to the initial margin as determined under the preceding calculation for the aggregate portfolio and, if greater, will become the initial margin requirement.
- If the initial margin requirement is increased, the maintenance margin for that same stock and its derivatives will increase to approximately 90% of the initial requirement for the aggregate portfolio.
Overview of ESMA CFD Rules Implementation at IBKR (UK) - Retail Investors Only
|
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage.
61% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with IBKR.
You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money. |
The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) enacted new rules applicable to retail clients trading CFDs, effective 1st August 2018. Professional clients are unaffected.
The rules consist of: 1) leverage limits; 2) a margin close out rule on a per account basis; 3) negative balance protection on a per account basis; 4) a restriction on the incentives offered to trade CFDs; and 5) a standardized risk warning.
Most clients (excepting regulated entities) are initially categorised as Retail Clients. IBKR may in certain circumstances agree to reclassify a Retail Client as a Professional Client, or a Professional Client as a Retail Client. Please see MiFID Categorisation for further detail.
The following sections detail how IBKR (UK) has implemented the ESMA Decision.
1 Leverage Limits
1.1 ESMA Margins
Leverage limits were set by ESMA at different levels depending on the underlying:
- 3.33% for major currency pairs; Major currency pairs are any combination of USD; CAD; EUR; GBP; CHF; JPY
- 5% for non-major currency pairs and major indices;
- Non-major currency pairs are any combination that includes a currency not listed above, e.g. USD.CNH
- Major indices are IBUS500; IBUS30; IBUST100; IBGB100; IBDE40; IBEU50; IBFR40; IBJP225; IBAU200
- 10% for non-major equity indices; IBES35; IBCH20; IBNL25; IBHK50
- 20% for individual equities
1.2 Applied Margins - Standard Requirement
In addition to the ESMA Margins, IBKR (UK) establishes its own margin requirements (IB Margins) based on the historical volatility of the underlying, and other factors. We will apply the IB Margins if they are higher than those prescribed by ESMA.
Details of applicable IB and ESMA margins can be found here.
1.2.1 Applied Margins - Concentration Minimum
A concentration charge is applied if your portfolio consists of a small number of CFD positions, or if the three largest positions have a dominant weight. We stress the portfolio by applying a 30% adverse move on the three largest positions and a 5% adverse move on the remaining positions. The total loss is applied as the maintenance margin requirement if it is greater than the standard requirement.
1.3 Funds Available for Initial Margin
You can only use cash to post initial margin to open a CFD position. Realized CFD profits are included in cash and are available immediately; the cash does not have to settle first. Unrealized profits however cannot be used to meet initial margin requirements.
1.4 Automatic Funding of Initial Margin Requirements (F-segments)
IBKR (UK) automatically transfers funds from your main account to the F-segment of your account to fund initial margin requirements for CFDs.
Note however that no transfers are made to satisfy CFD maintenance margin requirements. Therefore if qualifying equity (defined below) becomes insufficient to meet margin requirements, a liquidation will occur even if you have ample funds in your main account. If you wish to avoid a liquidation you must transfer additional funds to the F-segment in Account Management.
2 Margin Close Out Rule
2.1 Maintenance Margin Calculations & Liquidations
ESMA requires IBKR to liquidate CFD positions latest when qualifying equity falls below 50% of the initial margin posted to open the positions. IBKR may close out positions sooner if our risk view is more conservative. Qualifying equity for this purpose includes cash in the F-segment (excluding cash in any other account segment) and unrealized CFD P&L (positive and negative).
The basis for the calculation is the initial margin posted at the time of opening a CFD position. In other words, and unlike margin calculations applicable to non-CFD positions, the initial margin amount does not change when the value of the open position changes.
2.1.1 Example
You have EUR 2000 cash in your CFD account. You want to buy 100 CFDs of XYZ at a limit price of EUR 100. You are first filled 50 CFDs and then the remaining 50. Your available cash reduces as your trades are filled:
| Cash | Equity* | Position | Price | Value | Unrealized P&L | IM | MM | Available Cash | MM Violation | |
| Pre Trade | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | |||||||
| Post Trade 1 | 2000 | 2000 | 50 | 100 | 5000 | 0 | 1000 | 500 | 1000 | No |
| Post Trade 2 | 2000 | 2000 | 100 | 100 | 10000 | 0 | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | No |
*Equity equals Cash plus Unrealized P&L
The price increases to 110. Your equity is now 3000, but you cannot open additional positions because your available cash is still 0, and under the ESMA rules IM and MM remain unchanged:
| Cash | Equity | Position | Price | Value | Unrealized P&L | IM | MM | Available Cash | MM Violation | |
| Change | 2000 | 3000 | 100 | 110 | 11000 | 1000 | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | No |
The price then drops to 95. Your equity declines to 1500 but there is no margin violation since it is still greater than the 1000 requirement:
| Cash | Equity | Position | Price | Value | Unrealized P&L | IM | MM | Available Cash | MM Violation | |
| Change | 2000 | 1500 | 100 | 95 | 9500 | (500) | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | No |
The price falls further to 85, causing a margin violation and triggering a liquidation:
| Cash | Equity | Position | Price | Value | Unrealized P&L | IM | MM | Available Cash | MM Violation | |
| Change | 2000 | 500 | 100 | 85 | 8500 | (1500) | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | Yes |
3 Negative Equity Protection
The ESMA Decision limits your CFD-related liability to the funds dedicated to CFD-trading. Other financial instruments (e.g. shares or futures) cannot be liquidated to satisfy a CFD margin-deficit.*
Therefore assets in the security and commodity segments of your main account, and non-CFD assets held in the F-segment, are not part of your capital at risk for CFD trading. However, all cash in the F-segment can be used to cover losses arising from CFD trading.
As Negative Equity Protection represents additional risk to IBKR, we will charge retail investors an additional financing spread of 1% for CFD positions held overnight. You can find detailed CFD financing rates here.
*Although we cannot liquidate non-CFD positions to cover a CFD deficit, we can liquidate CFD positions to cover a non-CFD deficit.
4 Incentives Offered to trade CFDs
The ESMA Decision imposes a ban on monetary and certain types of non-monetary benefits related to CFD trading. IBKR does not offer any bonus or other incentives to trade CFDs.
Risk Navigator: Alternative Margin Calculator
IB routinely reviews margin levels and will implement changes which serve to increase requirements above statutory minimums as market conditions warrant. To assist clients with understanding the effects of such changes on their portfolio, a feature referred to as the "Alternative Margin Calculator" is provided within the Risk Navigator application. Outlined below are the steps for creating a “what-if” portfolio for the purpose of determining the impact of such margin changes.
Step 1: Open a new “What-if” portfolio
From the Classic TWS trading platform, select the Analytical Tools, Risk Navigator, and then Open New What-If menu options (Exhibit1).
Exhibit 1
.png)
From the Mosaic TWS trading platform, select New Window, Risk Navigator, and then Open New What-If menu options.
Step 2: Define starting portfolio
A pop-up window will appear (Exhibit 2) from which you will be prompted to define whether you would like to create a hypothetical portfolio starting from your current portfolio or a newly created portfolio. Clicking on the "yes" button will serve to download existing positions to the new “What-If” portfolio.
Exhibit 2
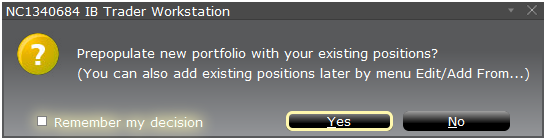
Clicking on the "No" button will open up the “What – If” Portfolio with no positions.
Risk Dashboard
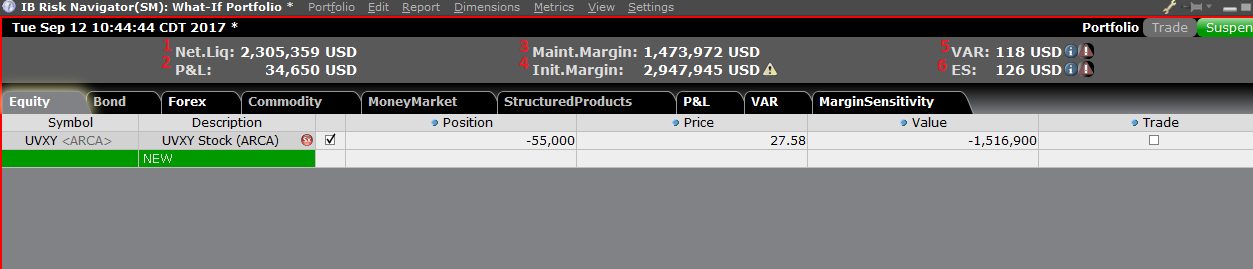
The Risk Dashboard is pinned along the top of the product tab-sets, and is and is available for what-if as well as active portfolios. The values are calculated on demand for what-if portfolios. The dashboard provides at-a-glance account information including:
1) Net Liquidation Value: The total Net Liquidation Value for the account
2) P&L: The total daily P&L for the entire portfolio
3) Maintenance Margin: Total current maintenance margin
4) Initial Margin: Total initial margin requirements
5) VAR: Shows the Value at risk for the entire portfolio
6) Expected Shortfall (ES): Expected Shortfall (average value at risk) is expected return of the portfolio in the worst case
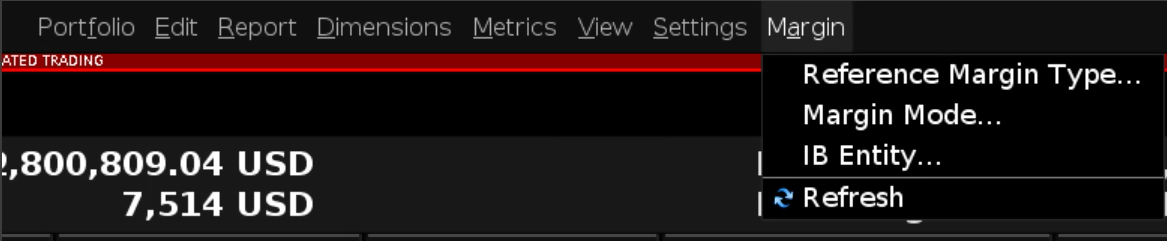
Alternative Margin Calculator
The Alternative Margin Calculator, accessed from the Margin menu and clicking on the Margin Mode (Exhibit 3), shows how the margin change will affect the overall margin requirement, once fully implemented.
Exhibit 3
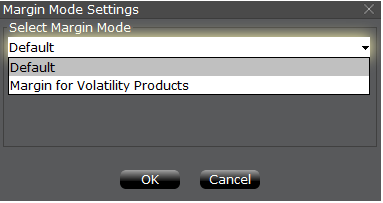
Step 3: Selecting Margin Mode Settings
A pop-up window will appear (Exhibit 4) entitled Margin Mode Setting. You can use the drop-down menu in that window to change the margin calculations from Default (being the current policy) to the new title of the new Margin Setting (being the new margin policy). Once you have made a selection click on the OK button in that window.
Exhibit 4
Once the new margin mode setting is specified, the Risk Navigator Dashboard will automatically update to reflect your choice. You can toggle back and forth between the Margin Mode settings. Note that the current Margin Mode will be shown in the lower left hand corner of the Risk Navigator window (Exhibit 5).
Exhibit 5
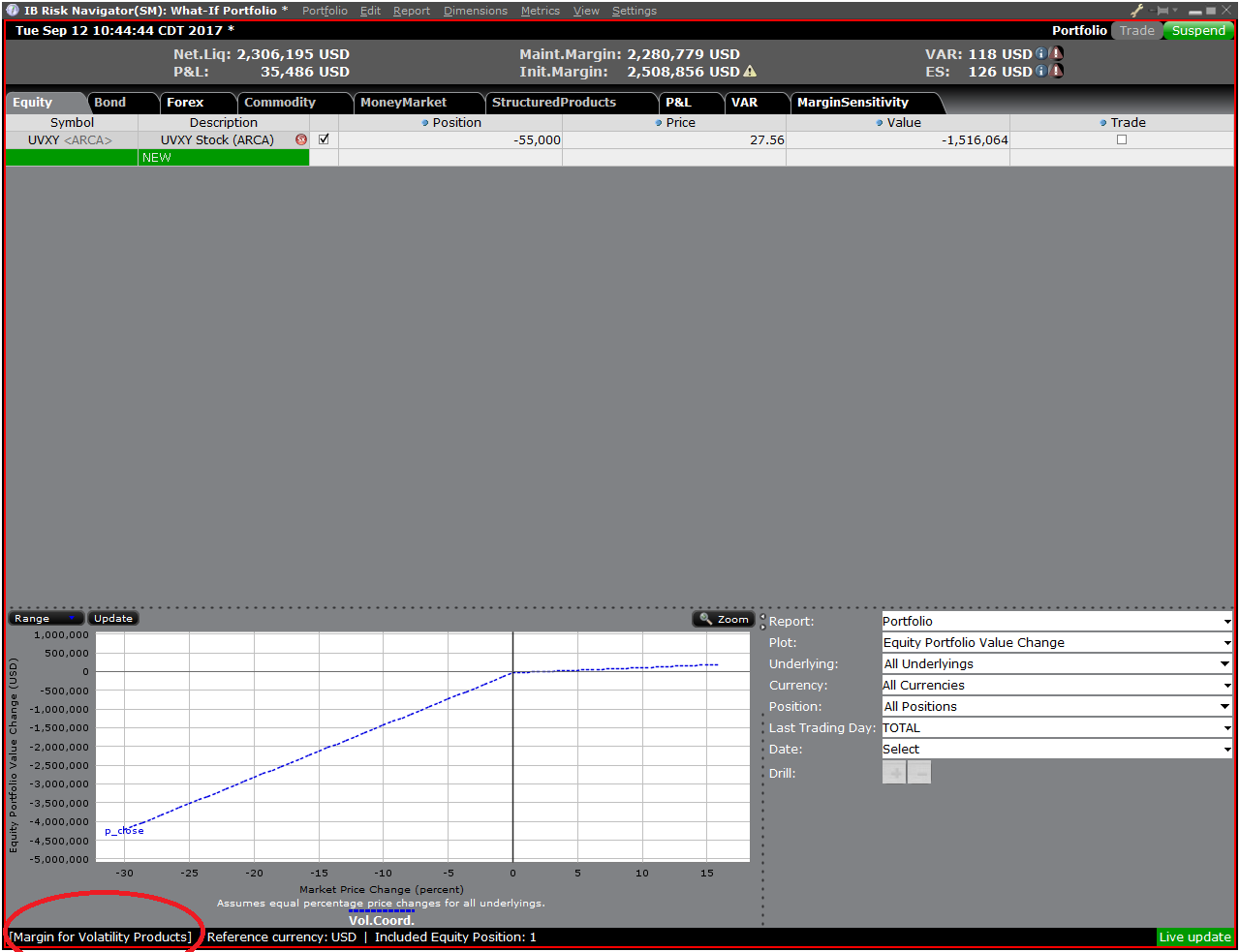
Step 4: Add Positions
To add a position to the "What - If" portfolio, click on the green row titled "New" and then enter the underlying symbol (Exhibit 6), define the product type (Exhibit 7) and enter position quantity (Exhibit 8)
Exhibit 6
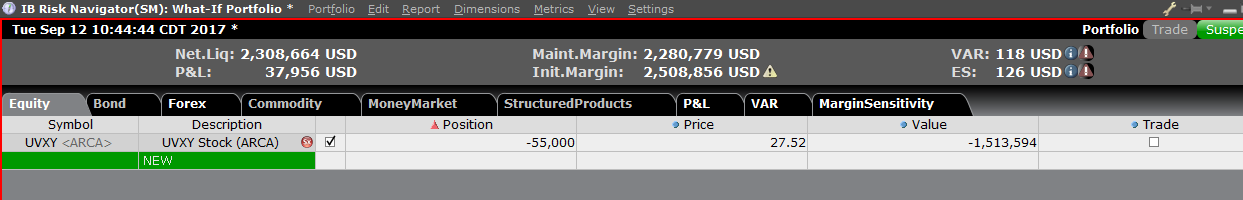
Exhibit 7
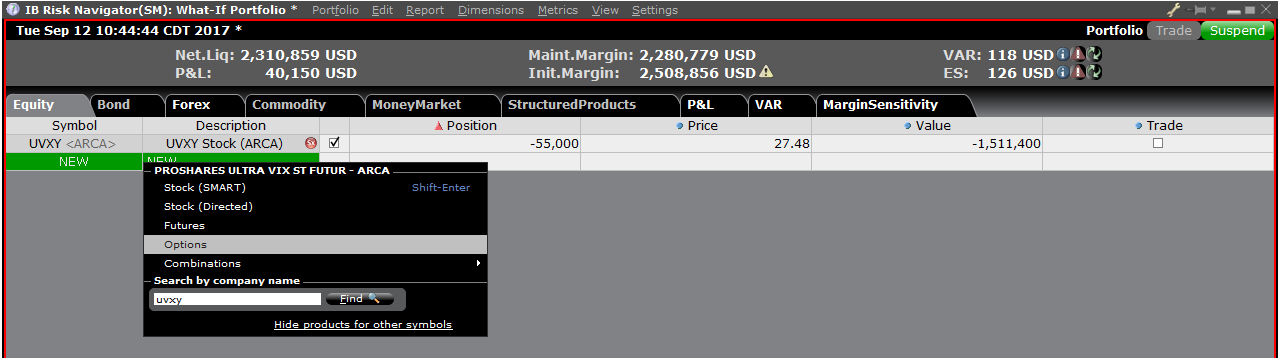
Exhibit 8
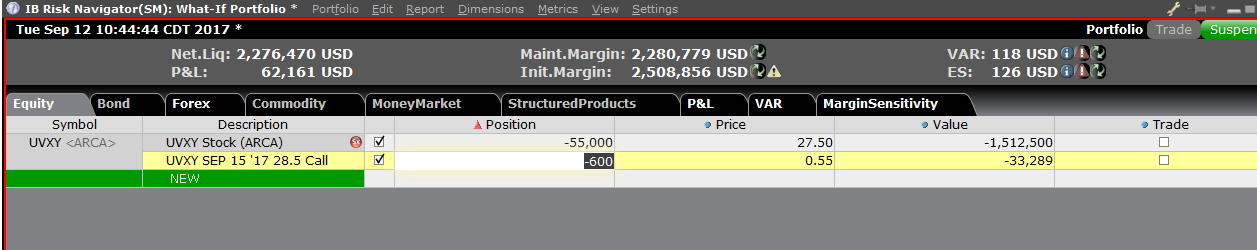
You can modify the positions to see how that changes the margin. After you altered your positions you will need to click on the recalculate icon (![]() ) to the right of the margin numbers in order to have them update. Whenever that icon is present the margin numbers are not up-to-date with the content of the What-If Portfolio.
) to the right of the margin numbers in order to have them update. Whenever that icon is present the margin numbers are not up-to-date with the content of the What-If Portfolio.
Margin Considerations for IB LLC Commodities Accounts
Introduction
As a global broker offering futures trading in 19 countries, IB is subject to various regulations, some of which retain the concept of margin as a single, end of day computation as opposed to the continuous, real-time computations IB performs. To satisfy commodity regulatory requirements and manage economic exposure in a pragmatic fashion, two margin computations are performed at the market close, both which must be met to remain fully margin compliant. An overview of these computations is outlined below.
Overview
All orders are subject to an initial margin check prior to execution and continuous maintenance margin checks thereafter. As certain products may be offered intraday margin at rates less than the exchange minimum and to ensure end of day margin compliance overall, IB will generally liquidate positions prior to the close rather than issue a margin call. If, however, an account remains non-compliant at the close, our practice is to issue a margin call, restrict the account to margin reducing transactions and liquidate positions by the close of the 3rd business day if the initial requirement has not then been satisfied.
In determining whether a margin call is required, IB performs both a real-time and regulatory computation, which in certain circumstances, can generate different results:
Real-Time: under this method, initial margin is computed using positions and prices collected at a common point in time, regardless of a product’s listing exchange and official closing time; an approach we believe appropriate given the near continuous trading offered by most exchanges.
Regulatory: under this method, initial margin is computed using positions and prices collected at the official close of regular trading hours for each individual exchange. So, for example, a client trading futures listed on each of the Hong Kong, EUREX and CME exchanges would have a requirement calculated based upon information collected at the close of each respective exchange.
Impact
Clients trading futures listed within a single country and session are not expected to be impacted. Clients trading both the daytime and after hours sessions of a given exchange or on exchanges located in different countries where the closing times don’t align are more likely to be impacted. For example, a client opening a futures contract during the Hong Kong daytime session and closing it during U.S. hours, would have only the opening position considered for purposes of determining the margin requirement. This implies a different margin requirement and a possible margin call under the revised computation that may not have existed under the current. An example of this is provided in the chart below.
Example
This example attempts to demonstrate how a client trading futures in both the Asia and U.S. timezones would be impacted were that client to trade in an extended hours trading session (i.e., outside of the regular trading hours after which the day's official close had been determined). Here, the client opens a position during the Hong Kong regular hours trading session, closes it during the extended hours session, thereby freeing up equity to open a position in the U.S. regular hours session. For purposes of illustration, a $1,000 trading loss is assumed. This example illustrates that the regulatory end of day computation may not recognize margin reducing trades conducted after the official close, thereby generating an initial margin call.
| Day | Time (ET) | Event |
Start Position |
End Position | IB Margin | Regulatory Margin | |||
| Equity With Loan | Maintenance | Initial | Overnight | Margin Call | |||||
| 1 | 22:00 | Buy 1 HHI.HK | None | Long 1 HHI.HK | $10,000 | $3,594 | $4,493 | N/A | N/A |
| 2 | 04:30 | Official HK Close | Long 1 HHI.HK | Long 1 HHI.HK | $10,000 | $7,942 | $9,927 | $4,493 | N/A |
| 2 | 08:00 | Sell 1 HHI.HK | Long 1 HHI.HK | None | $9,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | N/A |
| 2 | 10:00 | Buy 1 ES | None | Long 1 ES | $9,000 | $2,942 | $3,677 | N/A | N/A |
| 2 | 17:00 | Official U.S. Close | Long 1 ES | Long 1 ES | $9,000 | $5,884 | $7,355 | $9,993 | Yes |
| 3 | 17:00 | Official U.S. Close | Long 1 ES | Long 1 ES | $9,000 | $5,884 | $7,355 | $5,500 | No |
Allocation of Partial Fills
How are executions allocated when an order receives a partial fill because an insufficient quantity is available to complete the allocation of shares/contracts to sub-accounts?
Overview:
From time-to-time, one may experience an allocation order which is partially executed and is canceled prior to being completed (i.e. market closes, contract expires, halts due to news, prices move in an unfavorable direction, etc.). In such cases, IB determines which customers (who were originally included in the order group and/or profile) will receive the executed shares/contracts. The methodology used by IB to impartially determine who receives the shares/contacts in the event of a partial fill is described in this article.
Background:
Before placing an order CTAs and FAs are given the ability to predetermine the method by which an execution is to be allocated amongst client accounts. They can do so by first creating a group (i.e. ratio/percentage) or profile (i.e. specific amount) wherein a distinct number of shares/contracts are specified per client account (i.e. pre-trade allocation). These amounts can be prearranged based on certain account values including the clients’ Net Liquidation Total, Available Equity, etc., or indicated prior to the order execution using Ratios, Percentages, etc. Each group and/or profile is generally created with the assumption that the order will be executed in full. However, as we will see, this is not always the case. Therefore, we are providing examples that describe and demonstrate the process used to allocate partial executions with pre-defined groups and/or profiles and how the allocations are determined.
Here is the list of allocation methods with brief descriptions about how they work.
· AvailableEquity
Use sub account’ available equality value as ratio.
· NetLiq
Use subaccount’ net liquidation value as ratio
· EqualQuantity
Same ratio for each account
· PctChange1:Portion of the allocation logic is in Trader Workstation (the initial calculation of the desired quantities per account).
· Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user
· Inline Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user.
· Model1:
Roughly speaking, we use each account NLV in the model as the desired ratio. It is possible to dynamically add (invest) or remove (divest) accounts to/from a model, which can change allocation of the existing orders.
Basic Examples:
Details:
CTA/FA has 3-clients with a predefined profile titled “XYZ commodities” for orders of 50 contracts which (upon execution) are allocated as follows:
Account (A) = 25 contracts
Account (B) = 15 contracts
Account (C) = 10 contracts
Example #1:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 10 am (ET) the order begins to execute2but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 2 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 7 of the 50 contracts are filled or 14%). For each account the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 14% of 25 = 3.5 rounded down to 3
Account (B) = 14% of 15 = 2.1 rounded down to 2
Account (C) = 14% of 10 = 1.4 rounded down to 1
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.10).
A: final allocation of 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 2 contract, which is 2/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.20)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #2:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be filled3 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 1 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is executed (i.e., 5 of the 50 contracts are filled or 10%).For each account, the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 10% of 25 = 2.5 rounded down to 2
Account (B) = 10% of 15 = 1.5 rounded down to 1
Account (C) = 10% of 10 = 1 (no rounding necessary)
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. to Account B which currently has a ratio of 0.067).
A: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #3:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be executed2 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 12 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 3 of the 50 contracts are filled or 6%). Normally the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers, however for a fill size of less than 4 shares/contracts, IB first allocates based on the following random allocation methodology.
In this case, since the fill size is 3, we skip the rounding fractional amounts down.
For the first share/contract, all A, B and C have the same initial fill ratio and fill quantity, so we randomly pick an account and allocate this share/contract. The system randomly chose account A for allocation of the first share/contract.
To Summarize3:
A: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
C: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
Next, the system will perform a random allocation amongst the remaining accounts (in this case accounts B & C, each with an equal probability) to determine who will receive the next share/contract.
The system randomly chose account B for allocation of the second share/contract.
A: 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
The system then allocates the final [3] share/contract to an account(s) with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.00).
A: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Available allocation Flags
Besides the allocation methods above, user can choose the following flags, which also influence the allocation:
· Strict per-account allocation.
For the initially submitted order if one or more subaccounts are rejected by the credit checking, we reject the whole order.
· “Close positions first”1.This is the default handling mode for all orders which close a position (whether or not they are also opening position on the other side or not). The calculation are slightly different and ensure that we do not start opening position for one account if another account still has a position to close, except in few more complex cases.
Other factor affects allocations:
1) Mutual Fund: the allocation has two steps. The first execution report is received before market open. We allocate based onMonetaryValue for buy order and MonetaryValueShares for sell order. Later, when second execution report which has the NetAssetValue comes, we do the final allocation based on first allocation report.
2) Allocate in Lot Size: if a user chooses (thru account config) to prefer whole-lot allocations for stocks, the calculations are more complex and will be described in the next version of this document.
3) Combo allocation1: we allocate combo trades as a unit, resulting in slightly different calculations.
4) Long/short split1: applied to orders for stocks, warrants or structured products. When allocating long sell orders, we only allocate to accounts which have long position: resulting in calculations being more complex.
5) For non-guaranteed smart combo: we do allocation by each leg instead of combo.
6) In case of trade bust or correction1: the allocations are adjusted using more complex logic.
7) Account exclusion1: Some subaccounts could be excluded from allocation for the following reasons, no trading permission, employee restriction, broker restriction, RejectIfOpening, prop account restrictions, dynamic size violation, MoneyMarketRules restriction for mutual fund. We do not allocate to excluded accountsand we cancel the order after other accounts are filled. In case of partial restriction (e.g. account is permitted to close but not to open, or account has enough excess liquidity only for a portion of the desired position).
Footnotes:
Overview of Dividend Payments in Lieu ("PIL")
Payment In Lieu of a Dividend (“payment in lieu” or “PIL”) is a term commonly used to describe a cash payment to an account in an amount equivalent to the ordinary dividend. Generally, the amount paid is per share owned. In addition, the dividend in most cases is paid quarterly (i.e., four times per year). The dividend payment is classified as follows: (1) ordinary dividend; and/or (2) payment in lieu of dividend. The former designation is for a payment received directly from the issuer or its paying agent. The latter designation is used when a cash payment is received from other than the issuer or the issuer’s agent.
Payment in lieu of an ordinary dividend may be received when the shares have been bought on margin, or when the account has a subsequent margin loan due to borrowing money to facilitate the payment for additional purchases of shares or as the result of a withdrawal from the margin account. Payment in lieu of a dividend may also be received when shares are owed to the brokerage firm and have not been received by the dividend record date.
To better understand the difference between an ordinary dividend and a payment in lieu, we will explain the steps taken by IB to comply with US regulations. Each business day, the Firm analyzes the positions in each customer account, every borrow, every loan, every pledge of shares for each security held by its customers to determine how many shares are held on margin and the associated margin loan balances. For each security that is fully paid, we are required to segregate those shares in a good control location (for example, a depository or a US bank. See KB1964). For shares that are held as collateral for a margin loan we are allowed to hypothecate and re-hypothecate shares valued up to 140 percent of the total debit balance in the customer account (See KB1967).
While the guidelines noted above for segregation of securities are clear, there are exceptions that are outside of the Firm's control. For instance, through no fault of its own, IB may have a deficit in segregated shares due to customer activity that changes the Firm’s overall segregation requirement for a security. This may be for a variety of reasons including a delay in receiving shares that have been loaned out to a counterparty after segregation requirements are recalculated and the Firm has issued a stock loan recall, sales of securities by one or more customers that reduce or eliminate margin loans, the deposit of cash by customers that similarly reduce or eliminate margin loans, or a failure of a counterparty to deliver shares for a trade settlement.
Upon issuing a recall of shares loaned, rules permit the borrower of the shares up to 3 business days to return them. The borrower of the shares is required to return them to us when we issue a recall, but if by business day 3 the shares have not been returned, IB may then issue a buy-in notice to begin the process of regaining possession of the shares. An additional 3 business days is generally needed for the purchased shares to settle and be delivered to the firm. Similarly if a counterparty fails to deliver by settlement date, shares to IB to settle a customer purchase, IB can issue a buy-in notice but the purchase of such shares are also subject to trade settlement in 3 days.
To summarize, if by the record date of a dividend certain shares have not been delivered to IB, the Firm will be paid an amount of cash that is equivalent to the dividend amount, but IB will not receive a qualified dividend payment directly from the issuer. In such cases, the Firm will receive PIL and will have no choice but to allocate such payment in lieu to customer accounts. The firm first allocates PIL to those accounts who hold the shares as collateral for a margin loan. If, after PIL is allocated to all shareholders whose accounts are not fully paid, any portion of PIL remains to be paid, it is allocated on a pro-rata basis to each remaining client account.
Account holders should be aware that a PIL may have different tax consequences than an ordinary dividend and should consult a tax advisor to understand such differences and whether they apply to their particular situation.
